目录
- 前言
- 安装
- 创建 Store
- State
- 定义State
- 获取 state
- 修改 state
- Getters
- Actions
- 异步 action
- action 间相互调用
- 数据持久化
- 安装
- 使用
- 自定义 key
- 持久化部分 state
- 最后
前言
Pinia.js 是新一代的状态管理器,由 Vue.js团队中成员所开发的,因此也被认为是下一代的 Vuex,即 Vuex5.x,在 Vue3.0 的项目中使用也是备受推崇。
Pinia.js 有如下特点:
- 完整的 typescript 的支持;
- 足够轻量,压缩后的体积只有1.6kb;
- 去除 mutations,只有 state,getters,actions(这是我最喜欢的一个特点);
- actions 支持同步和异步;
- 没有模块嵌套,只有 store 的概念,store 之间可以自由使用,更好的代码分割;
- 无需手动添加 store,store 一旦创建便会自动添加;
安装
npm install pinia --save
创建 Store
新建 src/store 目录并在其下面创建 index.ts,导出 store
// src/store/index.ts
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
const store = createPinia()
export default store
在 main.ts 中引入并使用。
// src/main.ts
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from './store'
const app = createApp(App)
app.use(store)
State
定义State
在 src/store 下面创建一个user.ts
//src/store/user.ts
import { defineStore } from 'pinia'
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user', // id必填,且需要唯一
state: () => {
return {
name: '张三'
}
}
})
获取 state
<template>
<div>{{ userStore.name }}</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'
const userStore = useUserStore()
</script>
也可以结合 computed 获取。
const name = computed(() => userStore.name)
state 也可以使用解构,但使用解构会使其失去响应式,这时候可以用 pinia 的 storeToRefs。
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia'
const { name } = storeToRefs(userStore)
修改 state
可以像下面这样直接修改 state
userStore.name = '李四'
但一般不建议这么做,建议通过 actions 去修改 state,action 里可以直接通过 this 访问。
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
state: () => {
return {
name: '张三'
}
},
actions: {
updateName(name) {
this.name = name
}
}
})
<script lang="ts" setup>
import { useUserStore } from '@/store/user'
const userStore = useUserStore()
userStore.updateName('李四')
</script>
Getters
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
state: () => {
return {
name: '张三'
}
},
getters: {
fullName: (state) => {
return state.name + '丰'
}
}
})
userStore.fullName // 张三丰
Actions
异步 action
action 可以像写一个简单的函数一样支持 async/await 的语法,让你愉快的应付异步处理的场景。
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
actions: {
async login(account, pwd) {
const { data } = await api.login(account, pwd)
return data
}
}
})
action 间相互调用
action 间的相互调用,直接用 this 访问即可。
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
actions: {
async login(account, pwd) {
const { data } = await api.login(account, pwd)
this.setData(data) // 调用另一个 action 的方法
return data
},
setData(data) {
console.log(data)
}
}
})
在 action 里调用其他 store 里的 action 也比较简单,引入对应的 store 后即可访问其内部的方法了。
// src/store/user.ts
import { useAppStore } from './app'
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
actions: {
async login(account, pwd) {
const { data } = await api.login(account, pwd)
const appStore = useAppStore()
appStore.setData(data) // 调用 app store 里的 action 方法
return data
}
}
})
// src/store/app.ts
export const useAppStore = defineStore({
id: 'app',
actions: {
setData(data) {
console.log(data)
}
}
})
数据持久化
插件 pinia-plugin-persist 可以辅助实现数据持久化功能。
安装
npm i pinia-plugin-persist --save
使用
// src/store/index.ts
import { createPinia } from 'pinia'
import piniaPluginPersist from 'pinia-plugin-persist'
const store = createPinia()
store.use(piniaPluginPersist)
export default store
接着在对应的 store 里开启 persist 即可。
export const useUserStore = defineStore({
id: 'user',
state: () => {
return {
name: '张三'
}
},
// 开启数据缓存
persist: {
enabled: true
}
})
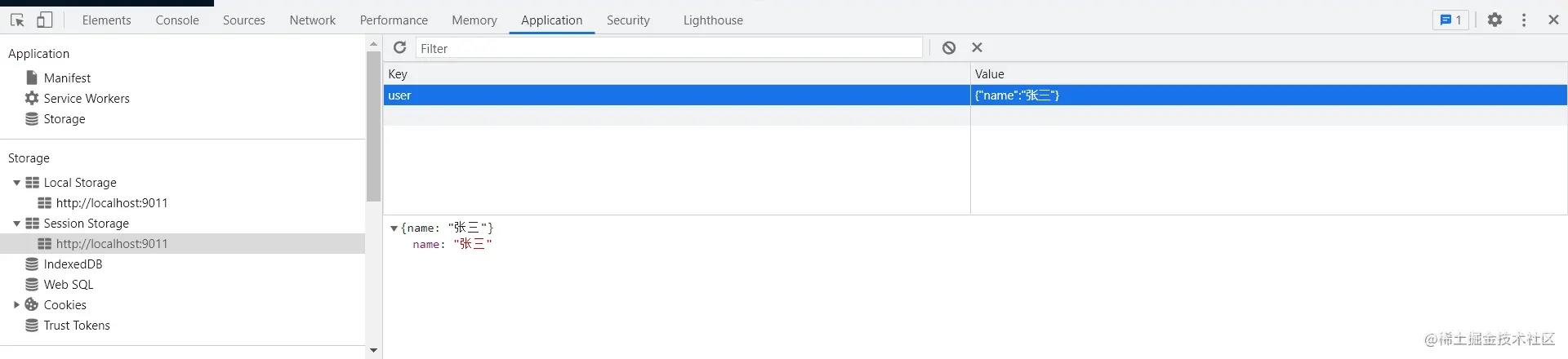
数据默认存在 sessionStorage 里,并且会以 store 的 id 作为 key。
自定义 key
你也可以在 strategies 里自定义 key 值,并将存放位置由 sessionStorage 改为 localStorage。
persist: {
enabled: true,
strategies: [
{
key: 'my_user',
storage: localStorage,
}
]
}
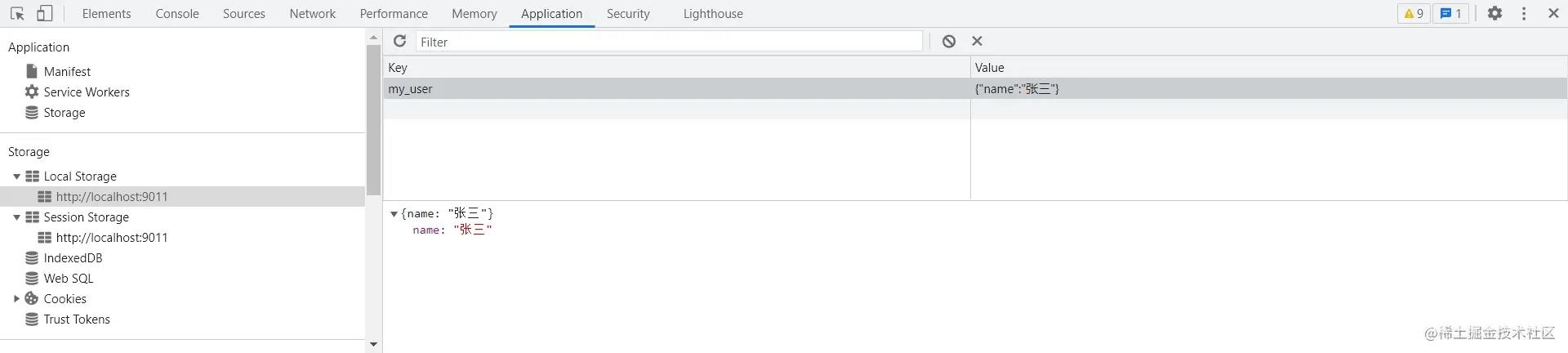
持久化部分 state
默认所有 state 都会进行缓存,你可以通过 paths 指定要持久化的字段,其他的则不会进行持久化。
state: () => {
return {
name: '张三',
age: 18,
gender: '男'
}
},
persist: {
enabled: true,
strategies: [
{
storage: localStorage,
paths: ['name', 'age']
}
]
}
上面我们只持久化 name 和 age,并将其改为localStorage, 而 gender 不会被持久化,如果其状态发送更改,页面刷新时将会丢失,重新回到初始状态,而 name 和 age 则不会。
最后
以上就是关于 Pinia.js 用法的一些介绍,Pinia.js 的内容还远不止这些,更多内容及使用有待大家自己探索。Pinia文档
以上就是Pinia.js状态管理器上手使用指南的详细内容,更多关于Pinia.js状态管理器的资料请关注易盾网络其它相关文章!
