前言
最近在看王清培前辈的.NET框架设计时,当中有提到扩展方法 .
开头的一句话是:扩展方法是让我们在不改变类原有代码的情况下动态地添加方法的方式,这给面向对象设计 模块设计带来了质的提升
很明显,扩展方法在框架设计或者平时码代码中,是能够提升我们整个架构的灵活性的
简介
扩展方法被定义为静态方法,但它们是通过实例方法语法进行调用的。 它们的第一个参数指定该方法作用于哪个类型,并且该参数以 this 修饰符为前缀。 扩展方法当然不能破坏面向对象封装的概念,所以只能是访问所扩展类的public成员。
扩展方法使您能够向现有类型“添加”方法,而无需创建新的派生类型、重新编译或以其他方式修改原始类型。扩展方法是一种特殊的静态方法,但可以像扩展类型上的实例方法一样进行调用。
C#扩展方法第一个参数指定该方法作用于哪个类型,并且该参数以 this 修饰符为前缀。
扩展方法的目的就是为一个现有类型添加一个方法,现有类型既可以是int,string等数据类型,也可以是自定义的数据类型。
一..net自带扩展方法和自定义扩展方法
在使用linq时就能够使用到很多.net自带的扩展方法,比如where select等等
where的扩展方法定义
public static IEnumerable<TSource> Where<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate);
Select的扩展方法定义
public static IEnumerable<TResult> Select<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, TResult> selector);
(1)自己实现where和select的扩展方法
// where自实现
public static IEnumerable<TSource> ExtenSionWhere<TSource>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, bool> predicate)
{
if (source == null)
{
throw new Exception(nameof(source));
}
if (predicate == null)
{
throw new Exception(nameof(predicate));
}
List<TSource> satisfySource = new List<TSource>();
foreach (var sou in source)
{
if (predicate(sou))
{
satisfySource.Add(sou);
}
}
return satisfySource;
}
// select 自实现
public static IEnumerable<TResult> ExtenSionSelect<TSource, TResult>(this IEnumerable<TSource> source, Func<TSource, TResult> selector)
{
if(source==null)
{
throw new Exception(nameof(source));
}
if(selector==null)
{
throw new Exception(nameof(source));
}
List<TResult> resultList = new List<TResult>();
foreach(var sou in source)
{
resultList.Add(selector(sou));
}
return resultList;
}
(2)自实现where和select调用
static void Main(string[] args)
{
List<int> list = new List<int>() { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
//常规写法
var selectList = list.ExtenSionWhere(p => p > 3).ExtenSionSelect(p => p.ToString()).ToList();
//自定义泛型委托写法
Func<int, bool> whereFunc = (num) => num > 3;
Func<int, string> selectFunc = (num) => num.ToString();
var selectList1 = list.ExtenSionWhere(p => whereFunc(p)).ExtenSionSelect(p => selectFunc(p)).ToList();
}
二.使用扩展方法实现链式编程
我在项目中经常使用开源的Flurl进行http请求,在进行拼装请求报文时,就会使用到链式编程
如下代码所示

以上代码就是使用了扩展方法进行链式编程,从而使得整个请求信息可以在一句代码中体现出来
接下来,我们自己实现链式代码
public static class ContextExtension
{
public static RectangleContext SetLength(this RectangleContext context,int num)
{
RectangleContext.Config.Length = num;
return context;
}
public static RectangleContext SetWideth(this RectangleContext context, int num)
{
RectangleContext.Config.Wideth = num;
return context;
}
public static RectangleContext SetHeight(this RectangleContext context, int num)
{
RectangleContext.Config.Height = num;
return context;
}
}
public class RectangleContext
{
public static RectangleContext Config=new RectangleContext();
public int Length { get; set; }
public int Wideth { get; set; }
public int Height { get; set; }
}
调用和执行结果
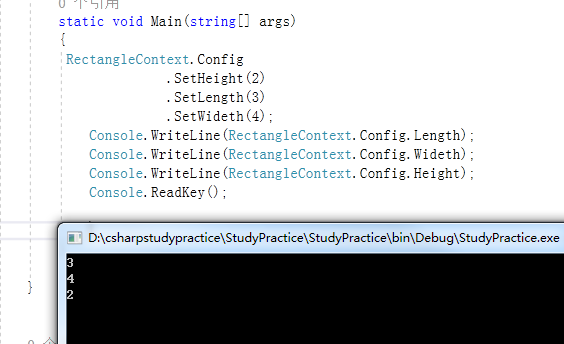
总结
1.使用扩展方法能在不修改原有类型的基础下,动态添加方法,这使得整个框架更具有灵活性
2.在使用上下文信息的时候,可以使用链式编程,使得调用时能够在一句代码中完成所有属性设置
3.扩展方法不能滥用.添加扩展方法应当使用最小影响原则,即尽量不要在父类使用扩展方法,比如object,这将影响性能
好了,以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对易盾网络的支持。
