In an attempt to address that helpless feeling that comes when a GDSII file will sometimes not work, a simple CPP program has been written to be able to look inside and experiment with a GDSII binary file.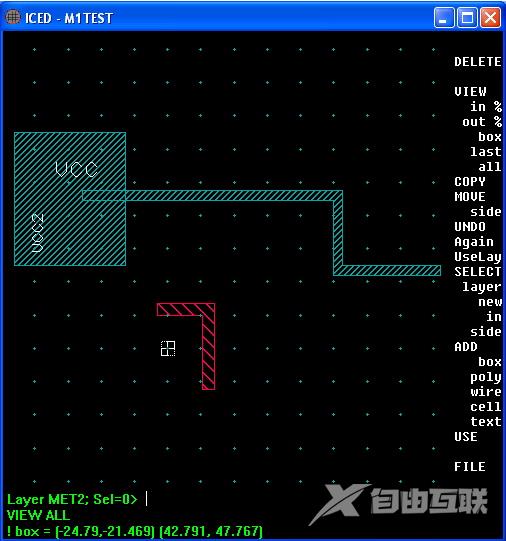
 转存失败重新上传取消
转存失败重新上传取消 An IC layout essentially involves the placement of objects often referred to as geometries. Geometries are things like boxes (polygons), paths (wires), text (strings), etc. Transistors are made out of a collection of geometries grouped together in a file which is called a cell. A circuit mainly involves just placing a bunch of transistor cells together and wiring all their nodes up using metal layer wires. Text can (should) be added to make the layout process much easier. The layout below adds an example of all those geometries.Both GDSII and layout files are normally stored in binary format. ICEDIT also has a way to print out a layout in text format.ICEDIT.txt! Selected components in M1TEST: ADD BOX LAYERMET1 ID1 AT (-23.1, 12.5) (-6.4, 32.5) ADD CELL "AT_ZERO" ID5 AT ( 0.0, 0.0) ADD TEXT"VCC2" LAYERMET1 ID4 SIZE2.000 JUSTLB R1 AT (-18.7, 14.4) ADD TEXT"VCC" LAYERMET1 ID3 SIZE3.000 JUSTLB AT (-17.0, 25.4) ADD WIRE LAYERMET2 ID6 TYPE2 WIDTH1.800 AT ( -0.7, 5.9) (6.2, 5.9) (6.2,-5.3) ADD WIRE LAYERMET1 ID2 TYPE2 WIDTH1.400 AT (-12.1, 23.0) GDSII.txt HEADER Release # 3 BGNLIB LIBNAME M1TEST.DB FONTS GDSII:CALMAFONT.TX GENERATIONS 3 UNITS 0.001 1e-09 BGNSTR STRNAME M1TEST BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -23100 32500 -23100 12500 -6400 12500 -6400 32500 -23100 32500 ENDEL PATH LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 PATHTYPE 2 WIDTH 1400 XY -12100 23000 25600 23000 25600 11700 40400 11700 ENDEL TEXT LAYER 8 TEXTTYPE 0 PRESENTATION 8 STRANS none MAG 3 XY -17000 25400 STRING VCC ENDEL TEXT LAYER 8 TEXTTYPE 0 PRESENTATION 8 STRANS none MAG 2 ANGLE 90 XY -18700 14400 STRING VCC2 ENDEL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL PATH LAYER 10 DATATYPE 0 PATHTYPE 2 WIDTH 1800 XY -700 5900 6200 5900 6200 -5300 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME AT_ZERO BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY -1000 0 -1000 -1000 0 -1000 0 0 -1000 0 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY 0 1000 0 0 1000 0 1000 1000 0 1000 ENDEL ENDSTR ENDLIB The listing above is from a printout from a simple GDSII file reader. This programs just reads each block one at a time and prints out the Block Name ID and the value(s) contained within. Hopefully it should be possible to read and printout a troublesome GDSII stream file until it gets into trouble. And then go in and maybe adjust some code to look at troublesome areas . There are some name changes between the ICEDIT format and GDSII.Boxes (polygons) are indicated by the BOUNDARY ID. Wires (path) are PATHS which have a width. A Cell seems to the geometries contained inside the BGNSTR and ENDSTR IDs. The placement of a cell appears to use the SREF ID. All Cells which are referenced are completely contained in the GDSII file. BiCMOSLAYERS.cmd VIEW OFF $ MENU "M1"; KEEP_LIBRARY_CELLSASK; DISPLAY CELL_DEPTH100; PATTERN "SAMPLE"; FILL MIXED ON AUTOPAN ON PIXELS100 SECONDS0.5; ARROW MODEEDIT DISPLAY CELL_LABELSON OUTLINE_DEPTH1 EDIT_STACKOFF CURSOR 1 SNAPON SPACER OFF SPACE0.0 TRACK_LAYERSOFF STYLE1 VIEW LIMIT ON SCALE0.100 DEPTH1 DOTS0 UNITS0.0 SHOW_LAYERS 1:* ARRAY DRAW_MODESIDES CELL_LIMIT1024 TEXT LOWER_CASEDISABLED MULTI_LINE_TEXTDISABLED ORIENTATIONS2 DISPLAY_ORIGINSOFF USE TEXT_JUSTIFICATIONLB WIRE_TYPE2 ARC_TYPE2 N_SIDES16 RESOLUTION STEP0.100 MODESOFT SNAP ANGLE45 STEP(0.100,0.100) OFFSET(0.000,0.000) NEAR UNITS0.05 DOTS4 GRID 1 ON COLORRED DOTS STEP1.0 GRID 2 ON COLORCYAN CROSSES STEP5 GRID 3 OFF COLORWHITE LINES STEP50000 LAYER 1 NAMENWEL WIDTH1.300 SPACE4.200 DIM_BLUE PAT13 PEN16 NO_CIF STREAM1,0 LAYER 2 NAMECOMP WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.700 ORANGE PAT29 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM2,0 LAYER 3 NAMEPFIELD WIDTH4.300 SPACE2.200 GRAY PAT0 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM3,0 LAYER 4 NAMEPOLY WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 GREEN PAT20 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM4,0 LAYER 5 NAMENPLUS WIDTH1.300 SPACE0.000 YELLOW PAT15 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM5,0 LAYER 6 NAMEPPLUS WIDTH1.300 SPACE0.000 ORANGE PAT15 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM6,0 LAYER 7 NAMECONT WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 WHITE PAT1 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM7,0 LAYER 8 NAMEMET1 WIDTH1.400 SPACE1.200 CYAN PAT3 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM8,0 LAYER 9 NAMEVIA WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 YELLOW PAT1 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM9,0 LAYER 10 NAMEMET2 WIDTH1.800 SPACE1.400 RED PAT13 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM10,0 LAYER 40 NAMENBURIED WIDTH1.000 SPACE0.000 YELLOW PAT34 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM21,0 There are some detail set by Process_Layer_File which will define things like resolution and calma number for each layer. A edited version of this file is shown above.Cell_Placement_DetailsThings like cell rotation and hierarchy need to be included in a GDSII file as well. The text printout for this layout above shows only cell placement and rotation information.
An IC layout essentially involves the placement of objects often referred to as geometries. Geometries are things like boxes (polygons), paths (wires), text (strings), etc. Transistors are made out of a collection of geometries grouped together in a file which is called a cell. A circuit mainly involves just placing a bunch of transistor cells together and wiring all their nodes up using metal layer wires. Text can (should) be added to make the layout process much easier. The layout below adds an example of all those geometries.Both GDSII and layout files are normally stored in binary format. ICEDIT also has a way to print out a layout in text format.ICEDIT.txt! Selected components in M1TEST: ADD BOX LAYERMET1 ID1 AT (-23.1, 12.5) (-6.4, 32.5) ADD CELL "AT_ZERO" ID5 AT ( 0.0, 0.0) ADD TEXT"VCC2" LAYERMET1 ID4 SIZE2.000 JUSTLB R1 AT (-18.7, 14.4) ADD TEXT"VCC" LAYERMET1 ID3 SIZE3.000 JUSTLB AT (-17.0, 25.4) ADD WIRE LAYERMET2 ID6 TYPE2 WIDTH1.800 AT ( -0.7, 5.9) (6.2, 5.9) (6.2,-5.3) ADD WIRE LAYERMET1 ID2 TYPE2 WIDTH1.400 AT (-12.1, 23.0) GDSII.txt HEADER Release # 3 BGNLIB LIBNAME M1TEST.DB FONTS GDSII:CALMAFONT.TX GENERATIONS 3 UNITS 0.001 1e-09 BGNSTR STRNAME M1TEST BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -23100 32500 -23100 12500 -6400 12500 -6400 32500 -23100 32500 ENDEL PATH LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 PATHTYPE 2 WIDTH 1400 XY -12100 23000 25600 23000 25600 11700 40400 11700 ENDEL TEXT LAYER 8 TEXTTYPE 0 PRESENTATION 8 STRANS none MAG 3 XY -17000 25400 STRING VCC ENDEL TEXT LAYER 8 TEXTTYPE 0 PRESENTATION 8 STRANS none MAG 2 ANGLE 90 XY -18700 14400 STRING VCC2 ENDEL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL PATH LAYER 10 DATATYPE 0 PATHTYPE 2 WIDTH 1800 XY -700 5900 6200 5900 6200 -5300 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME AT_ZERO BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY -1000 0 -1000 -1000 0 -1000 0 0 -1000 0 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY 0 1000 0 0 1000 0 1000 1000 0 1000 ENDEL ENDSTR ENDLIB The listing above is from a printout from a simple GDSII file reader. This programs just reads each block one at a time and prints out the Block Name ID and the value(s) contained within. Hopefully it should be possible to read and printout a troublesome GDSII stream file until it gets into trouble. And then go in and maybe adjust some code to look at troublesome areas . There are some name changes between the ICEDIT format and GDSII.Boxes (polygons) are indicated by the BOUNDARY ID. Wires (path) are PATHS which have a width. A Cell seems to the geometries contained inside the BGNSTR and ENDSTR IDs. The placement of a cell appears to use the SREF ID. All Cells which are referenced are completely contained in the GDSII file. BiCMOSLAYERS.cmd VIEW OFF $ MENU "M1"; KEEP_LIBRARY_CELLSASK; DISPLAY CELL_DEPTH100; PATTERN "SAMPLE"; FILL MIXED ON AUTOPAN ON PIXELS100 SECONDS0.5; ARROW MODEEDIT DISPLAY CELL_LABELSON OUTLINE_DEPTH1 EDIT_STACKOFF CURSOR 1 SNAPON SPACER OFF SPACE0.0 TRACK_LAYERSOFF STYLE1 VIEW LIMIT ON SCALE0.100 DEPTH1 DOTS0 UNITS0.0 SHOW_LAYERS 1:* ARRAY DRAW_MODESIDES CELL_LIMIT1024 TEXT LOWER_CASEDISABLED MULTI_LINE_TEXTDISABLED ORIENTATIONS2 DISPLAY_ORIGINSOFF USE TEXT_JUSTIFICATIONLB WIRE_TYPE2 ARC_TYPE2 N_SIDES16 RESOLUTION STEP0.100 MODESOFT SNAP ANGLE45 STEP(0.100,0.100) OFFSET(0.000,0.000) NEAR UNITS0.05 DOTS4 GRID 1 ON COLORRED DOTS STEP1.0 GRID 2 ON COLORCYAN CROSSES STEP5 GRID 3 OFF COLORWHITE LINES STEP50000 LAYER 1 NAMENWEL WIDTH1.300 SPACE4.200 DIM_BLUE PAT13 PEN16 NO_CIF STREAM1,0 LAYER 2 NAMECOMP WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.700 ORANGE PAT29 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM2,0 LAYER 3 NAMEPFIELD WIDTH4.300 SPACE2.200 GRAY PAT0 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM3,0 LAYER 4 NAMEPOLY WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 GREEN PAT20 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM4,0 LAYER 5 NAMENPLUS WIDTH1.300 SPACE0.000 YELLOW PAT15 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM5,0 LAYER 6 NAMEPPLUS WIDTH1.300 SPACE0.000 ORANGE PAT15 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM6,0 LAYER 7 NAMECONT WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 WHITE PAT1 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM7,0 LAYER 8 NAMEMET1 WIDTH1.400 SPACE1.200 CYAN PAT3 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM8,0 LAYER 9 NAMEVIA WIDTH1.000 SPACE1.000 YELLOW PAT1 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM9,0 LAYER 10 NAMEMET2 WIDTH1.800 SPACE1.400 RED PAT13 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM10,0 LAYER 40 NAMENBURIED WIDTH1.000 SPACE0.000 YELLOW PAT34 PEN* NO_CIF STREAM21,0 There are some detail set by Process_Layer_File which will define things like resolution and calma number for each layer. A edited version of this file is shown above.Cell_Placement_DetailsThings like cell rotation and hierarchy need to be included in a GDSII file as well. The text printout for this layout above shows only cell placement and rotation information.
 转存失败重新上传取消
转存失败重新上传取消 ICEDIT.txtADD CELL "NMOS" ID143 AT (-1.8, 7.3) ADD CELL "AT_ZERO" ID141 AT ( 0.0, 0.0) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID146 MY AT ( 6.3,-1.5) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID145 MX AT (16.4, 7.3) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID144 R1 AT ( 7.5, 6.6)This is not a problem for layout since the all the cell are usually contained in one directory. But the GDSII file needs to contain all cell geometries including cells that are placed inside other cells. GDSII.txt HEADER Release # 3 BGNLIB LIBNAME MYCELL.DB FONTS GDSII:CALMAFONT.TX GENERATIONS 3 UNITS 0.001 1e-09 BGNSTR STRNAME MYCELL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS none XY -1800 7300 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS none ANGLE 90 XY 7500 6600 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS reflect ANGLE 180 XY 16400 7300 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS reflect XY 6300 -1500 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME AT_ZERO BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY -1000 0 -1000 -1000 0 -1000 0 0 -1000 0 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY 0 1000 0 0 1000 0 1000 1000 0 1000 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME NMOS BOUNDARY LAYER 5 DATATYPE 0 XY -1500 3600 -1500 -3700 1500 -3700 1500 3600 -1500 3600 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY 2900 500 2900 -500 3900 -500 3900 500 2900 500 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY 2600 800 2600 -800 4200 -800 4200 800 2600 800 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 4 DATATYPE 0 XY 2200 1100 4500 1100 4500 -1200 2200 -1200 2200 -500 -2600 -500 -2600 500 2200 500 2200 1100 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY -500 -1700 -500 -2700 500 -2700 500 -1700 -500 -1700 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -800 -1400 -800 -3000 800 -3000 800 -1400 -800 -1400 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY -500 2500 -500 1500 500 1500 500 2500 -500 2500 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -800 2800 -800 1200 800 1200 800 2800 -800 2800 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 2 DATATYPE 0 XY -1100 -1100 -600 -1100 -600 900 -1100 900 -1100 3100 1100 3100 1100 900 500 900 500 -1100 1100 -1100 1100 -3300 -1100 -3300 -1100 -1100 ENDEL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL ENDSTR ENDLIB The GFDSII format of storing all information is shown above. Apparantly a mirror in the X direction is being done with a reflection and a 180 degree rotation. The simple GDSII_read_Program is given here for reference sake only. This program is written more in a style to make some hard to see critical details stand out. It was written on a MacBook and is intended more for personal debugging purposes. There are several GDSII translation programs online which do the same thing. The latest mac version is GdsDump-OSX. So far, the GdsDump-OSX program has yet to crash on a GDSII file. For information sake, the following are listings of the various types of blocks.GDSII_REFNr Code Mnemonic Data Type description 0 0002 HEADER Two-Byte Signed Integer version number 1 0102 BGNLIB Two-Byte Signed Integer begin of library, last modification date and time 2 0206 LIBNAME Two-Byte Signed Integer name of library 3 0305 UNITS Eight-Byte Real user and database units 4 0400 ENDLIB No Data end of library 5 0502 BGNSTR Two-Byte Signed Integer begin of structure creation and modification time 6 0606 STRNAME ASCII string name of structure 7 0700 ENDSTR No Data end of structure 8 0800 BOUNDARY No Data begin of boundary element 9 0900 PATH No Data begin of path element 10 0A00 SREF No Data begin of structure reference element 11 0B00 AREF No Data begin of array reference element 12 0C00 TEXT No Data begin of text element 13 0D02 LAYER Two-Byte Signed Integer layer number of element 14 0E02 DATATYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer Datatype number of element 15 0F03 WIDTH Four-Byte Signed Integer width of element in db units 16 1003 XY Four-Byte Signed Integer list of xy coordinates in db units 17 1100 ENDEL No Data end of element 18 1206 SNAME ASCII string name of structure reference 19 1302 COLROW Two-Byte Signed Integer number of colomns and rows in array reference 21 1500 NODE No Data begin of node element 22 1602 TEXTTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer texttype number 23 1701 PRESENTATION Bit Array text presentation, font 25 1906 STRING ASCII string character string for text element 26 1A01 STRANS Bit Array array reference, structure reference and text transform flags 27 1B05 MAG Eight Byte Real magnification factor for text and references 28 1C05 ANGLE Eight Byte Real rotation angle for text and references 31 1F06 REFLIBS ASCII string name of referenced libraries 32 2006 FONTS ASCII string name of text fonts definition files 33 2102 PATHTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer type of PATH element end ( rounded, square) 34 2202 GENERATIONS Two-Byte Signed Integer number of deleted structure ????? 35 2306 ATTRTABLE ASCII string attribute table, used in combination with element properties 38 2601 ELFLAGS Two-Byte Signed Integer template data 42 2A02 NODETYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer node type number for NODE element 43 2B02 PROPATTR Two-Byte Signed Integer attribute number 44 2C06 PROPVALUE ASCII string attribute name 45 2D00 BOX No Data begin of box element 46 2E02 BOXTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer boxtype for box element 47 2F03 PLEX Four-Byte Signed Integer plex number 50 3202 TAPENUM Two-Byte Signed Integer Tape Number 51 3302 TAPECODE Two-Byte Signed Integer Tape code 54 3602 FORMAT Two-Byte Signed Integer format type 55 3706 MASK ASCII string list of layers 56 3800 ENDMASKS No Data end of MASK
ICEDIT.txtADD CELL "NMOS" ID143 AT (-1.8, 7.3) ADD CELL "AT_ZERO" ID141 AT ( 0.0, 0.0) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID146 MY AT ( 6.3,-1.5) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID145 MX AT (16.4, 7.3) ADD CELL "NMOS" ID144 R1 AT ( 7.5, 6.6)This is not a problem for layout since the all the cell are usually contained in one directory. But the GDSII file needs to contain all cell geometries including cells that are placed inside other cells. GDSII.txt HEADER Release # 3 BGNLIB LIBNAME MYCELL.DB FONTS GDSII:CALMAFONT.TX GENERATIONS 3 UNITS 0.001 1e-09 BGNSTR STRNAME MYCELL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS none XY -1800 7300 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS none ANGLE 90 XY 7500 6600 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS reflect ANGLE 180 XY 16400 7300 ENDEL SREF SNAME NMOS STRANS reflect XY 6300 -1500 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME AT_ZERO BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY -1000 0 -1000 -1000 0 -1000 0 0 -1000 0 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 50 DATATYPE 1 XY 0 1000 0 0 1000 0 1000 1000 0 1000 ENDEL ENDSTR BGNSTR STRNAME NMOS BOUNDARY LAYER 5 DATATYPE 0 XY -1500 3600 -1500 -3700 1500 -3700 1500 3600 -1500 3600 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY 2900 500 2900 -500 3900 -500 3900 500 2900 500 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY 2600 800 2600 -800 4200 -800 4200 800 2600 800 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 4 DATATYPE 0 XY 2200 1100 4500 1100 4500 -1200 2200 -1200 2200 -500 -2600 -500 -2600 500 2200 500 2200 1100 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY -500 -1700 -500 -2700 500 -2700 500 -1700 -500 -1700 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -800 -1400 -800 -3000 800 -3000 800 -1400 -800 -1400 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 7 DATATYPE 0 XY -500 2500 -500 1500 500 1500 500 2500 -500 2500 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 8 DATATYPE 0 XY -800 2800 -800 1200 800 1200 800 2800 -800 2800 ENDEL BOUNDARY LAYER 2 DATATYPE 0 XY -1100 -1100 -600 -1100 -600 900 -1100 900 -1100 3100 1100 3100 1100 900 500 900 500 -1100 1100 -1100 1100 -3300 -1100 -3300 -1100 -1100 ENDEL SREF SNAME AT_ZERO STRANS none XY 0 0 ENDEL ENDSTR ENDLIB The GFDSII format of storing all information is shown above. Apparantly a mirror in the X direction is being done with a reflection and a 180 degree rotation. The simple GDSII_read_Program is given here for reference sake only. This program is written more in a style to make some hard to see critical details stand out. It was written on a MacBook and is intended more for personal debugging purposes. There are several GDSII translation programs online which do the same thing. The latest mac version is GdsDump-OSX. So far, the GdsDump-OSX program has yet to crash on a GDSII file. For information sake, the following are listings of the various types of blocks.GDSII_REFNr Code Mnemonic Data Type description 0 0002 HEADER Two-Byte Signed Integer version number 1 0102 BGNLIB Two-Byte Signed Integer begin of library, last modification date and time 2 0206 LIBNAME Two-Byte Signed Integer name of library 3 0305 UNITS Eight-Byte Real user and database units 4 0400 ENDLIB No Data end of library 5 0502 BGNSTR Two-Byte Signed Integer begin of structure creation and modification time 6 0606 STRNAME ASCII string name of structure 7 0700 ENDSTR No Data end of structure 8 0800 BOUNDARY No Data begin of boundary element 9 0900 PATH No Data begin of path element 10 0A00 SREF No Data begin of structure reference element 11 0B00 AREF No Data begin of array reference element 12 0C00 TEXT No Data begin of text element 13 0D02 LAYER Two-Byte Signed Integer layer number of element 14 0E02 DATATYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer Datatype number of element 15 0F03 WIDTH Four-Byte Signed Integer width of element in db units 16 1003 XY Four-Byte Signed Integer list of xy coordinates in db units 17 1100 ENDEL No Data end of element 18 1206 SNAME ASCII string name of structure reference 19 1302 COLROW Two-Byte Signed Integer number of colomns and rows in array reference 21 1500 NODE No Data begin of node element 22 1602 TEXTTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer texttype number 23 1701 PRESENTATION Bit Array text presentation, font 25 1906 STRING ASCII string character string for text element 26 1A01 STRANS Bit Array array reference, structure reference and text transform flags 27 1B05 MAG Eight Byte Real magnification factor for text and references 28 1C05 ANGLE Eight Byte Real rotation angle for text and references 31 1F06 REFLIBS ASCII string name of referenced libraries 32 2006 FONTS ASCII string name of text fonts definition files 33 2102 PATHTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer type of PATH element end ( rounded, square) 34 2202 GENERATIONS Two-Byte Signed Integer number of deleted structure ????? 35 2306 ATTRTABLE ASCII string attribute table, used in combination with element properties 38 2601 ELFLAGS Two-Byte Signed Integer template data 42 2A02 NODETYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer node type number for NODE element 43 2B02 PROPATTR Two-Byte Signed Integer attribute number 44 2C06 PROPVALUE ASCII string attribute name 45 2D00 BOX No Data begin of box element 46 2E02 BOXTYPE Two-Byte Signed Integer boxtype for box element 47 2F03 PLEX Four-Byte Signed Integer plex number 50 3202 TAPENUM Two-Byte Signed Integer Tape Number 51 3302 TAPECODE Two-Byte Signed Integer Tape code 54 3602 FORMAT Two-Byte Signed Integer format type 55 3706 MASK ASCII string list of layers 56 3800 ENDMASKS No Data end of MASK
http://www.idea2ic.com/PlayWithICEDIT/Look_Inside_GDSII.html
