/1 前言/
Elasticsearch 是一个开源的搜索引擎,建立在一个全文搜索引擎库 Apache Lucene™ 基础之上。

那么如何实现 Elasticsearch和 Python 的对接成为我们所关心的问题了 (怎么什么都要和 Python 关联啊)。
/2 Python 交互/
所以,Python 也就提供了可以对接 Elasticsearch的依赖库。
pip install elasticsearch登录后复制
初始化连接一个 Elasticsearch 操作对象。
def __init__(self, index_type: str, index_name: str, ip="127.0.0.1"):
# self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=('username', 'password'), port=9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch("localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name登录后复制默认端口 9200,初始化前请确保本地已搭建好 Elasticsearch的所属环境。
根据 ID 获取文档数据
def get_doc(self, uid):
return self.es.get(index=self.index_name, id=uid)登录后复制插入文档数据
def insert_one(self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def insert_array(self, docs: list):
for doc in docs:
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)登录后复制搜索文档数据
def search(self, query, count: int = 30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": ["title", "content", "link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_data
def __search(self, query: dict, count: int = 20): # count: 返回的数据大小
results = []
params = {
'size': count
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=query, params=params)
for hit in match_data['hits']['hits']:
results.append(hit['_source'])
return results登录后复制删除文档数据
def delete_index(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
pass登录后复制好啊,封装 search 类也是为了方便调用,整体贴一下。
from elasticsearch import Elasticsearch
class elasticSearch():
def __init__(self, index_type: str, index_name: str, ip="127.0.0.1"):
# self.es = Elasticsearch([ip], http_auth=('elastic', 'password'), port=9200)
self.es = Elasticsearch("localhost:9200")
self.index_type = index_type
self.index_name = index_name
def create_index(self):
if self.es.indices.exists(index=self.index_name) is True:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
self.es.indices.create(index=self.index_name, ignore=400)
def delete_index(self):
try:
self.es.indices.delete(index=self.index_name)
except:
pass
def get_doc(self, uid):
return self.es.get(index=self.index_name, id=uid)
def insert_one(self, doc: dict):
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def insert_array(self, docs: list):
for doc in docs:
self.es.index(index=self.index_name, doc_type=self.index_type, body=doc)
def search(self, query, count: int = 30):
dsl = {
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": query,
"fields": ["title", "content", "link"]
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"title": {}
}
}
}
match_data = self.es.search(index=self.index_name, body=dsl, size=count)
return match_data登录后复制尝试一下把 Mongodb 中的数据插入到 ES 中。
import json
from datetime import datetime
import pymongo
from app.elasticsearchClass import elasticSearch
client = pymongo.MongoClient('127.0.0.1', 27017)
db = client['spider']
sheet = db.get_collection('Spider').find({}, {'_id': 0, })
es = elasticSearch(index_type="spider_data",index_name="spider")
es.create_index()
for i in sheet:
data = {
'title': i["title"],
'content':i["data"],
'link': i["link"],
'create_time':datetime.now()
}
es.insert_one(doc=data)登录后复制到 ES 中查看一下,启动 elasticsearch-head 插件。
如果是 npm 安装的那么 cd 到根目录之后直接 npm run start 就跑起来了。
本地访问 http://localhost:9100/
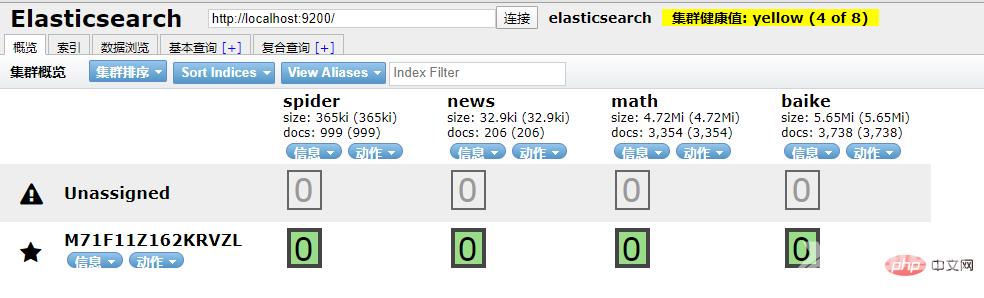
发现新加的 spider 数据文档确实已经进去了。
/3 爬虫入库/
要想实现 ES 搜索,首先要有数据支持,而海量的数据往往来自爬虫。
为了节省时间,编写一个最简单的爬虫,抓取 百度百科。
简单粗暴一点,先 递归获取 很多很多的 url 链接
import requests
import re
import time
exist_urls = []
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.1) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/62.0.3202.62 Safari/537.36',
}
def get_link(url):
try:
response = requests.get(url=url, headers=headers)
response.encoding = 'UTF-8'
html = response.text
link_lists = re.findall('.*?<a target=_blank href="/item/([^:#=<>]*?)".*?</a>', html)
return link_lists
except Exception as e:
pass
finally:
exist_urls.append(url)
# 当爬取深度小于10层时,递归调用主函数,继续爬取第二层的所有链接
def main(start_url, depth=1):
link_lists = get_link(start_url)
if link_lists:
unique_lists = list(set(link_lists) - set(exist_urls))
for unique_url in unique_lists:
unique_url = 'https://baike.baidu.com/item/' + unique_url
with open('url.txt', 'a+') as f:
f.write(unique_url + '\n')
f.close()
if depth < 10:
main(unique_url, depth + 1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_url = 'https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E7%99%BE%E5%BA%A6%E7%99%BE%E7%A7%91'
main(start_url)登录后复制把全部 url 存到 url.txt 文件中之后,然后启动任务。
# parse.py
from celery import Celery
import requests
from lxml import etree
import pymongo
app = Celery('tasks', broker='redis://localhost:6379/2')
client = pymongo.MongoClient('localhost',27017)
db = client['baike']
@app.task
def get_url(link):
item = {}
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_9_2) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/34.0.1847.131 Safari/537.36'}
res = requests.get(link,headers=headers)
res.encoding = 'UTF-8'
doc = etree.HTML(res.text)
content = doc.xpath("//div[@class='lemma-summary']/div[@class='para']//text()")
print(res.status_code)
print(link,'\t','++++++++++++++++++++')
item['link'] = link
data = ''.join(content).replace(' ', '').replace('\t', '').replace('\n', '').replace('\r', '')
item['data'] = data
if db['Baike'].insert(dict(item)):
print("is OK ...")
else:
print('Fail')登录后复制run.py 飞起来
from parse import get_url
def main(url):
result = get_url.delay(url)
return result
def run():
with open('./url.txt', 'r') as f:
for url in f.readlines():
main(url.strip('\n'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()登录后复制黑窗口键入
celery -A parse worker -l info -P gevent -c 10登录后复制
哦豁 !! 你居然使用了 Celery 任务队列,gevent 模式,-c 就是10个线程刷刷刷就干起来了,速度杠杠的 !!
啥?分布式? 那就加多几台机器啦,直接把代码拷贝到目标服务器,通过 redis 共享队列协同多机抓取。
这里是先将数据存储到了 MongoDB 上(个人习惯),你也可以直接存到 ES 中,但是单条单条的插入速度堪忧(接下来会讲到优化,哈哈)。
使用前面的例子将 Mongo 中的数据批量导入到 ES 中,OK !!!
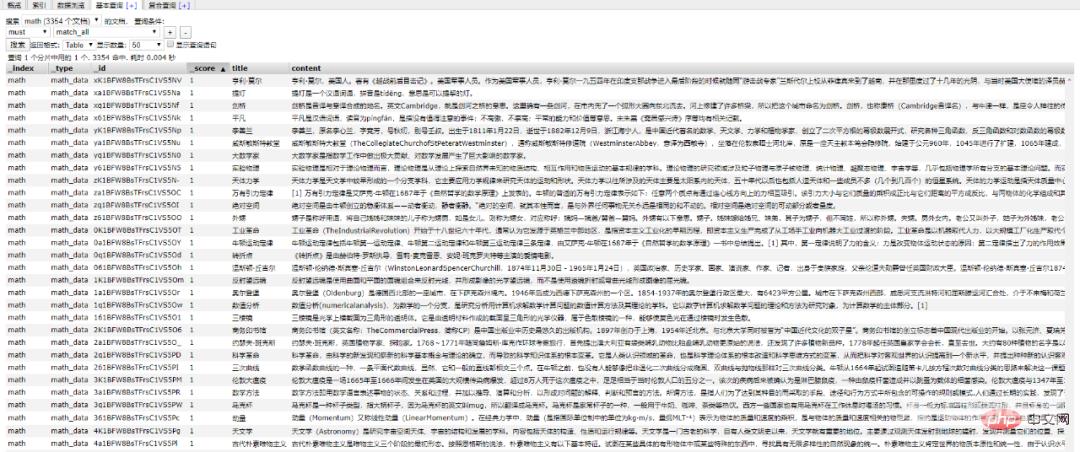
到这一个简单的数据抓取就已经完毕了。
好啦,现在 ES 中已经有了数据啦,接下来就应该是 Flask web 的操作啦,当然,Django,FastAPI 也很优秀。嘿嘿,你喜欢 !!
关于FastAPI 的文章可以看这个系列文章:
1、(入门篇)简析Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架
2、(进阶篇)Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架
3、(完结篇)Python web框架FastAPI——一个比Flask和Tornada更高性能的API 框架
/4 Flask 项目结构/

这样一来前期工作就差不多了,接下来剩下的工作主要集中于 Flask 的实际开发中,蓄力中 !!
