1、老师对大家的要求
- 课堂纪律
- 上课风格
- 课后作业
- 学习小组(班长,学委)
- 机房管理
- 违规管理
2、大家对老师的要求
3、软件工程专业的前景
https://www.lagou.com/
https://www.51job.com/
http://www.gaosan.com/gaokao/76642.html
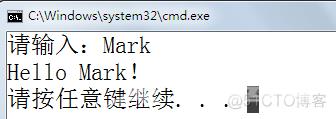
二、内部测试1、请使用C#编程实现在控制台输入你的姓名,输出问好信息,如:
请输入:张三
Hello,张三!
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace Test01 { class Program { //ctrl+f5 static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入:"); //定义变量,赋值为张三 //从键盘输入,赋值给变量name String name =Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("Hello "+name+"!"); } } }
结果:


String name = ""; do { Console.Write("请输入:"); //定义变量,赋值为张三 //从键盘输入,赋值给变量name name = Console.ReadLine(); Console.WriteLine("Hello " + name + "!"); } while (name != "");View Code
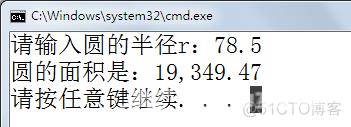
2、请使用C#实现计算圆的面积,输入半径,显示圆的面积,如:
请输入圆的半径r:5 圆的面积是:78.5
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace Test02 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //ctrl+k ctrl+c //2、请使用C#实现计算圆的面积,输入半径,显示圆的面积,如: // 请输入圆的半径r:5 // 圆的面积是:78.5 Console.Write("请输入圆的半径r:"); //从键盘输入字符类型的半径,转换成double类型 double r =Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine()); //计算面积 double area = 3.14 * r * r; //输出 Console.WriteLine("圆的面积是:{0:N2}",area); } } }
输出:
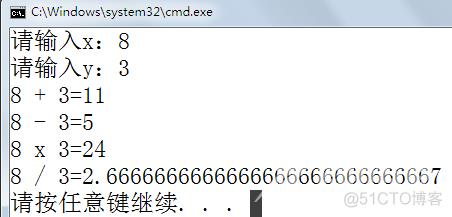
3、使用C#编程实现简单的四则运算,输入两个数,输出这两个数的加减乘除四则运算,如:
请输入x:8.5 请输入y:5.3
8.5+5.3=13.8 8.5-5.3=3.2 8.5*5.3=45.05 8.5/5.3=1.6
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace Test03 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //3、使用C#编程实现简单的四则运算,输入两个数,输出这两个数的加减乘除四则运算,如: // 复制代码 // 请输入x:8.5 // 请输入y:5.3 //提示 Console.Write("请输入x:"); //输入字符,转换成decimal类型,赋值给变量x decimal x =Convert.ToDecimal(Console.ReadLine()); Console.Write("请输入y:"); decimal y = Convert.ToDecimal(Console.ReadLine()); Console.WriteLine(x+" + "+y+"="+(x+y)); Console.WriteLine("{0} - {1}={2}",x,y,x-y); Console.WriteLine("{0} x {1}={2}", x, y, x * y); Console.WriteLine("{0} / {1}={2}", x, y, x / y); } } }
输出:
拓展:
1、当y为0时,提示用户输入错误,if判断
2、一次运行可以反复计算,do---while循环
三、运算符3.1、赋值运算符
C#中常见的赋值运算符:
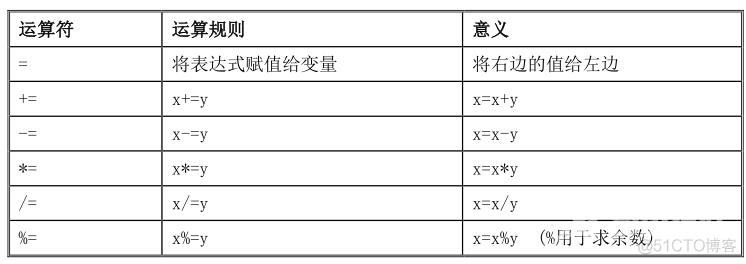
“=”号是基本赋值运算符,其它的+=、-=、*=、/=、%=称为复合赋值运算符。这些运算符的左边一定是变量,右边可以是表达式。复合赋值的运算规则简单说就是在左边变量原来值的基础上跟右边的表达式作相应运算,再把计算结果赋值给左边的变量。它们的使用请看如下代码:
int x=40; //将40赋给x变量 x+=30; //相当于x=x+30,此时得到x=70 x-=20; //相当于x=x-20,此时得到x=50 x*=2; //相当于x=x*2,此时得到x=100 x/=4; //相当于x=x/4,此时得到x=25 x%=3; //相当于x=x%3,此时得到x=1
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace P01 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int x=5,y=6; //x = x + y; //x += y; //x=x+y; //y += y; //y=y+y; //x += x; //x=x+x; //y += (y - x); //y=6+1 //y -= x + 3 * y; //y=y-(x+3*y) //求余 x%2=0 x%2=1 //y %=x; //y=y%x; y=6%5; x *= y % 2 - x + y; //x=x*(y%2-x+y) //x=5*(0-5+6) Console.WriteLine(x); } } }
3.2、算术运算符
C#中常见的算术运算符,如下表所示:
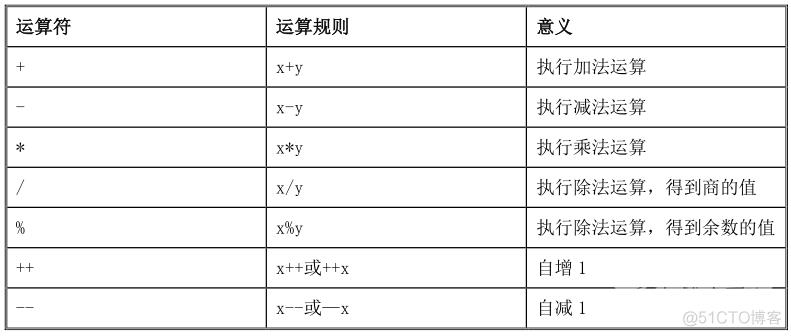
由算术运算符组成的表达式称为算术表达式。对这些运算符的说明如下:
+号除了表示加法运算以外,还可以表示字符串的连接或表示正数的正号;
-号表示减法运算外,还可以表示负数的负号;
/号表示除法运算;
%号表示求模运算,在商为整数的情况下,得到的余数作为结果;
++和--都有前缀和后缀两种形式,++表示自身的值增加 1,--表示自身的值减少 1。前缀和后
缀的差别主要在于优先级的不同,前缀优先级高,后缀优先级低。
课堂作业:
(1)int x=30,y=0; x+=10; y-=x; 请问 y 等于多少?
(2)int x=40; int y=--x + 10; 请问 y 等于多少?
3.3、关系运算符
C#中提供了多种关系运算符,如下表所示:


由关系运算符组成的表达式称为关系表达式。从上表中可以看出,关系表达式的结果只能是 true
或者 false,也就是布尔类型的结果。
注意:在程序中判断是否相等,要用两个等号。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace P03 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int x = 9, y = 2; Console.WriteLine(x==y); //false 假 Console.WriteLine(x != y); //true 真 Console.WriteLine(x > y); //true 真 Console.WriteLine(x >= y); //true 真 Console.WriteLine(x < y); //false 假 Console.WriteLine(x <= y); //false 假 } } }
3.4、逻辑运算符
C#中的逻辑运算符有 3 种,如下表所示:
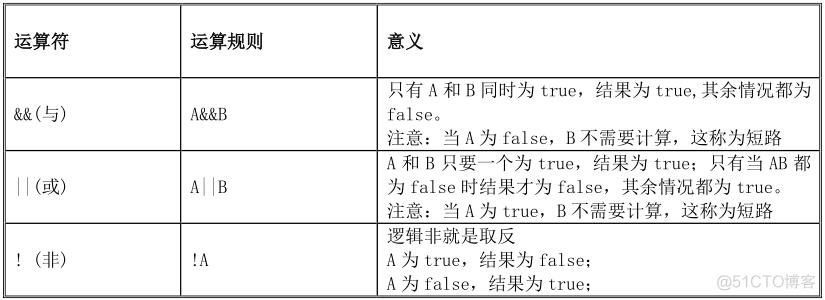
由逻辑运算符组成的表达式称为逻辑表达式,跟关系表达式一样,它的结果也只能是 true 或
false。关系表达式和逻辑表达式也可称为布尔表达式。布尔表达式通常出现在选择、循环等语句中表
示判断条件。
int x=5,y=10,z=15; char c='x'; Console.WriteLine(x==y); //false Console.WriteLine(x<=y); //true Console.WriteLine(x<y&&y<z); //true Console.WriteLine(x>y||y<z); //true Console.WriteLine(!(x<y)); //false Console.WriteLine(c>='a'&&c<='z'); //true
课堂作业:使用关系或逻辑运算符分别写出如下问题的表达式。
(1)一个整数 a 是偶数;
(2)一个学生的成绩 b 在 0 到 100 之间;
(3)一个数 c 小于 1 或者大于 12
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace P04 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int x = 9, y = 2,z=1; //&& 与运算,同时为真时结果为真,其余情况都为假 Console.WriteLine(x>y&&x>z); //真true 假false Console.WriteLine(x<y&&x>z); //真true 假false //|| 或运算,同时为假时,结果为假,其余情况都为真 Console.WriteLine(x > y || x > z); //真true 假false Console.WriteLine(x < y || x > z); //真true 假false Console.WriteLine(x <= y || x <= z); //真true 假false //! 非运算,真变假,假变真 Console.WriteLine(!(x>y)); Console.WriteLine(!(x<z)); } } }
3.5、运算符的优先级
当计算有两个或两个以上运算符的表达式时,就需要考虑运算符的优先级。下表给出了常见运算
符的优先级关系。
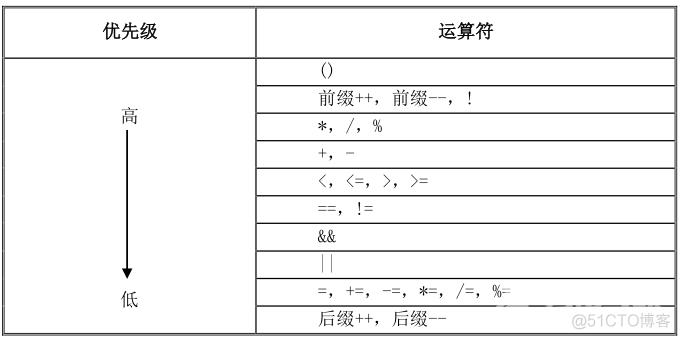
在实际的应用中,擅于给表达式中某些优先运算部分加(),是一个很好的做法。这样就能更清楚
知道表达式的计算顺序了。
课堂作业:计算出下列表达式的结果。
(1) 30 / (7 + 2) < 4 || 6 % 5 == 1;
(2) 30 > 6 * 2 && 40 - 4 * 3 / 6 < 40;


using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace p06 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //int n =Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); for (int n = 0; n <= 10000; n++) { if (n % 2 == 0) { Console.Write("{0}偶数",n); } else { Console.Write("{0}奇数", n); } } Console.WriteLine("over"); } } }View Code 四、选择语句
在生活中,经常要作出选择,比如,当一个人走到岔路口时,摆在面前有两条路,那么应该选择
哪条路走呢?这种情况也经常出现在程序中,选择语句也就派上了用场。选择语句也可称为分支流程
结构,主要包括两种语句:if 和 switch。
4.1、 if 语句
if 语句,主要有 3 种形式。
(1) 形式一 ,单分支流程语句,语法结构如下:
if(布尔表达式) { 语句块; }
例 3.1 输入成绩,判断是否及格。
(2) 形式二 ,双分支流程语句,语法结构如下:
if(布尔表达式) { 语句块1; } else { 语句块2; }
此种语法的含义是,当布尔表达式的值为 true 时,执行语句块 1;否则,执行语句块 2。
例 3.2 在上面的例 3.1 中使用了单分支形式的 if 语句,当及格时显示恭喜您,当不及格时则程
序什么都不做,如果我们希望不及格也要有对应的提示信息则需要使用双分支的 if 语句,代码如下:
三目运算符
对于双分支的 if…else 语句,在 C#中,有一个可以达到类似效果的运算符:三目运算符(?:)。
在某些情况下使用,它可以简化我们的程序代码。三目运算符需要三个操作数,使用形式如下:
布尔表达式?表达式1:表达式2
它的求值规则为:计算布尔表达式的值,如果为 true,则返回表达式 1 的结果;如果为 false,
则返回表达式 2 的结果。
(3) 形式三 ,多分支流程语句,语法结构如下:
if(布尔表达式1) { 语句块1; } else if(布尔表达式2) { 语句块2; } … //else if部分可以出现任意次 else //else部分并不是必需的,可以没有 { 语句块; }
此种语法的含义是,从上往下判断布尔表达式,某个布尔表达式为 true,则执行相应的语句块,
并结束整个结构。当所有的布尔表达式都为 false 时,则执行 else 部分的语句块。简单来说,就是 N
条路中选择一条路走,选择了一条路其它的路就不能走了;所有的语句块,最后只会执行一个。
例 3.5 在上面的例 3.2 中使用了双分支形式的 if 语句,要么显示及格,要么显示不及格,如果
我们希望要经过判断分别显示优良中差,则需要使用多分支的 if 语句,代码如下:
4.2、switch语句
switch 是多路选择语句,它根据某个值来使程序多个分支中选择一个用于执行。与 if 语句不同
的是,if 可以说任意情况下都可以使用,而 switch 一般只用于等值判断,在某些时候可以简化 if 语
句,并且提高执行效率。
C#中 switch 语句的语法格式如下:
switch(表达式) { case 【常量表达式】:语句块;break; case 【常量表达式】:语句块;break; … case 【常量表达式】:语句块;break; default:语句块;break; }
语法的含义是,计算表达式的值,跟每个 case 后的【常量表达式】比较,当表达式的值等于某个
case 后【常量表达式】的值时,执行该 case 后的语句块。如果表达式的值与所有 case 后的【常量表
达式】都不相等时,则执行 default 后的语句块。
switch 语句的使用过程需要注意以下几点问题:
- 每个 case 后的【常量表达式】的值必须是与“表达式”的类型相同的一个常量,不能是
- 变量;
- 多个 case 后指定的常量值不能出现重复;
- default 语句是可选的,一个 switch 语句中最多只能有一个 default 语句;
- case 和 default 语句先后顺序允许变动,一般 default 语句放在最后写;
- 当 case 后面有处理语句时,break 将不能省略。否则,将提示错误。
示例1:
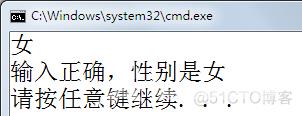
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace C33 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { String sex = Console.ReadLine(); switch (sex) { case "男": Console.WriteLine("输入正确,性别是男"); break; case "女": Console.WriteLine("输入正确,性别是女"); break; default: Console.WriteLine("输入错误"); break; } } } }
输出:
示例2:
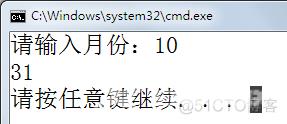
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace C34 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("请输入月份:"); int month = Convert.ToInt32(Console.ReadLine()); switch (month) { case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12: Console.WriteLine(31); break; case 4: case 6: case 9: case 11: Console.WriteLine(30); break; case 2: Console.WriteLine(28); break; default: Console.WriteLine("输入错误"); break; } } } }
输出:
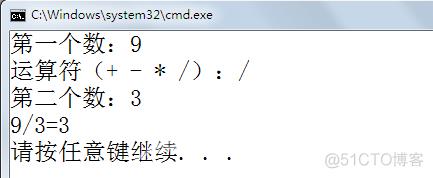
if与switch嵌套
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; namespace C35 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Console.Write("第一个数:"); double m = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine()); Console.Write("运算符(+ - * /):"); String mark = Console.ReadLine(); Console.Write("第二个数:"); double n = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine()); switch (mark) { case "+": Console.WriteLine("{0}+{1}={2}", m, n, m + n); break; case "-": Console.WriteLine("{0}-{1}={2}", m, n, m - n); break; case "*": Console.WriteLine("{0}x{1}={2}", m, n, m * n); break; case "/": if (n != 0) { Console.WriteLine("{0}/{1}={2}", m, n, m / n); } else { Console.WriteLine("除数不能为零。"); } break; default: Console.WriteLine("运算符错误,只支持+-*/运算。"); break; } } } }
5.1、完成第1章、第2章所有课后练习
5.2、完成第3章所有课后练习
