我们在服务器上安装了JDK17以及Maven,然后有个脚本会从不同的仓库拉取源码并通过mvn compile命令进行编译。不同的源码采用不同版本的jdk进行编辑,那么只有一个JDK17可以满足编译需求吗?
在说明该问题前我们先回顾下Java文件的编译
一、回顾Java的编译
首先,所谓的源文件本身就是个文本文件,文本中保存的字符都有一个特定的编码,所以我们只需要在系统里面创建一个文本,然后开始写以下的代码
package com.demo;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
public class Demo {
DateTimeFormatter formatter = DateTimeFormatter
.ofPattern("yyyy-MMM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public List<String> getEmptyList(){
return new ArrayList<>() ;
}
public String formatTime(){
return formatter.format(LocalDateTime.now());
}
}然后按Java语言的要求将文件命名为Demo.java。上面文本中的字符和格式是按照Java语言的语法来输入的,如果是想编写其它开发语言的源码文件,使用相应的语法即可。那么接下来我们需要对文本文件进行编译,可使用javac命令来完成。
javac命令读取文本,根据java语句和关键字生成抽象语法树,再经过一系列的处理生成可被JVM解析的字节码格式文件。
当然为了能让其不会读到乱码,我们还应该告诉它文本文件的编码格式
那么我们应该用哪个版本JDK中的javac命令来对文件进行编译呢?这个我们可以从以下方面来考虑如何选择
- 文本中是否有啥关键字或语法格式或者引入的对象限制必须至少使用哪个版本的JDK?
- 你希望将编译后的文件放在哪些版本的JVM中运行?
基于这两点,我们看看上面编写的源码应该用哪个版本的JDK来编译
- 文本中使用了从JDK8才引入的类型DateTimeFormatter、LocalDateTime
- 我希望运行在jdk1.8以上的虚拟机中
基于第一点,要想成功编译则至少要使用jdk1.8来对源码进行编译;基于第二点,则要求我们编译出来的字节码都能被Java1.8版本虚拟机所识别;
有人可能会问,不就直接用jdk1.8编译就可以了么,还有其它选项?
那假设我现在只有jdk17,并且想将源文件编译的结果放到1.8版本的虚拟机上使用呢?接下来我们直接看看javac这个编译程序的使用方法吧
javac [options] [sourcefiles]可选项(只列出与本主题有关的参数)
1)-encoding encoding
指定源文件使用的字符编码,如EUC-JP和UTF-8。如果未指定-encoding选项,则使用平台默认编码。
2)--release release
根据Java编程语言的规则为指定的Java SE版本编译源代码,生成针对该版本的类文件。源代码是针对指定版本的Java SE和JDK API组合编译的。release支持的值是当前的Java SE版本和有限数量的以前的版本。
注意:当使用--release时,您不能同时使用--source/-source或--target/-target选项;
从JDK 9开始,javac不再支持小于或等于5的-source版本设置。如果使用小于或等于5的设置,则javac命令的行为就像指定了-source 6一样。
2)-source release
根据Java编程语言的规则编译指定Java SE版本的源代码。release支持的值是当前的Java SE版本和有限数量的以前的版本。
如果未指定该选项,则默认是根据当前Java SE发行版的Java编程语言规则编译源代码。
4)-target release
生成适合于指定Java SE发行版的类文件。release支持的值是当前的Java SE版本和有限数量的以前的版本。
注意:目标版本必须等于或高于源版本(--source)
从上面的参数可见,我们完全可以使用jdk17编译出支持在1.8版本的jvm运行的字节码。
javac -srouce 1.8 -target 1.8
通过上面命令,就会使用jdk17的javac程序来根据1.8版本的语法规则将其源码文件编译成支持1.8版本jvm上可运行的字节码文件。
二、再看Maven的编译
我们会通过mvn compile命令来进行源码的编译,那会有几个问题
- maven使用的是哪个jdk来对源码进行编译的?
- maven怎么知道源码文件时按照哪个版本的java规范编辑的?
- maven怎么知道编译后的文件至少要在哪个版本的jvm中运行?
maven是通过插件来完成对源码的编译
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.11.0</version>
<configuration>
<!-- 一般而言,target与source是保持一致的,但是,有时候为了让程序能在其他版本的jdk中运行(对于低版本目标jdk,源代码中不能使用低版本jdk中不支持的语法),会存在target不同于source的情况 -->
<source>1.8</source> <!-- 源代码使用的JDK版本 -->
<target>1.8</target> <!-- 需要生成的目标class文件的编译版本 -->
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding><!-- 字符集编码 -->
<skipTests>true</skipTests><!-- 跳过测试 -->
<verbose>true</verbose>
<showWarnings>true</showWarnings>
<fork>true</fork><!-- 要使compilerVersion标签生效,还需要将fork设为true,用于明确表示编译版本配置的可用 -->
<executable><!-- path-to-javac --></executable><!-- 使用指定的javac命令,例如:<executable>${JAVA_1_4_HOME}/bin/javac</executable> -->
<compilerVersion>1.3</compilerVersion><!-- 指定插件将使用的编译器的版本 -->
<meminitial>128m</meminitial><!-- 编译器使用的初始内存 -->
<maxmem>512m</maxmem><!-- 编译器使用的最大内存 -->
<compilerArgument>-verbose -bootclasspath ${java.home}\lib\rt.jar</compilerArgument><!-- 这个选项用来传递编译器自身不包含但是却支持的参数选项 -->
</configuration>
</plugin>那么这个插件是如何应对上面提出的三个问题呢?
在maven-compiler-plugin中入口类如下
@Mojo(
name = "compile",
defaultPhase = LifecyclePhase.COMPILE,
threadSafe = true,
requiresDependencyResolution = ResolutionScope.COMPILE)
public class CompilerMojo extends AbstractCompilerMojo {
/**
* The source directories containing the sources to be compiled.
*/
@Parameter(defaultValue = "${project.compileSourceRoots}", readonly = false, required = true)
private List<String> compileSourceRoots;
/**
* The directory for compiled classes.
*/
@Parameter(defaultValue = "${project.build.outputDirectory}", required = true, readonly = true)
private File outputDirectory;
//开始执行代码的编译
public void execute() throws MojoExecutionException, CompilationFailureException {
if (skipMain) {
getLog().info("Not compiling main sources");
return;
}
if (multiReleaseOutput && release == null) {
throw new MojoExecutionException("When using 'multiReleaseOutput' the release must be set");
}
//调用父类
super.execute();
if (outputDirectory.isDirectory()) {
projectArtifact.setFile(outputDirectory);
}
}
......
}父类AbstractCompilerMojo
*/
public abstract class AbstractCompilerMojo extends AbstractMojo {
protected static final String PS = System.getProperty("path.separator");
private static final String INPUT_FILES_LST_FILENAME = "inputFiles.lst";
static final String DEFAULT_SOURCE = "1.8";
static final String DEFAULT_TARGET = "1.8";
// Used to compare with older targets
static final String MODULE_INFO_TARGET = "1.9";
@Parameter(property = "maven.compiler.source",
defaultValue = DEFAULT_SOURCE)
protected String source;
@Parameter(property = "maven.compiler.target",
defaultValue = DEFAULT_TARGET)
protected String target;
@Parameter(property = "maven.compiler.release")
protected String release;
@Parameter(property = "encoding",
defaultValue = "${project.build.sourceEncoding}")
private String encoding;
/*
* 允许在单独的进程中运行编译器。
* 如果为false,则使用内置编译器,
* 而如果为true,则使用可执行文件。
*/
@Parameter(property = "maven.compiler.fork", defaultValue = "false")
private boolean fork;
//设置当fork为true时编译器要使用的可执行文件
@Parameter(property = "maven.compiler.executable")
private String executable;
//设置要传递给编译器的参数
@Parameter
protected List<String> compilerArgs;
//如果fork为true,要运行编译器的目录
@Parameter(defaultValue = "${basedir}", required = true,
readonly = true)
private File basedir;
//如果fork为true,则编译器的目标目录
@Parameter(defaultValue = "${project.build.directory}",
required = true, readonly = true)
private File buildDirectory;
@Override
public void execute() throws MojoExecutionException, CompilationFailureException {
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Look up the compiler. This is done before other code than can
// cause the mojo to return before the lookup is done possibly resulting
// in misconfigured POMs still building.
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
//编译器
Compiler compiler;
try {
//compilerId : javac
compiler = compilerManager.getCompiler(compilerId);
} catch (NoSuchCompilerException e) {
throw new MojoExecutionException("No such compiler '" + e.getCompilerId() + "'.");
}
// -----------toolchains start here ----------------------------------
// use the compilerId as identifier for toolchains as well.
Toolchain tc = getToolchain();
if (tc != null) {
getLog().info("Toolchain in maven-compiler-plugin: " + tc);
if (executable != null) {
getLog().warn("Toolchains are ignored, 'executable' parameter is set to " + executable);
} else {
fork = true;
// TODO somehow shaky dependency between compilerId and tool executable.
executable = tc.findTool(compilerId);
}
}
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Create the compiler configuration
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
CompilerConfiguration compilerConfiguration = new CompilerConfiguration();
compilerConfiguration.setOutputLocation(getOutputDirectory().getAbsolutePath());
compilerConfiguration.setOptimize(optimize);
compilerConfiguration.setDebug(debug);
// ... ...
//将配置的参数
compilerConfiguration.setExecutable(executable);
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
// Compile!
// ----------------------------------------------------------------------
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(compilerConfiguration.getSourceEncoding())) {
getLog().warn("File encoding has not been set, using platform encoding " + ReaderFactory.FILE_ENCODING
+ ", i.e. build is platform dependent!");
}
CompilerResult compilerResult;
if (useIncrementalCompilation) {
incrementalBuildHelperRequest.outputDirectory(getOutputDirectory());
incrementalBuildHelper.beforeRebuildExecution(incrementalBuildHelperRequest);
getLog().debug("incrementalBuildHelper#beforeRebuildExecution");
}
try {
compilerResult = compiler.performCompile(compilerConfiguration);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: don't catch Exception
throw new MojoExecutionException("Fatal error compiling", e);
}
// .......
}
}整个过程大体是获取Compiler实例,组装配置的参数信息,然后调用compiler的接口完成编译。而这个实例就是JavacCompiler
在plexus-compiler-api中有这样一个接口
public interface Compiler
{
String ROLE = Compiler.class.getName();
CompilerOutputStyle getCompilerOutputStyle();
String getInputFileEnding( CompilerConfiguration configuration )
throws CompilerException;
String getOutputFileEnding( CompilerConfiguration configuration )
throws CompilerException;
String getOutputFile( CompilerConfiguration configuration )
throws CompilerException;
boolean canUpdateTarget( CompilerConfiguration configuration )
throws CompilerException;
/**
* Performs the compilation of the project. Clients must implement this
* method.
*
* @param configuration the configuration description of the compilation
* to perform
* @return the result of the compilation returned by the language processor
* @throws CompilerException
*/
CompilerResult performCompile( CompilerConfiguration configuration )
throws CompilerException;
/**
* Create the command line that would be executed using this configuration.
* If this particular compiler has no concept of a command line then returns
* null.
*
* @param config the CompilerConfiguration describing the compilation
* @return an array of Strings that make up the command line, or null if
* this compiler has no concept of command line
* @throws CompilerException if there was an error generating the command
* line
*/
String[] createCommandLine( CompilerConfiguration config )
throws CompilerException;
/**
* Based on this flag the caller can decide the strategy how to compile. E.g. is incrementCompilation is not supported,
* it could decide to clear to outputDirectory to enforce a complete recompilation.
*
* @return {@code true} if incrementalCompilation is supported, otherwise {@code false}
*/
default boolean supportsIncrementalCompilation() {
return false;
}
}与此同时在plexus-compiler-javac也有一个实现类JavacCompiler
/**
* @author <a href="mailto:trygvis@inamo.no">Trygve Laugstøl</a>
* @author <a href="mailto:matthew.pocock@ncl.ac.uk">Matthew Pocock</a>
* @author <a href="mailto:joerg.wassmer@web.de">Jörg Waßmer</a>
* @author Others
*
*/
@Component( role = Compiler.class, hint = "javac ")
public class JavacCompiler
extends AbstractCompiler {
@Override
public String getCompilerId() {
return "javac";
}
//开始执行编译
@Override
public CompilerResult performCompile( CompilerConfiguration config )
throws CompilerException {
File destinationDir = new File( config.getOutputLocation() );
if ( !destinationDir.exists() ) {
destinationDir.mkdirs();
}
//要编译的源文件
String[] sourceFiles = getSourceFiles(config );
if (( sourceFiles == null ) || ( sourceFiles.length == 0 )){
return new CompilerResult();
}
//构建编译所需的参数
String[] args = buildCompilerArguments( config, sourceFiles );
CompilerResult result;
if (config.isFork()) {
//从配置文件获取可执行文件
String executable = config.getExecutable();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(executable )) {
try{
//获取执行Java编译的可执行文件
//获取javac工具可执行文件的路径:
//尝试根据操作系统或java.home系统属性
//或JAVA_HOME环境变量。
executable = getJavacExecutable();
}catch ( IOException e ){
if ( (getLogger() != null ) && getLogger().isWarnEnabled()) {
getLogger().warn( "Unable to autodetect 'javac' path, using 'javac' from the environment." );
}
//直接用javac命令
executable = "javac";
}
}
//在外部进程中编译java源代码,调用外部可执行文件,如javac。
result = compileOutOfProcess( config, executable, args );
} else {
if (isJava16() && !config.isForceJavacCompilerUse()){
// use fqcn to prevent loading of the class on 1.5 environment !
result =
inProcessCompiler().compileInProcess(args, config, sourceFiles );
} else {
//执行编译
//使用com.sun.tools.javac.Main类编译
//当前JVM中的java源代码,而不调用外部可执行文件
result = compileInProcess( args, config );
}
}
return result;
}
protected CompilerResult compileOutOfProcess( CompilerConfiguration config, String executable, String[] args )
throws CompilerException
{
Commandline cli = new Commandline();
cli.setWorkingDirectory( config.getWorkingDirectory()
.getAbsolutePath() );
//设置可执行文件
cli.setExecutable( executable );
// ... ...
}从上面的源码大体可知,maven可以通过以下方式查询javac命令文件
- 编译插件中配置的
executable属性(fork设置为true) - 从
java.home系统属性和JAVA_HOME环境变量获取可执行文件(fork设置为true)(fork设置为true) - 直接执行
javac命令(fork设置为true) - 使用
com.sun.tools.javac.Main类进行编译 【默认都是这个】
至于编译时候需要的-source和-target参数则是通过在pom.xml文件中配置而来(或插件上),如下所示:
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>可见,maven的默认行为是使用运行maven的jdk的com.sun.tools.javac.Main来进行编译。
所以,通过指定编译参数时可以满足一个jdk版本编译其它版本的源码文件的问题。
似乎可以完美解决通过JDK17编译JDK8等版本的源码问题,但实际并不会这么顺利。JDK版本的变更除了语法可能有变化外,更重要的是某些特性的变更导致自身代码和依赖的其它包都出问题。
下面显示了在实际编译源码过程中出现的问题,
三、Maven编译过程的错误
1)does not xx to unnamed module错误
我在使用JDK17编译的时候,某些项目却有如下的异常出现
Fatal error compiling: java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError: Unable to make field private com.sun.tools.javac.processing.JavacProcessingEnvironment$DiscoveredProcessors com.sun.tools.javac.processing.JavacProcessingEnvironment.discoveredProcs accessible: module jdk.compiler does not "opens com.sun.tools.javac.processing" to unnamed module @388c519 -> [Help 1]
这个错误主要时因为项目中使用了lombok导致,有人说调整版本可以解决,但如果源码不是你的怎么办,网上有人提供了以下方案:
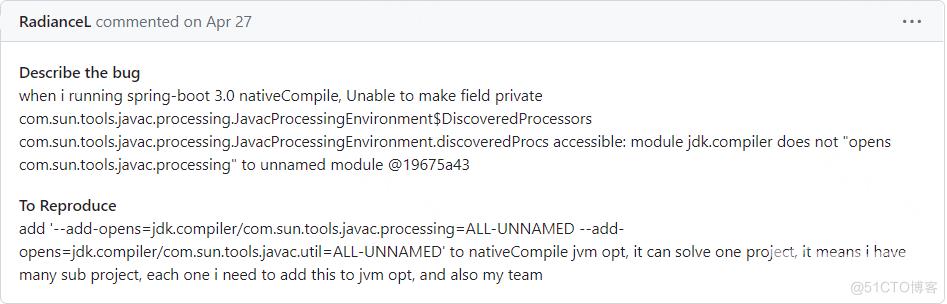
也就是通过--add-opens参数来打开相应模块的包权限以供访问(原文:https://github.com/projectlombok/lombok/issues/3417)
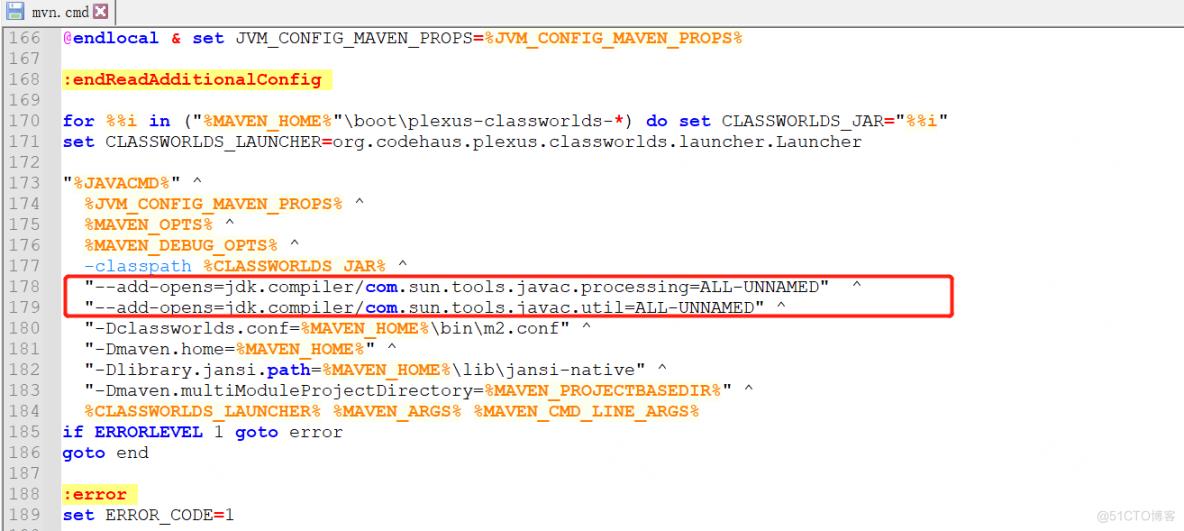
按其所说添加了参数(如上图所示),但是又报了以下错误
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:
maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:compile (default-compile)
on project xx-micro-basic: Fatal error compiling:
java.lang.IllegalAccessError: superclass access check failed:
class lombok.javac.apt.LombokFileObjects$Java9Compiler$FileManagerWrapper
(in unnamed module @0x68f6e55d) cannot access class com.sun.tools.javac.file.BaseFileManager (in module jdk.compiler)
because module jdk.compiler does not export com.sun.tools.javac.file to unnamed module @0x68f6e55d -> [Help 1]可见似乎只添加两个是不够的,按照这种方式我添加了如下的选项
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.processing=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.util=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.file=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.main=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.jvm=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.code=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.tree=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.model=ALL-UNNAMED" ^
"--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.parser=ALL-UNNAMED" ^添加完后是否就可以了呢,事实告诉我没有。。
说明:Java 16和Java 17封装了JDK内部api,这会影响各种框架,如Lombok。您可能会看到诸如module jdk.compiler does not export com.sun.tools.javac.processing to unnamed module的错误,这意味着您的应用程序不再能够访问JDK的那一部分。
一般来说,建议升级使用这些内部组件的所有依赖项,并确保您自己的代码不再使用它们。如果这是不可能的,有一个解决方案,使您的应用程序仍然能够访问内部。例如,如果您需要访问comp模块,请使用以下命令:
--add-opens=jdk.compiler/com.sun.tools.javac.comp=ALL-UNNAMED也就是可以根据错误提示,缺少就添加啥。
2)java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError错误
添加完--add-opens后执行编译出现了如下的错误
[ERROR] Failed to execute goal org.apache.maven.plugins:maven-compiler-plugin:3.1:compile (default-compile) on project xx-micro-basic: Fatal error compiling: java.lang.ExceptionInInitializerError: com.sun.tools.javac.code.TypeTags -> [Help 1]
此错误可能出现在1.9之后的jdk版本,版本必须是10或11或12或14或17。
在1.9版本之后java版本不应该以“1.xx”开头。否则将看到的大多是“Java lang exceptionininitializererror”错误。要修复此错误,您需要更改java版本,如下所示。
<!-- 不能是1.11 -->
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>但该项目使用的是jdk1.8,配置的值也是1.8,所以不是上面这点导致;那么应该是依赖项的问题(版本可能需要升级),查看项目的以下依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.16.20</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>1)可以从https://projectlombok.org/changelog查看支持的版本;
2)如果将其版本升级为<version>1.16.22</version>后则不会报错;但这似乎不是我想要的,因为前提条件是我不能修改源码;
3)还有个版本就是降低使用的JDK版本,但有的应用又用的是JDK17(示例项目用的是JDK8);
尝试将其版本先修改为1.16.22,所有模块编译成功;但如果通过修改lombok的版本来解决问题,那不如升级到支持JDK17特性的版本,这样前面提到的--add-opens参数也不需要了,但要解决TypeTags的问题又得升级版本才行。
附:javac-code-typetags异常方案
四、最终解决方案
既然JDK版本的影响那么大,那是否可以通过配置的方式来告知每个应用应该使用的jdk版本,然后在编译的时候为环境设置不同的JAVA_HOME或PATH环境变量; 或者预先复制mvn脚本后在内部指定对应jdk的路径,随后根据不同的jdk版本信息来执行不同的脚本;
这里介绍通过ProcessBuilder来执行mvn命令,同时修改环境变量的方式。
下面展示如何修改环境变量部分,其它可参考 Java中使用ProcessBuilder执行命令 一文
ProcessBuilder builder = new ProcessBuilder(execCommands);
//外部传递进来
File javaHome = null ;
if(javaHome != null && javaHome.exists()
&& javaHome.isDirectory()){
//设置或修改环境变量
Map<String,String> environment = builder.environment() ;
environment.put("JAVA_HOME",javaHome.getAbsolutePath()) ;
}
Process process = builder.start();衍生阅读:https://blogs.oracle.com/javamagazine/post/its-time-to-move-your-applications-to-java-17-heres-why-and-heres-how
