In a row of dominoes, A[i] and B[i] represent the top and bottom halves of the i -th domino. (A domino is a tile with two numbers from 1 to 6 - one on each half of the tile.) We may rotate the i -th domino, so that A[i] and B[i] swap values
In a row of dominoes, A[i] and B[i] represent the top and bottom halves of the i-th domino. (A domino is a tile with two numbers from 1 to 6 - one on each half of the tile.)
We may rotate the i-th domino, so that A[i] and B[i] swap values.
Return the minimum number of rotations so that all the values in A are the same, or all the values in B are the same.
If it cannot be done, return -1.
Example 1:
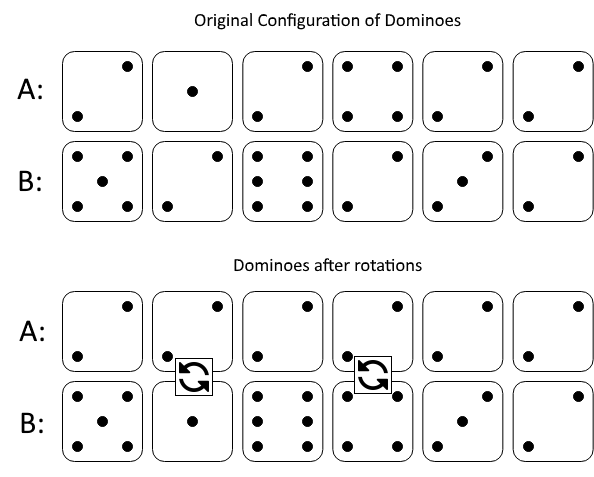
Input: A = [2,1,2,4,2,2], B = [5,2,6,2,3,2] Output: 2 Explanation: The first figure represents the dominoes as given by A and B: before we do any rotations. If we rotate the second and fourth dominoes, we can make every value in the top row equal to 2, as indicated by the second figure.
Example 2:
Input: A = [3,5,1,2,3], B = [3,6,3,3,4] Output: -1 Explanation: In this case, it is not possible to rotate the dominoes to make one row of values equal.
Note:
1 <= A[i], B[i] <= 62 <= A.length == B.length <= 20000
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
这个题是贪心题,我们可以从i = 1到6循环,然后判断A和B中对应的位置是否有i,如果都没有,那就说明无论反转多少都不可能得到关于有这个i的相同的一组数。
C++代码:
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; class Solution { public: int minDominoRotations(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B) { int n = A.size(); int best = INF; for(int i = 1; i <= 6; i++){ int ca = 0,cb = 0; for(int j = 0; j < n; j++){ if(A[j] != i && B[j] != i){ ca = cb = INF; break; } if(A[j] != i){ ca++; } if(B[j] != i){ cb++; } } best = min(best,min(ca,cb)); } return best == INF ? -1 : best; } };
