1:默认扫描启动类所在路径下所有的bean 2:可以在启动类中添加注解,手动指定扫描路径: @ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.xxx.service1.*","com.xxx.service2.**"}) 补充:SpringBoot 是如何通过 @SpringBoo
1:默认扫描启动类所在路径下所有的bean
2:可以在启动类中添加注解,手动指定扫描路径:
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.xxx.service1.*","com.xxx.service2.**"})
补充:SpringBoot 是如何通过 @SpringBootApplication 扫描项目中的 Bean
原因
首先因为 XXXXXXXApplication 附带 @SpringBootApplication 注解,而 @SpringBootApplication 注解的层次如下:
SpringBootApplication ----@Inherited ----@SpringBootConfiguration --------@Configuration ----@EnableAutoConfiguration --------@Inherited --------@AutoConfigurationPackage ------------@Inherited ------------@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class) --------@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) ----@ComponentScan --------@Repeatable(ComponentScans.class)
实现
可以看到 @SpringBootApplication 继承 @ComponentScan 与 @Configuration 用处如下;
扫描方法开始流程:
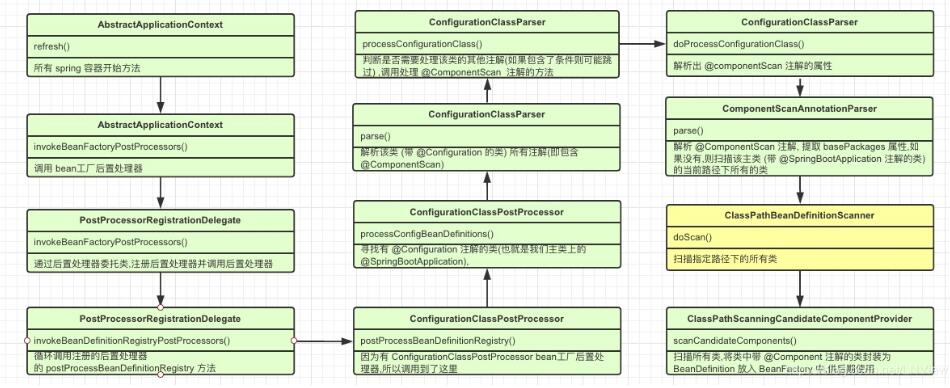
主要观察黄色方块的方法,是具体扫描路径的地方,具体实现流程如下:
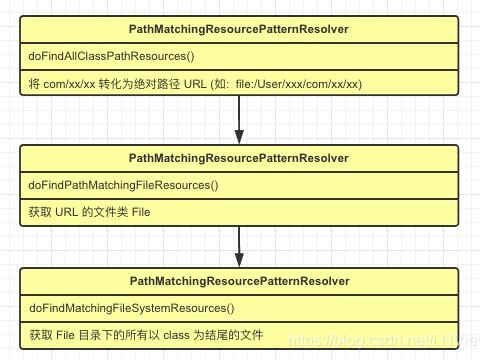
获取 File 目录下的所有以 class 为结尾的文件后,扫描工作就完成了, 剩下的就是 spring 判断是否要管理此类的逻辑(例如:该类是否存在 @Component )
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。如有错误或未考虑完全的地方,望不吝赐教。
