本文实例为大家分享了java awt实现计算器的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 上课老师演示了一遍他的写法,由于没给代码,因此按着他的思路撸了一遍,感觉还很简单。 代码以及
本文实例为大家分享了java awt实现计算器的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
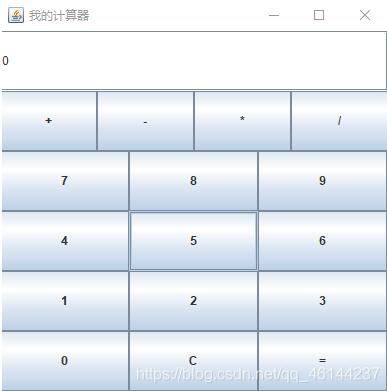
上课老师演示了一遍他的写法,由于没给代码,因此按着他的思路撸了一遍,感觉还很简单。
代码以及解释如下:
import java.awt.GridLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.JTextField;
public class Caculate1 {
static String s1="";
static String s2="";
static int f=9;
static int num1=0,num2=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x=0,y=0,z=0;
JFrame jf=new JFrame( "我的计算器");
jf.setBounds(0,0,300,400);
// jf.setBackground(bgColor);
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
JTextField show=new JTextField("0");
//此处为布局:也就是定义五个容器,(也可以理解为将定义的JFrame空间分为5个容器)
JPanel jp1=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));//存储:
JPanel jp2=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel jp3=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel jp4=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JPanel jp5=new JPanel(new GridLayout(1,3));
JButton bt_add=new JButton("+");
JButton bt_sub=new JButton("-");
JButton bt_mul=new JButton("*");
JButton bt_div=new JButton("/");
JButton bt_7=new JButton("7");
JButton bt_8=new JButton("8");
JButton bt_9=new JButton("9");
JButton bt_4=new JButton("4");
JButton bt_5=new JButton("5");
JButton bt_6=new JButton("6");
JButton bt_1=new JButton("1");
JButton bt_2=new JButton("2");
JButton bt_3=new JButton("3");
JButton bt_0=new JButton("0");
JButton bt_c=new JButton("C");
JButton bt_equal=new JButton("=");
jf.setLayout(new GridLayout(6,1));
//容器1 :添加 '+','-','*','/'按钮
jp1.add(bt_add);
jp1.add(bt_sub);
jp1.add(bt_mul);
jp1.add(bt_div);
//容器2:添加'7','8','9'按钮
jp2.add(bt_7);
jp2.add(bt_8);
jp2.add(bt_9);
//容器3:添加'4','5','6'按钮
jp3.add(bt_4);
jp3.add(bt_5);
jp3.add(bt_6);
//容器4:添加'1','2','3'按钮
jp4.add(bt_1);
jp4.add(bt_2);
jp4.add(bt_3);
//容器5:添加'0','C','='
jp5.add(bt_0);
jp5.add(bt_c);
jp5.add(bt_equal);
jf.add(show);
jf.add(jp1);
jf.add(jp2);
jf.add(jp3);
jf.add(jp4);
jf.add(jp5);
//元素已经定义好了,思路也很简单:(1)JFrame定义一个大容器jf,jf= 1个显示框(show)+5个容器,分别定义显示框和容器,
//(2)类似树形添加元素的数据结构,为jf添加元素
//下面便是时间监听了(又称加载驱动)
bt_9.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+9;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_8.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+8;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_7.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+7;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_6.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+6;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_5.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+5;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_4.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+4;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_3.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+3;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_0.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+0;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_2.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+2;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_1.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+1;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_0.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s1=s1+0;
show.setText(s1);
}
});
bt_equal.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
num1=Integer.valueOf(s2);
num2=Integer.valueOf(s1);
int z=0;
char fg=' ';
switch(f){
case 0:
z=num1+num2;
fg='+';
break;
case 1:
z=num1-num2;
fg='-';
break;
case 2:
z=num1*num2;
fg='*';
break;
case 3:
fg='/';
if(num2==0)
num2=num2+1;
z=num1/num2;
break;
default:
break;
}
show.setText(s2+" "+fg+" "+s1+" = "+z);
}
});
bt_add.addActionListener(new ActionListener(){
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
s2=s1;
s1="";
f=0;
show.setText(s2+"+");
}
});
bt_sub.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
s2 = s1;
s1 = "";
f = 1;
show.setText(s2 + " - ");
}
});
bt_mul.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
s2 = s1;
s1 = "";
f = 2;
show.setText(s2 + " * ");
}
});
bt_div.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
s2 = s1;
s1 = "";
f = 3;
show.setText(s2 + " / ");
}
});
bt_c.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
s2 = "";
s1 = "";
num1 = 0;
num2 = 0;
f = 9;
show.setText("0");
}
});
}
}
关于计算器的精彩文章请查看《计算器专题》 ,更多精彩等你来发现!
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。
