目录
- 一、负载均衡算法简介
- 1、轮询法
- 2、随机法
- 3、源地址哈希法
- 4、加权轮询法
- 5、加权随机法
- 二、代码实现负载均衡五种算法
- 1.轮询法
- 2.加权轮询法
- 3.随机法
- 4.加权随机
- 5.源地址哈希法

前言:
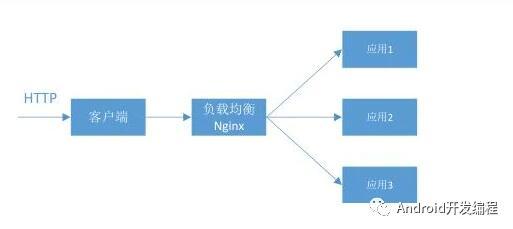
什么是负载均衡:
指由多台服务器以对称的方式组成一个服务器集合,每台服务器都具有等价的地位,都可以单独对外提供服务而无须其他服务器的辅助。通过某种 负载分担技术,将外部发送来的请求均匀分配到对称结构中的某一台服务器上,而接收到请求的服务器独立地回应客户的请求。负载均衡能够平均分配客户请求到服 务器阵列,借此提供快速获取重要数据,解决大量并发访问服务问题,这种集群技术可以用最少的投资获得接近于大型主机的性能;
一、负载均衡算法简介
1、轮询法
将请求按顺序轮流地分配到后端服务器上,它均衡地对待后端的每一台服务器,而不关心服务器实际的连接数和当前的系统负载;
2、随机法
通过系统的随机算法,根据后端服务器的列表大小值来随机选取其中的一台服务器进行访问。由概率统计理论可以得知,随着客户端调用服务端的次数增多, 其实际效果越来越接近于平均分配调用量到后端的每一台服务器,也就是轮询的结果;
3、源地址哈希法
源地址哈希的思想是根据获取客户端的IP地址,通过哈希函数计算得到的一个数值,用该数值对服务器列表的大小进行取模运算,得到的结果便是客服端要访问服务器的序号。采用源地址哈希法进行负载均衡,同一IP地址的客户端,当后端服务器列表不变时,它每次都会映射到同一台后端服务器进行访问;
4、加权轮询法
不同的后端服务器可能机器的配置和当前系统的负载并不相同,因此它们的抗压能力也不相同。给配置高、负载低的机器配置更高的权重,让其处理更多的请;而配置低、负载高的机器,给其分配较低的权重,降低其系统负载,加权轮询能很好地处理这一问题,并将请求顺序且按照权重分配到后端;
5、加权随机法
与加权轮询法一样,加权随机法也根据后端机器的配置,系统的负载分配不同的权重。不同的是,它是按照权重随机请求后端服务器,而非顺序;
二、代码实现负载均衡五种算法
1.轮询法
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class TestRoundRobin {
// 1.定义map, key-ip,value-weight
static Map<String,Integer> ipMap= new HashMap<>();
static {
ipMap.put("192.168.13.1",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.2",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.3",1);
}
// Integer sum=0;
Integer pos = 0;
public String RoundRobin(){
Map<String,Integer> ipServerMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ipServerMap.putAll(ipMap);
// 2.取出来key,放到set中
Set<String> ipset=ipServerMap.keySet();
// 3.set放到list,要循环list取出
ArrayList<String> iplist=new ArrayList<String>();
iplist.addAll(ipset);
String serverName=null;
// 4.定义一个循环的值,如果大于set就从0开始
synchronized(pos){
if (pos>=ipset.size()){
pos=0;
}
serverName=iplist.get(pos);
//轮询+1
pos ++;
}
return serverName;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRoundRobin testRoundRobin=new TestRoundRobin();
for ( int i=0;i<10;i++){
String serverIp=testRoundRobin.RoundRobin();
System.out.println(serverIp);
}
}
}
2.加权轮询法
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class TestWeightRobin {
// 1.map, key-ip,value-weight
static Map<String,Integer> ipMap= new HashMap<>();
static {
ipMap.put("192.168.13.1",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.2",2);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.3",4);
}
Integer pos=0;
public String WeightRobin(){
Map<String,Integer> ipServerMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ipServerMap.putAll(ipMap);
Set<String> ipSet=ipServerMap.keySet();
Iterator<String> ipIterator=ipSet.iterator();
//定义一个list放所有server
ArrayList<String> ipArrayList=new ArrayList<String>();
//循环set,根据set中的可以去得知map中的value,给list中添加对应数字的server数量
while (ipIterator.hasNext()){
String serverName=ipIterator.next();
Integer weight=ipServerMap.get(serverName);
for ( int i = 0;i < weight ;i++){
ipArrayList.add(serverName);
}
}
String serverName=null;
if (pos>=ipArrayList.size()){
pos=0;
}
serverName=ipArrayList.get(pos);
//轮询+1
pos ++;
return serverName;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestWeightRobin testWeightRobin=new TestWeightRobin();
for ( int i =0;i<10;i++){
String server=testWeightRobin.WeightRobin();
System.out.println(server);
}
}
}
3.随机法
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class TestRandom {
// 1.定义map, key-ip,value-weight
static Map<String,Integer> ipMap= new HashMap<>();
static {
ipMap.put("192.168.13.1",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.2",2);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.3",4);
}
public String Random() {
Map<String,Integer> ipServerMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ipServerMap.putAll(ipMap);
Set<String> ipSet=ipServerMap.keySet();
//定义一个list放所有server
ArrayList<String> ipArrayList=new ArrayList<String>();
ipArrayList.addAll(ipSet);
//循环随机数
Random random=new Random();
//随机数在list数量中取(1-list.size)
int pos=random.nextInt(ipArrayList.size());
String serverNameReturn= ipArrayList.get(pos);
return serverNameReturn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRandom testRandom=new TestRandom();
for ( int i =0;i<10;i++){
String server=testRandom.Random();
System.out.println(server);
}
}
}
4.加权随机
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class TestRobinRandom {
// 1.定义map, key-ip,value-weight
static Map<String,Integer> ipMap= new HashMap<>();
static {
ipMap.put("192.168.13.1",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.2",2);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.3",4);
}
public String RobinRandom(){
Map<String,Integer> ipServerMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ipServerMap.putAll(ipMap);
Set<String> ipSet=ipServerMap.keySet();
Iterator<String> ipIterator=ipSet.iterator();
//定义一个list放所有server
ArrayList<String> ipArrayList=new ArrayList<String>();
//循环set,根据set中的可以去得知map中的value,给list中添加对应数字的server数量
while (ipIterator.hasNext()){
String serverName=ipIterator.next();
Integer weight=ipServerMap.get(serverName);
for ( int i=0;i<weight;i++){
ipArrayList.add(serverName);
}
}
//循环随机数
Random random=new Random();
//随机数在list数量中取(1-list.size)
int pos=random.nextInt(ipArrayList.size());
String serverNameReturn= ipArrayList.get(pos);
return serverNameReturn;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRobinRandom testRobinRandom=new TestRobinRandom();
for ( int i =0;i<10;i++){
String server=testRobinRandom.RobinRandom();
System.out.println(server);
}
}
}
5.源地址哈希法
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
public class ipHash {
// 1.定义map, key-ip,value-weight
static Map<String,Integer> ipMap= new HashMap<>();
static {
ipMap.put("192.168.13.1",1);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.2",2);
ipMap.put("192.168.13.3",4);
}
public String ipHash(String clientIP){
Map<String,Integer> ipServerMap=new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
ipServerMap.putAll(ipMap);
// 2.取出来key,放到set中
Set<String> ipset=ipServerMap.keySet();
// 3.set放到list,要循环list取出
ArrayList<String> iplist=new ArrayList<String>();
iplist.addAll(ipset);
//对ip的hashcode值取余数,每次都一样的
int hashCode=clientIP.hashCode();
int serverListsize=iplist.size();
int pos=hashCode%serverListsize;
return iplist.get(pos);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ipHash iphash=new ipHash();
String servername= iphash.ipHash("192.168.21.2");
System.out.println(servername);
}
}
到此这篇关于Java 负载均衡的 5 种算法实现原理的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java 负载均衡的 算法实现原理内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
