目录 多任务、多线程 程序、进程、线程 学着看jdk文档 线程的创建 1.继承Thread类 2.实现Runable接口 理解并发的场景 龟兔赛跑场景 实现callable接口 理解函数式接口 理解线程的状态 线程停
目录
- 多任务、多线程
- 程序、进程、线程
- 学着看jdk文档
- 线程的创建
- 1.继承Thread类
- 2.实现Runable接口
- 理解并发的场景
- 龟兔赛跑场景
- 实现callable接口
- 理解函数式接口
- 理解线程的状态
- 线程停止
- 线程休眠sleep
- 1.网路延迟
- 2.倒计时等
- 线程礼让yield
- 线程强制执行
- 观察线程状态
- 线程的优先级
- 守护线程
- 线程同步机制
- 1.synchronized 同步方法
- 2.同步块synchronized(Obj){}
- lock
- synchronized与lock
多任务、多线程
在多任务场景下,两件事看上去同时在做,但实际上,你的大脑在同一时间只做一件事,间隔时间可能很少,但这似乎让你感觉这两件事是同时在做
考虑阻塞问题,引入多线程的场景,多线程并发场景
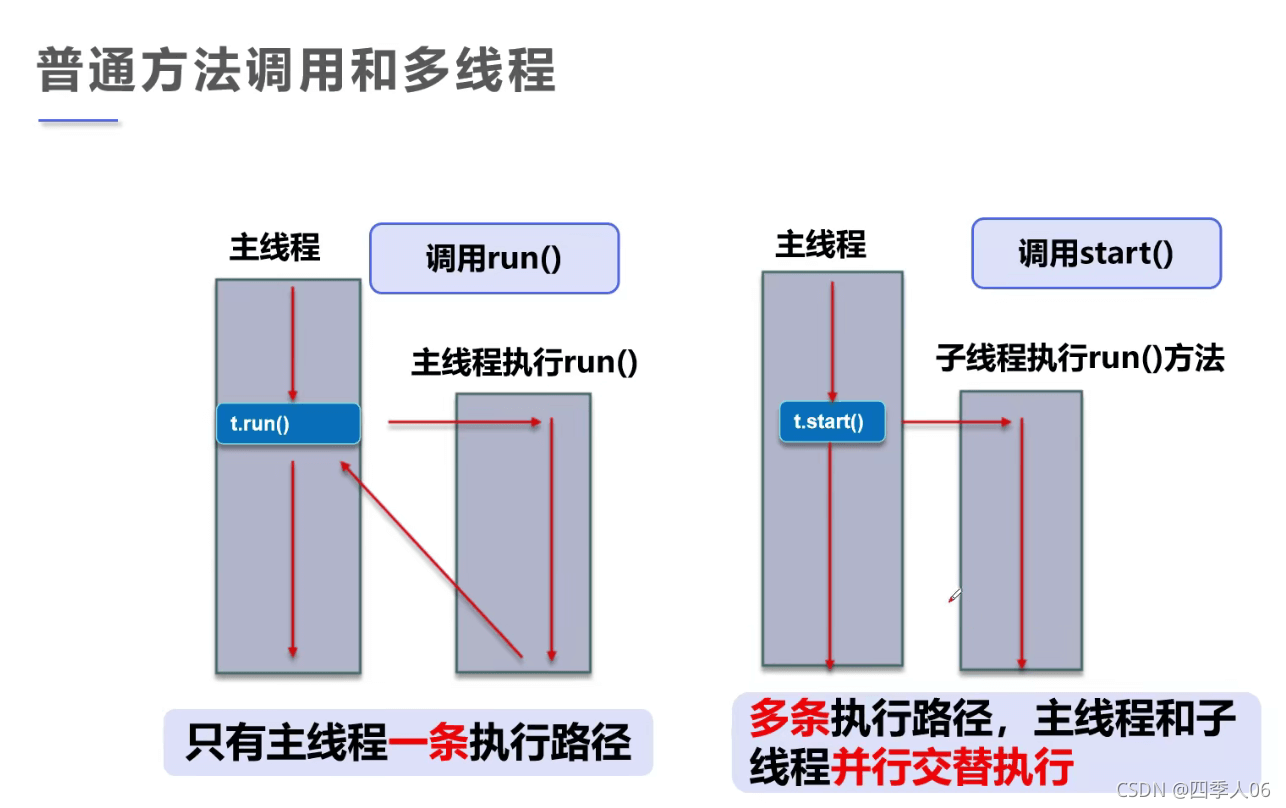
程序、进程、线程
程序=指令+数据(静态的)
在操作系统中运行的程序就是进程,一个进程可以有多个线程
比如,看视频时听声音,看图像,看弹幕等
学着看jdk文档
比如你要看Thread
你可以搜索,然后阅读
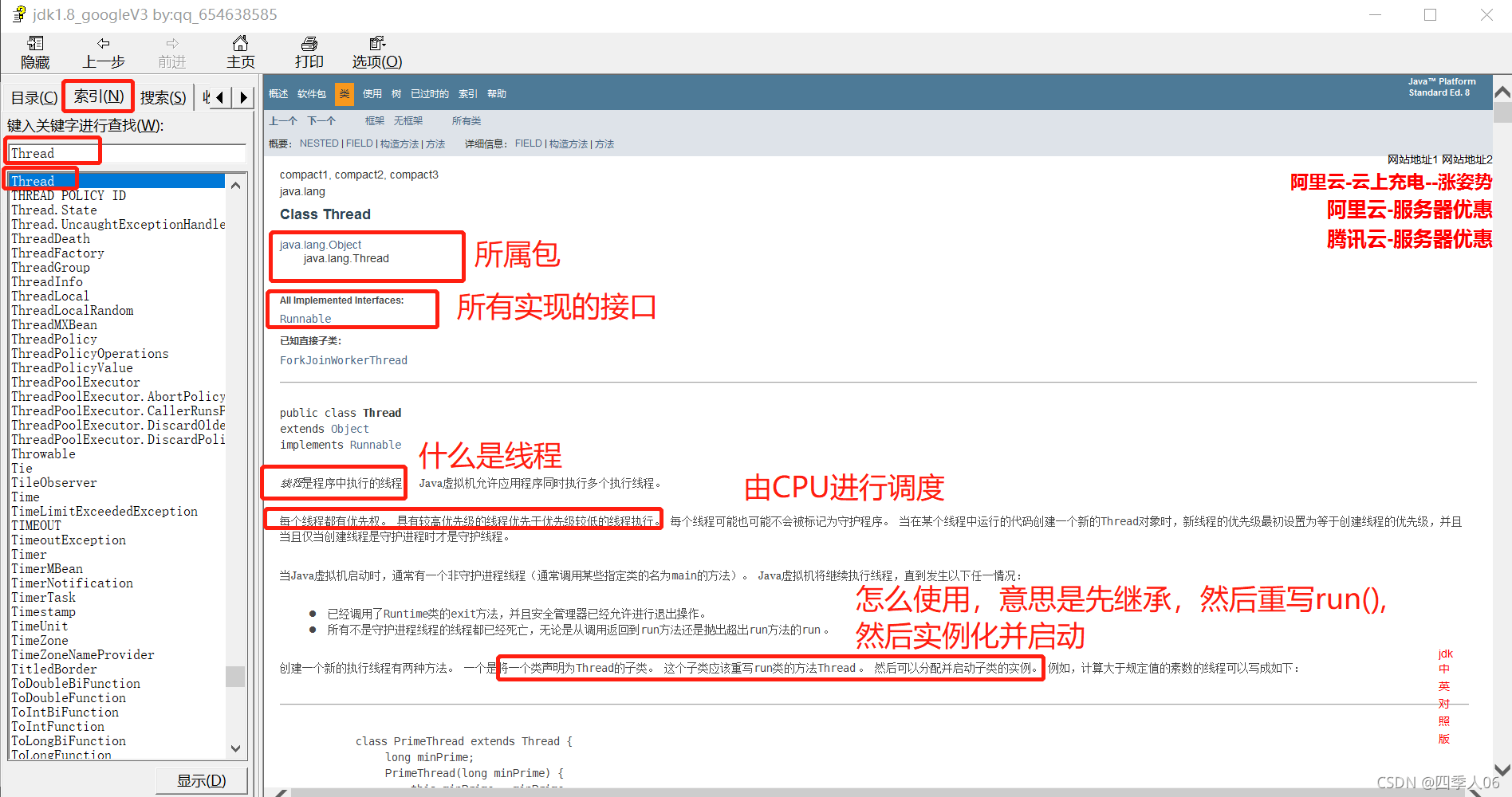
往下翻你会看到:
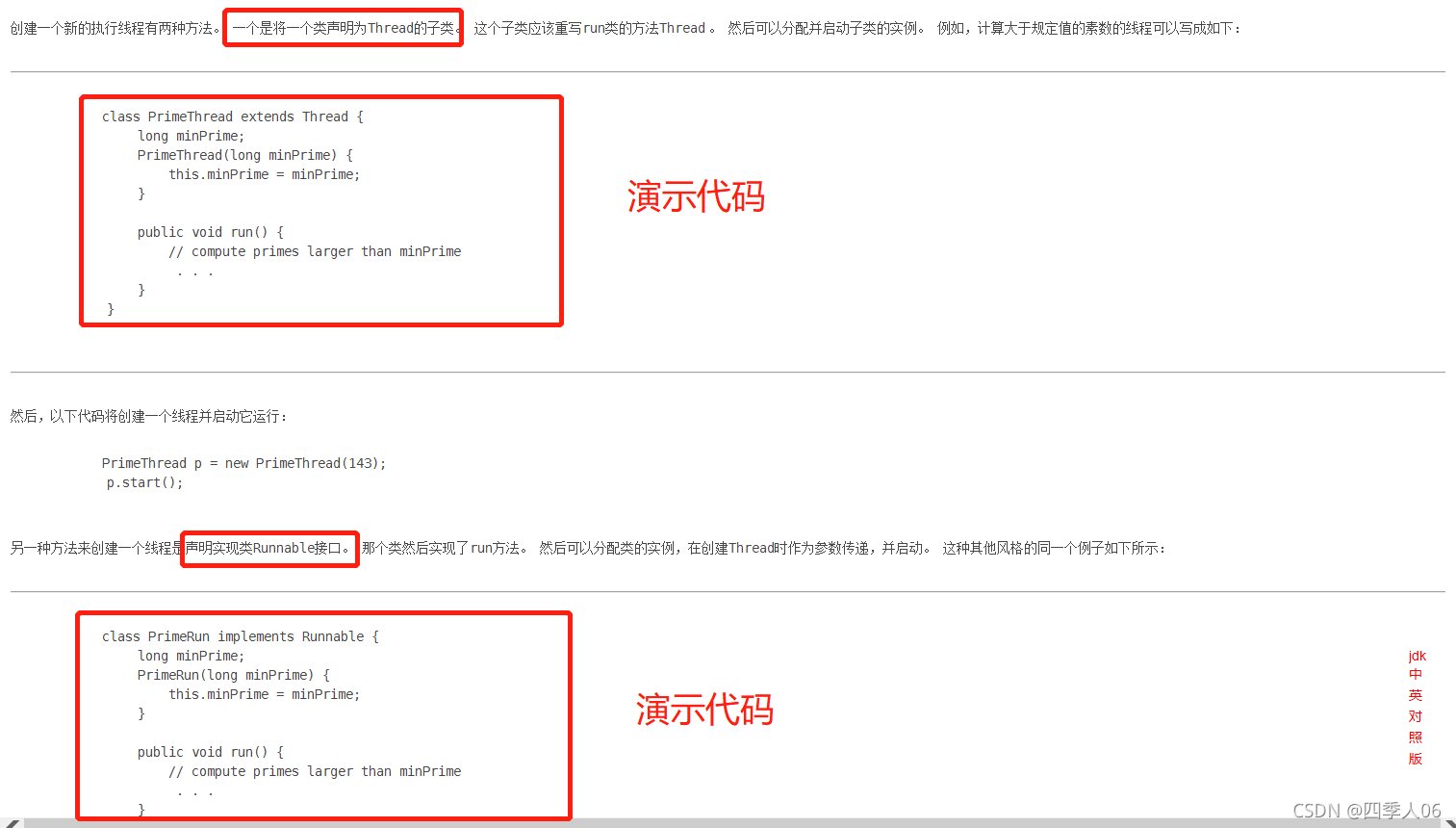

线程的创建
1.继承Thread类
//创建线程方式一:继承Thread类,重写run方法,调用start()方法开启线程
public class TestThread1 extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
//run()方法线程体
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在看代码"+i);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个线程对象
TestThread1 testThread1=new TestThread1();
//调用start()方法,启动线程,不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
testThread1.start();
//主方法 main方法
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在学习多线程"+i);
});
}
}
一个小练习:
//练习thread实现对线程同步下载图片
public class TestThread2 extends Thread{
private String url;
private String name;
public TestThread2(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
WebDownload webDownload=new WebDownload();
webDownload.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名:"+name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread2 t1=new TestThread2("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","1.jpg");
TestThread2 t2=new TestThread2("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","2.jpg");
TestThread2 t3=new TestThread2("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","3.jpg");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
//下载器
class WebDownload{
//下载方法
public void downloader(String url,String name) {
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("IO异常,downloader方法出错");
}
}
}
2.实现Runable接口
//创建线程的方法2:实现Runable接口
public class TestThread3 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
//run()方法线程体
IntStream.range(0,20).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在看代码"+i);
});
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个线程对象
TestThread3 testThread3=new TestThread3();
//调用start()方法,启动线程,不一定立即执行,由cpu调度执行
// Thread thread=new Thread(testThread3);
// thread.start();
//或者这样简写
new Thread(testThread3).start();
//主方法 main方法
IntStream.range(0,100).forEach(i->{
System.out.println("我在学习多线程"+i);
});
}
}
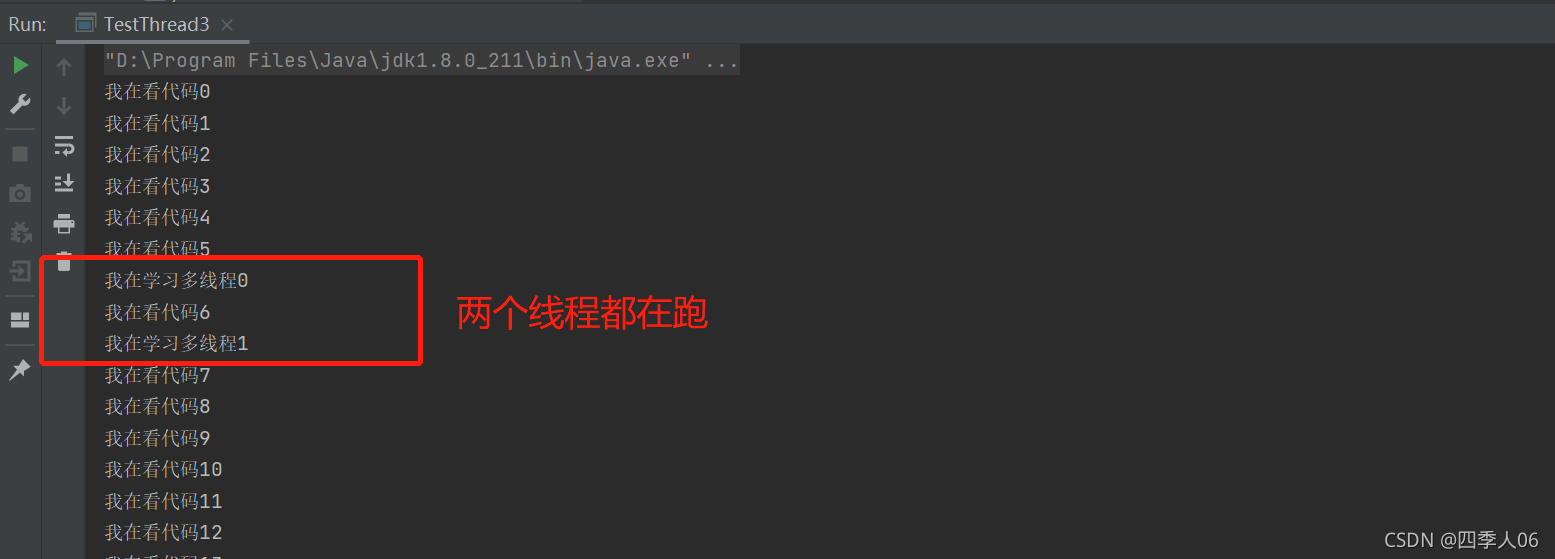
理解并发的场景
当多个线程使用同一个资源时,会出现问题,看看下面这个买火车票的例子:
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable{
//票数
private int ticketNums=10;
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
if (ticketNums<=0){
break;
}
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestThread4 ticket=new TestThread4();
new Thread(ticket,"小明").start();
new Thread(ticket,"张三").start();
new Thread(ticket,"李四").start();
}
}
看看运行的结果:
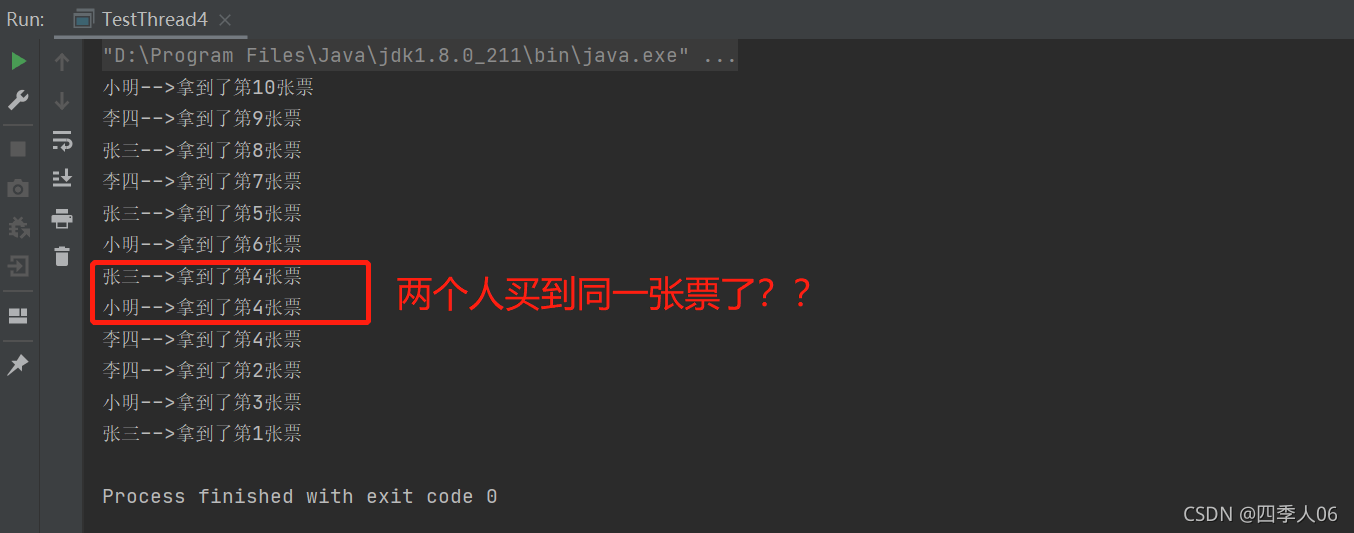
可以看到案例中的线程不安全问题,同时数据也是不正确的
龟兔赛跑场景
/**
* 模拟龟兔赛跑
*/
public class Race implements Runnable{
//胜利者
private static String winner;
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<=100;i++){
//模拟兔子休息
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("兔子")&&i%10==0){
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
boolean flag=gameOver(i);
if (flag){ //判断比赛是否结束
break;
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->跑了"+i+"步");
}
}
/**
* 判断比赛是否结束
*/
private boolean gameOver(int steps){
//判断是否有胜利者
if (winner !=null){
//已经存在胜利者
return true;
}else if (steps >= 100){
winner=Thread.currentThread().getName();
System.out.println("胜利者是:"+winner);
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Race race=new Race();
new Thread(race,"兔子").start();
new Thread(race,"乌龟").start();
}
}
实现callable接口
//线程创建方式3
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Boolean> {
private String url;
private String name;
public TestCallable(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public Boolean call() {
com.sxh.thread.WebDownload webDownload=new com.sxh.thread.WebDownload();
webDownload.downloader(url,name);
System.out.println("下载了文件名:"+name);
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t1=new TestCallable("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","1.jpg");
TestCallable t2=new TestCallable("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","2.jpg");
TestCallable t3=new TestCallable("https://profile.csdnimg.cn/B/D/2/3_sxh06","3.jpg");
//创建执行服务
ExecutorService ser= Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
//提交执行
Future<Boolean> r1=ser.submit(t1);
Future<Boolean> r2=ser.submit(t2);
Future<Boolean> r3=ser.submit(t3);
//获取结果
boolean rs1=r1.get();
boolean rs2=r2.get();
boolean rs3=r3.get();
//关闭服务
ser.shutdownNow();
}
}
理解函数式接口
任何接口,只包含唯一一个抽象方法,就是函数式接口
/**
* lambdab表达式的发展
*/
public class TestLambda1 {
//3.静态内部类
static class Like2 implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ILike like=new Like();
like.lambda();
like=new Like2();
like.lambda();
//4.局部内部类
class Like3 implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda3");
}
}
like=new Like3();
like.lambda();
//5.匿名内部类
like=new ILike() {
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda4");
}
};
like.lambda();
//6.用lambda简化
like=()->{
System.out.println("i like lambda5");
};
like.lambda();
}
}
//1.定义一个函数式接口
interface ILike{
void lambda();
}
//2.实现类
class Like implements ILike{
@Override
public void lambda() {
System.out.println("i like lambda");
}
}
理解线程的状态
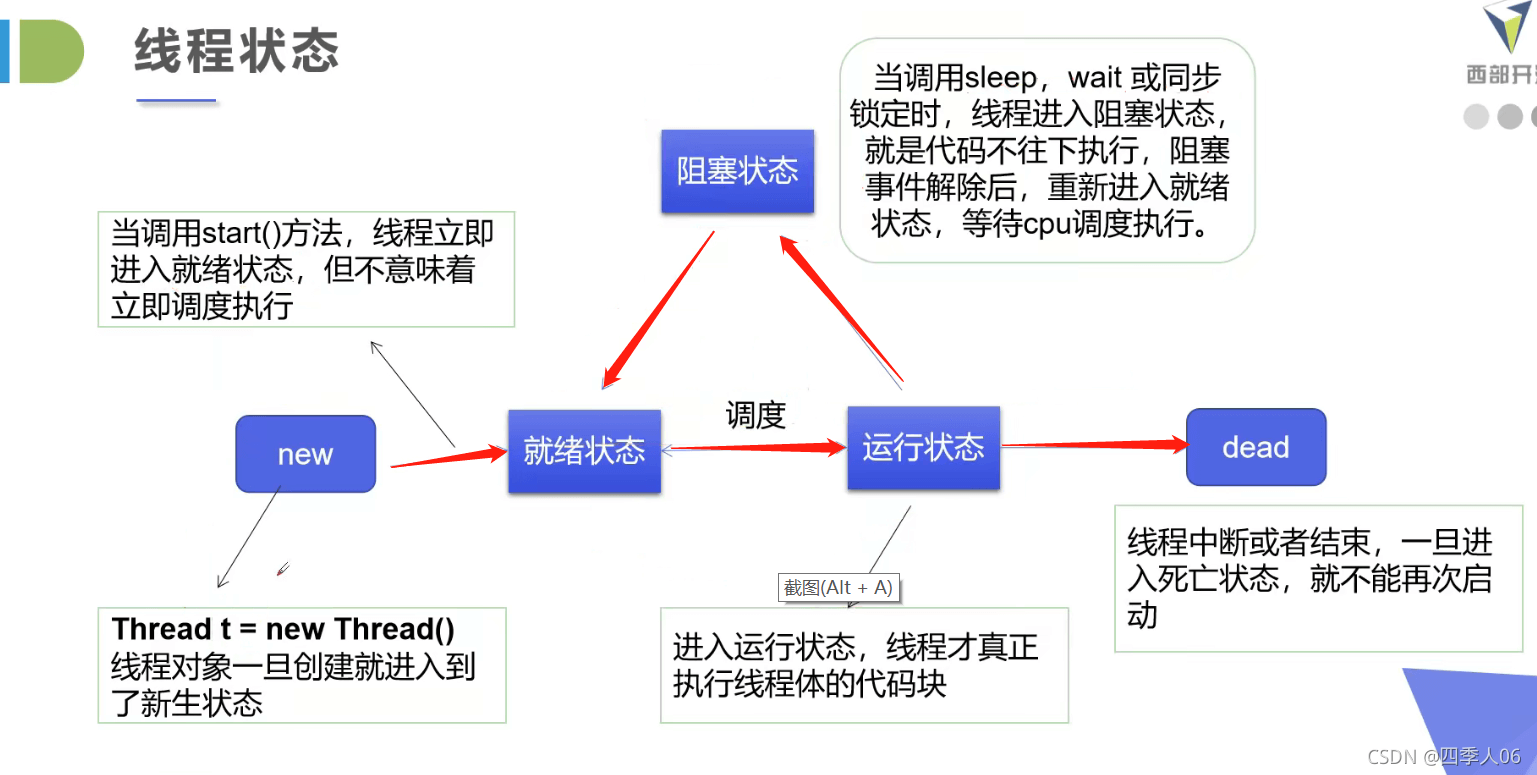
线程停止
public class TestStop implements Runnable{
//1.设置一个标志位
private boolean flag=true;
@Override
public void run() {
int i=0;
while (flag){
System.out.println("run...thread.."+i++);
}
}
//2.设置一个公开的方法停止线程,转换标志位
public void stop(){
this.flag=false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestStop stop=new TestStop();
new Thread(stop).start();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
if (i==900){
//调用stop方法,让线程停止
stop.stop();
System.out.println("线程该停止了");
}
}
// IntStream.range(0,1000).forEach(i->{
//
// });
}
}
线程休眠sleep
每个对象都有一把锁,sleep不会释放锁
1.网路延迟
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(200); //ms
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
2.倒计时等
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
tendown();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void tendown() throws InterruptedException {
int num=10;
while (true){
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(num--);
if(num<=0)
{
break;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//打印系统当前时间
Date startTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
while (true){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));
startTime=new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());//更新时间
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
线程礼让yield
//线程礼让 礼让不一定成功,由cpu重新调度
public class TestYield {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyYield myYield=new MyYield();
new Thread(myYield,"a").start();
new Thread(myYield,"b").start();
}
}
class MyYield implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程开始执行");
Thread.yield();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"线程停止执行");
}
}
线程强制执行
//测试join方法 想象为插队
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
System.out.println("线程vip来了"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
//启动线程
TestJoin testJoin=new TestJoin();
Thread thread=new Thread(testJoin);
thread.start();
//主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
if (i==200){
thread.join(); //插队
}
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
观察线程状态
public class TestState {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread=new Thread(()->{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("//");
});
//观察状态
Thread.State state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //NEW
//启动后
thread.start();
state=thread.getState();
System.out.println(state); //Run
while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED)
{
Thread.sleep(100);
state=thread.getState();//更新线程状态
System.out.println(state); //Run
}
}
}
线程的优先级
//测试线程的优先级
public class TestPriority {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//主线程默认优先级
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
MyPriority myPriority=new MyPriority();
Thread t1=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t2=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t3=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t4=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t5=new Thread(myPriority);
Thread t6=new Thread(myPriority);
//先设置优先级,在启动
t1.start();
t2.setPriority(1);
t2.start();
t3.setPriority(4);
t3.start();
t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY);
t4.start();
t5.setPriority(-1);
t5.start();
t6.setPriority(11);
t6.start();
}
}
class MyPriority implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"--->"+Thread.currentThread().getPriority());
}
}
守护线程
线程分为用户线程和守护线程
//测试守护线程
public class TestDaemon {
public static void main(String[] args) {
God god=new God();
You you=new You();
Thread thread=new Thread(god);
thread.setDaemon(true); //默认是false表示用户线程
thread.start();
new Thread(you).start();
}
}
class God implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("上帝保佑着你");
}
}
}
class You implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 36000; i++) {
System.out.println("你活着"+i);
}
System.out.println("goodbye!!");
}
}
线程同步机制
解决安全性问题:队列+锁
1.synchronized 同步方法
默认锁的是this,如需锁其他的,使用下面的同步块
//synchronized 同步方法
private synchronized void buy(){
if (ticketNums<=0){
flag=false;
return;
}
//模拟延迟
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//买票
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"-->拿到了第"+ticketNums--+"张票");
}
2.同步块synchronized(Obj){}
锁的对象是变化的量,需要增删改的对象
obj称之为同步监视器,即监视对象
public class UnsafeList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list=new ArrayList<String>();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
new Thread(()->{
synchronized (list){
list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}).start();
}
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(list.size());
}
}
lock
class A{
//ReentrantLock 可重入锁
private final ReentrantLock lock=new ReentrantLock();
public void f(){
lock.lock();//加锁
try{
//.....
}
finally{
lock.unlock();//释放锁
}
}
}
synchronized与lock
- lock是显示锁需要手动开关,synchronized是隐式锁,出了作用域自动释放
- lock只有代码块锁,synchronized有代码块锁和方法锁
- JVM将花费更少的时间来调度线程,性能更好,更有扩展性
- 优先使用:Lock>同步代码块>同步方法
到此这篇关于Java多线程学习笔记的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java 多线程内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
