前言说明:仍然是伪集群,所有的Redis节点,都在一个服务器上,采用不同配置文件,不同端口的形式实现
前提:已经安装好了Redis,本文的redis的版本是redis-6.2.3
Redis的下载、安装参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/rxx1005/p/15754565.html
文章中,Redis的安装目录为:/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
本文使用到的工具:
- SSH工具:MobaXterm
- 截图工具:FSCapture
redis cluster 的两种部署方式:
- 方法1:自定义配置文件安装,下文中的第一种,推荐使用此种办法
- 方法2:使用redis自带的cluster-create工具:不推荐使用,玩玩就行了
此步骤是个人习惯,可以不复制,后面使用命令时,直接使用src目录的即可。
在编译Redis之后,会在 redis的src目录下生成一些脚本
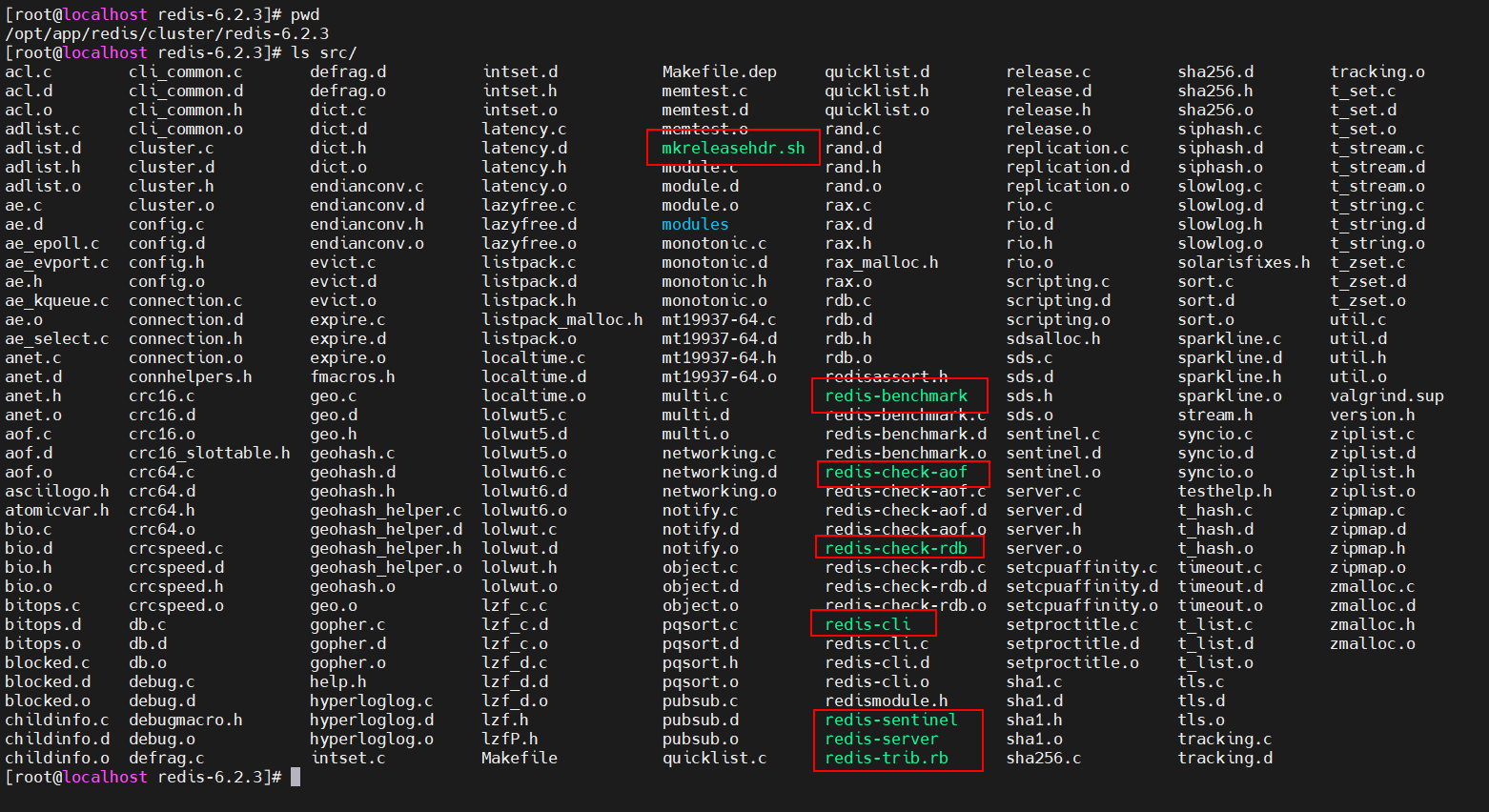
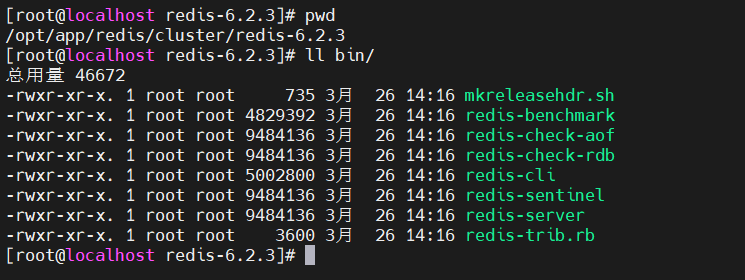
我把这些常用脚本,使用 cp 命令,拷贝到 resdis 根目录下的 bin 目录下(bin目录自己创建的)
安装ruby(redis5.0之后不需要安装)
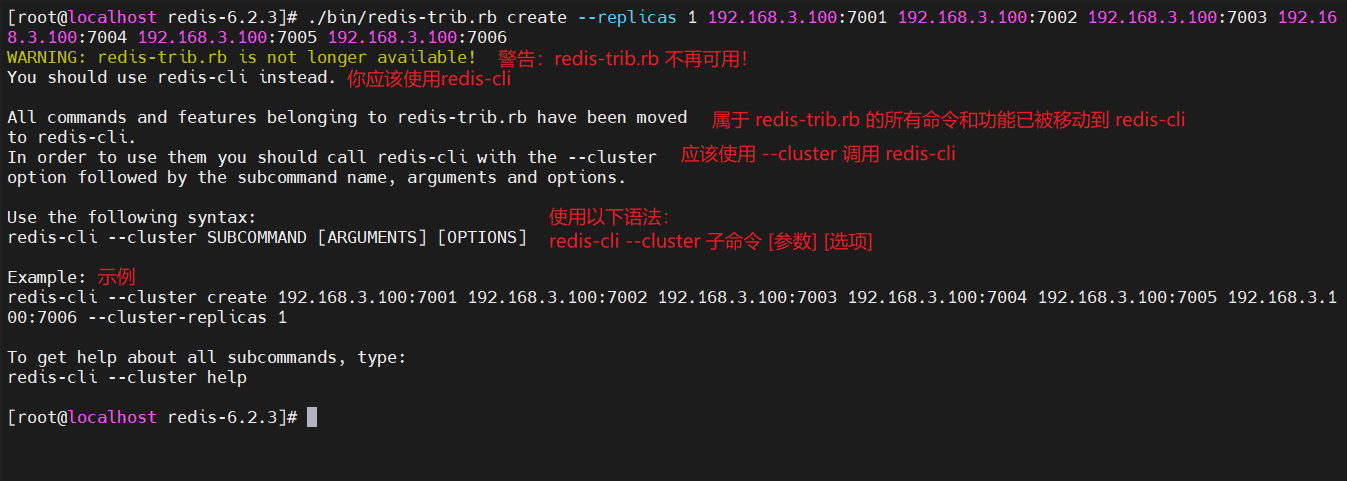
此处可跳过!!! 我使用的是redis-6.2.3,创建集群的时候,不再使用redis-trib.rb,而是用 redis-cli --cluster ,使用redis-cli
--cluster创建集群,不需要安装ruby,下面是安装ruby的办法。
注意:不要直接在Linux上执行 yum install ruby ,因为这样安装的ruby版本太低了
低版本redis搭建 cluster集群,需要用到redis得src目录下的 redis-trib.rb ,此脚本需要依赖 ruby 语言,现安装 ruby,在Linux上,直接使用wget
命令,下载ruby安装包,也可以去官网下载之后,上传到Linux,官网:http://www.ruby-lang.org/en/downloads/
[root@localhost conf]# wget https://cache.ruby-lang.org/pub/ruby/3.1/ruby-3.1.1.tar.gz
解压,编译,编译约1~2分钟
[root@localhost app]# tar -zxvf ruby-3.1.1.tar.gz
[root@localhost ruby-3.1.1]# cd ruby-3.1.1
[root@localhost ruby-3.1.1]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/ruby --enable-shared
[root@localhost ruby-3.1.1]# make & make install
添加环境变量:
编辑 /etc/profile 文件,在文件末尾加上以下内容
export RUBY_HOME=/usr/local/ruby
export PATH=$RUBY_HOME/bin:$RUBY_HOME/lib:$PATH
保存,退出,重新加载文件
[root@localhost ~]# source /etc/profile
执行 ruby -v,如果出现版本号,说明安装成功
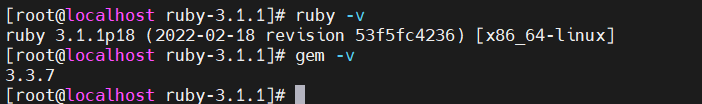
安装redis库
[root@localhost ruby-3.1.1]# gem install redis
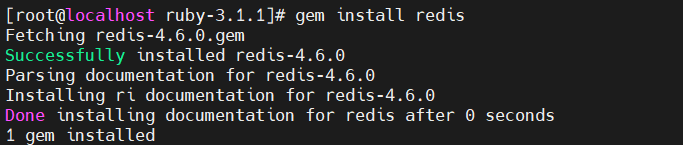
至此,ruby就安装好了。
自定义配置文件集群搭建 配置
在redis根目录下,创建一个conf文件夹,并在conf文件夹下,创建6个文件夹,用于存集群每个节点的配置文件、数据文件等
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# mkdir conf
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# cd conf/
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir 7001 7002 7003 7004 7005 7006
在 7001 文件夹内,创建一个redis 的配置文件:
[root@localhost conf]# cd 7001/
[root@localhost 7001]# touch redis.conf
在 redis.conf 配置文件内,加入以下配置:
# 将bind这一行注释掉,或者修改为0:0:0:0,这表示任意地址都可以连接此Redis服务
# bind 127.0.0.1
# 关闭保护模式,如果开启的话,外部客户端就连不上Redis
protected-mode no
# 配置redis的端口号(不同节点使用不同的端口号)
port 7001
# 以守护进程运行(后台运行redis)
daemonize yes
# 服务启动后记录线程号的文件
pidfile "redis.pid"
# 日志
logfile "/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/conf/7001/log.log"
# 数据库的个数
databases 16
# 设置数据保存到数据文件中的save规则,3600秒内修改1次key,进行一次磁盘保存操作
save 3600 1
save 300 100
save 60 10000
# 指定存储至本地数据库时是否压缩数据,默认是yes,redis采用LZF压缩,需要消耗CPU资源
rdbcompression yes
# 保存rdb文件时,是否对rdb文件进行校验
rdbchecksum yes
# 保存数据的文件名字
dbfilename "dump.rdb"
# 保存数据的目录,这个目录需要提前创建出来
dir "/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/conf/7001"
# 是否开启aof持久化
appendonly yes
# aof文件名字
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
# 集群配置文件,自动生成,不能人为维护
cluster-config-file "nodes.conf"
#开启cluster集群
cluster-enabled yes
#Redis集群节点超时时限
cluster-node-timeout 15000
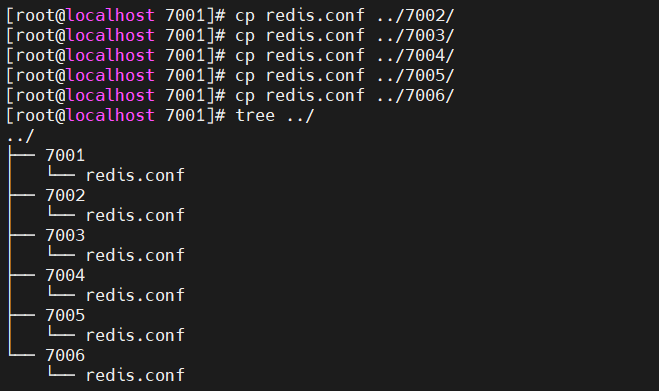
将这个配置文件,复制5份到 7002 7003 7004 7005 7006 目录下
[root@localhost 7001]# cp redis.conf ../7002/
[root@localhost 7001]# cp redis.conf ../7003/
[root@localhost 7001]# cp redis.conf ../7004/
[root@localhost 7001]# cp redis.conf ../7005/
[root@localhost 7001]# cp redis.conf ../7006/
效果如下:
将每个目录下的配置文件里面,所有的7001,改成和目录一样的数字(替换所有配置文件中的7001),要替换三个位置。
启动 redis 服务[root@localhost conf]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/conf
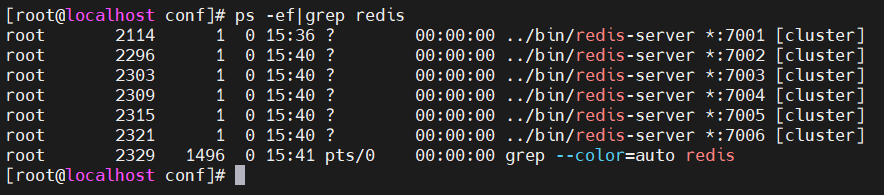
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7001/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7002/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7003/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7004/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7005/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ../bin/redis-server 7006/redis.conf
使用 redis-cli --cluster 搭建集群,注意下面的IP,建议使用具体的IP,不要使用127.0.0.1,防止有坑
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster create 192.168.3.100:7001 192.168.3.100:7002 192.168.3.100:7003 192.168.3.100:7004 192.168.3.100:7005 192.168.3.100:7006 --cluster-replicas 1
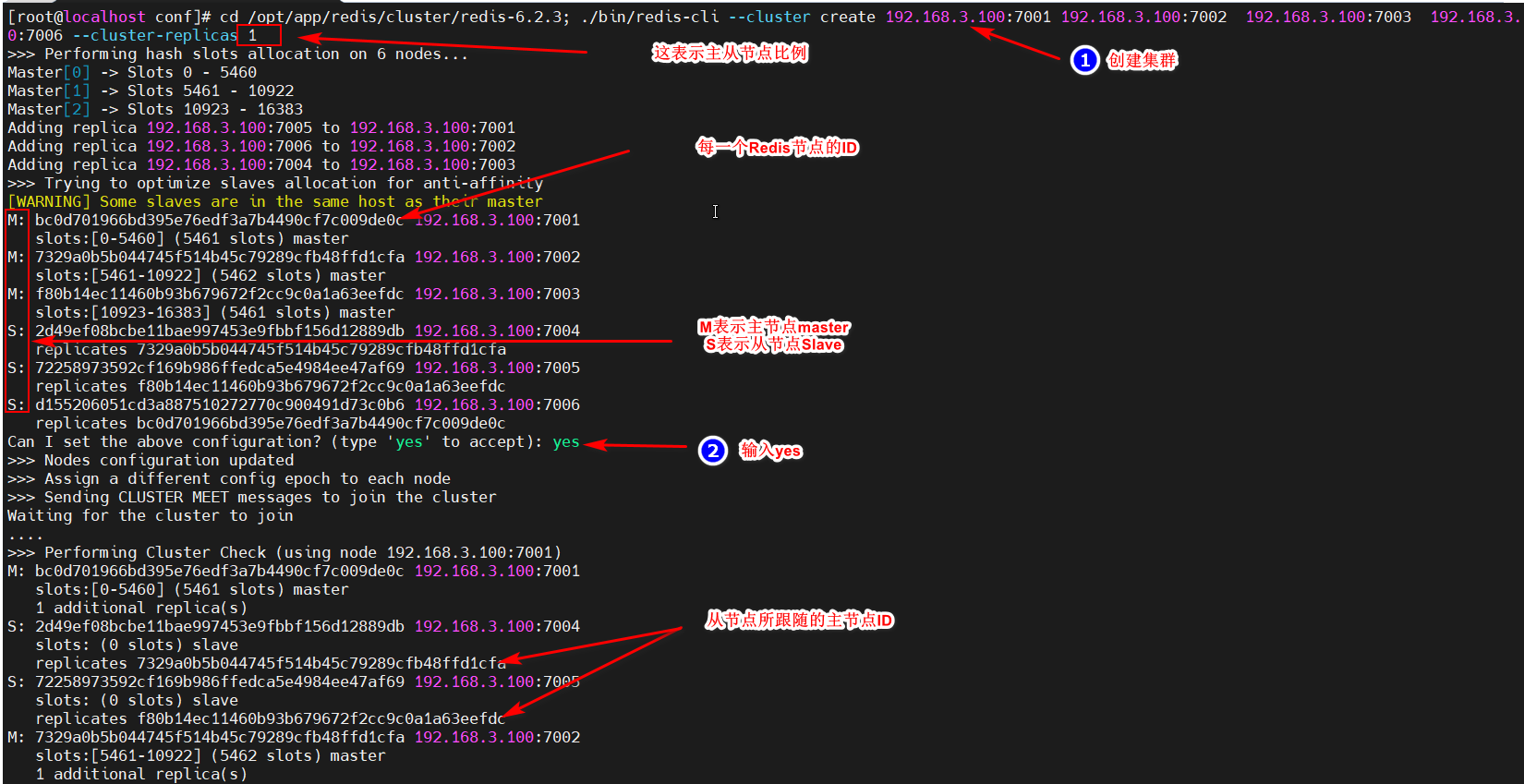
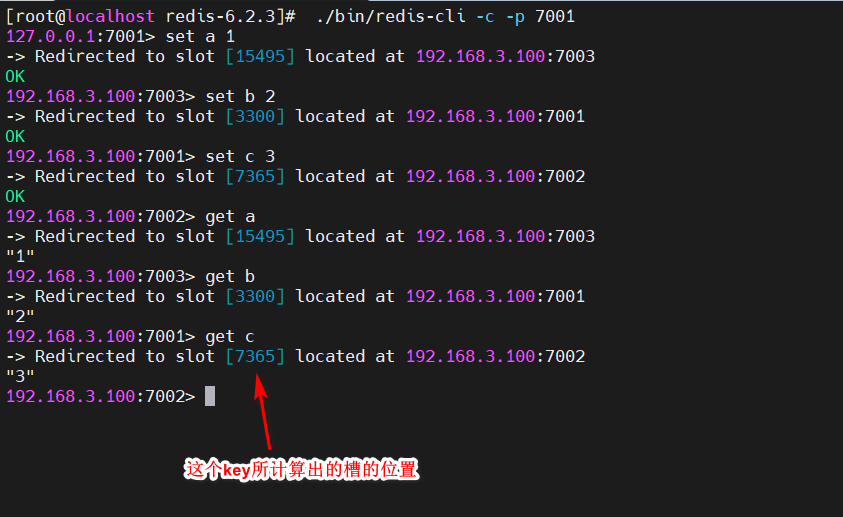
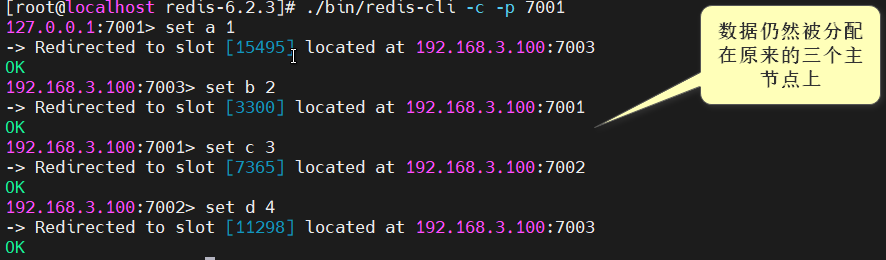
至此,集群就搭建好了,可以测试一下,连接集群,注意下面的命令,一定要带上 -c ,表示以集群的模式访问:
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli -c -p 7001
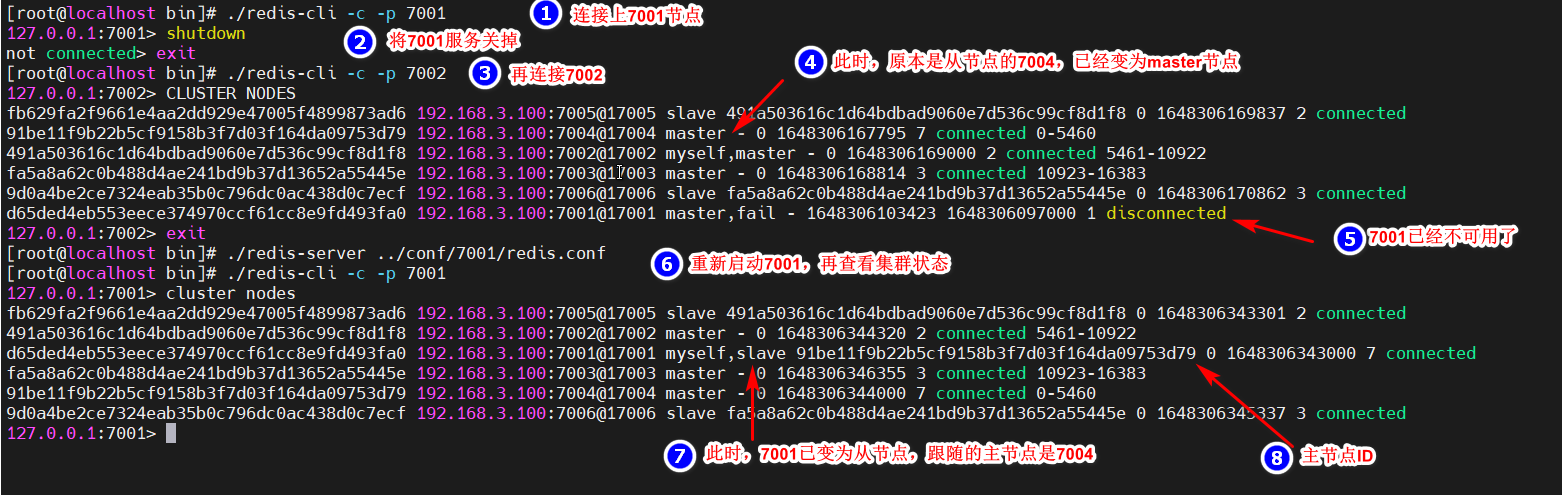
如果集群中,其中一个节点挂掉,从节点会自动变为主节点,若原主节点重连,会自动变为从节点
关闭集群办法:
[root@localhost bin]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/bin
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7001 shutdown
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7002 shutdown
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7003 shutdown
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7004 shutdown
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7005 shutdown
[root@localhost bin]# ./redis-cli -c -p 7006 shutdown
# 如果需要删除集群数据,看清楚当前位置
[root@localhost 7001]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/conf/7001
[root@localhost 7001]# rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
[root@localhost 7001]# cd ../7002/ ; rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
[root@localhost 7002]# cd ../7003/ ; rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
[root@localhost 7003]# cd ../7004/ ; rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
[root@localhost 7004]# cd ../7005/ ; rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
[root@localhost 7005]# cd ../7006/ ; rm -rf appendonly.aof dump.rdb log.log nodes.conf
使用 cluster-create 创建集群PS:一开始,我用redis-trib.rb搭建集群,但报出警告说,redis-trib.rb已经不可用了,让使用redis-cli --cluster代替,下图的示例后面的命令,是已经帮助我替换好的命令
脚本位置建议这块只做了解,实践中,使用上一种创建方式,其实这块创建集群,使用的仍然是redis-cli --cluster创建
在redis的/redis-6.2.3/utils/create-cluster目录下,有一个create-cluster脚本,可以使用此脚本创建集群
先编辑一下这个脚本,打开之后,可能需要修改前面几行配置
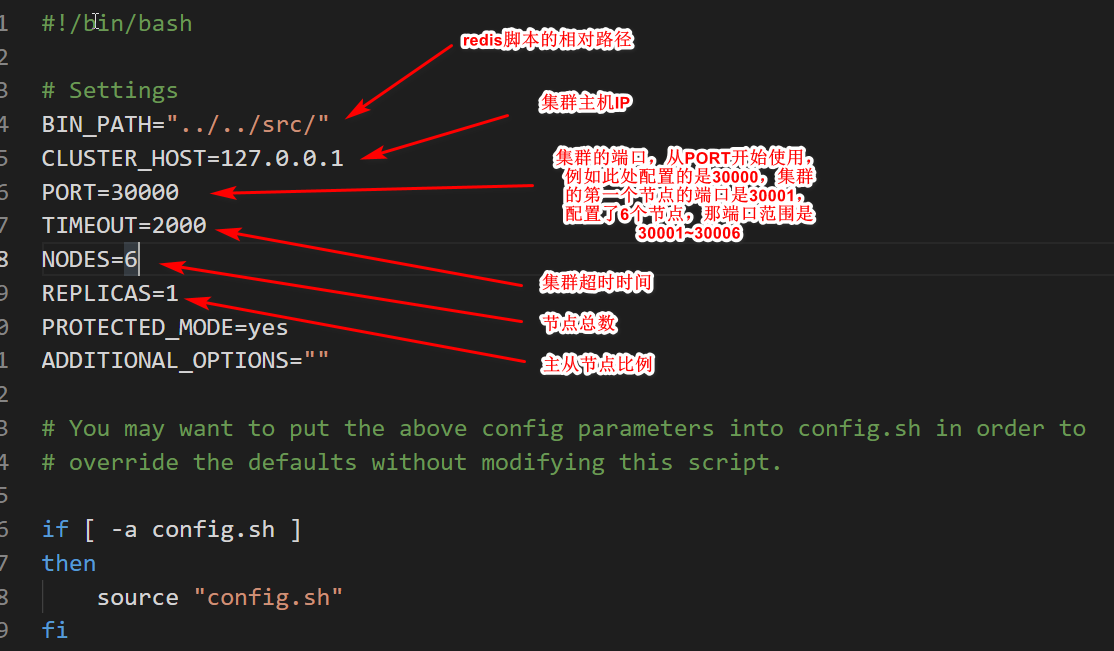
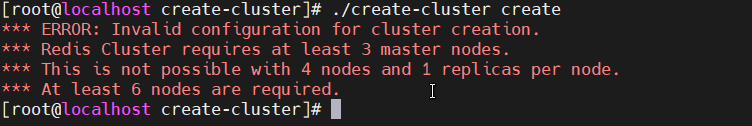
启动集群注意:集群节点的数量,必须大于6个,否则启动集群,会有如下错误:
启动redis服务,创建集群
[root@localhost create-cluster]# ./create-cluster start
Starting 30001
Starting 30002
Starting 30003
Starting 30004
Starting 30005
Starting 30006
[root@localhost create-cluster]# ./create-cluster create
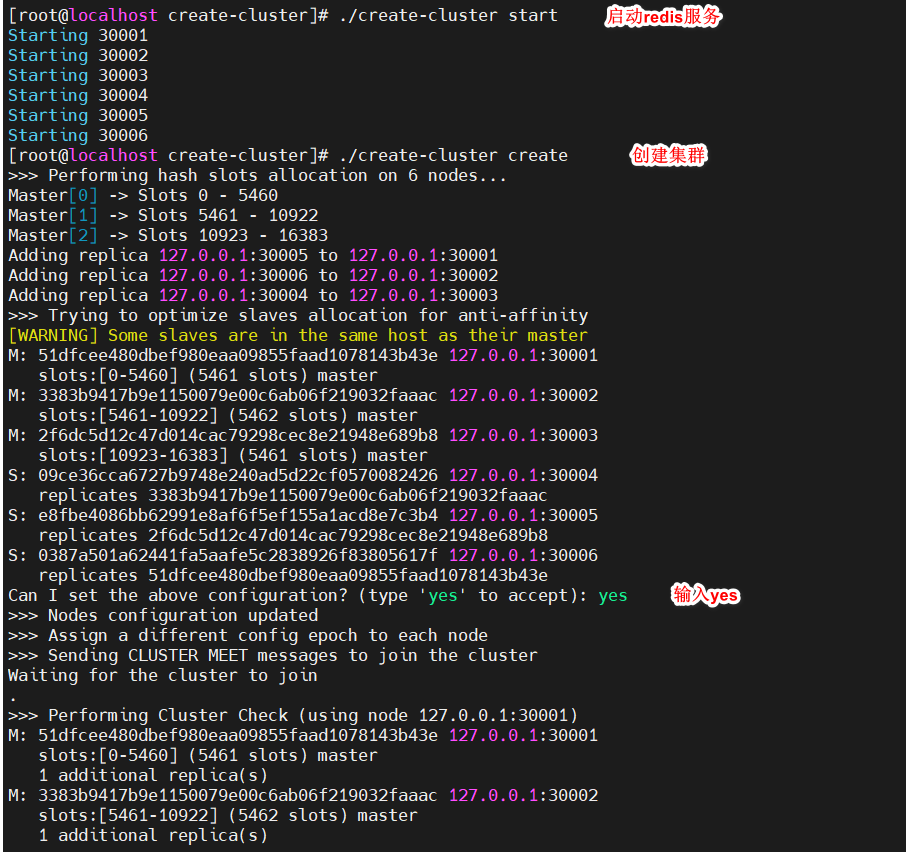
启动之后,会在create-cluster脚本的位置,自动生成配置文件、数据文件、log文件等
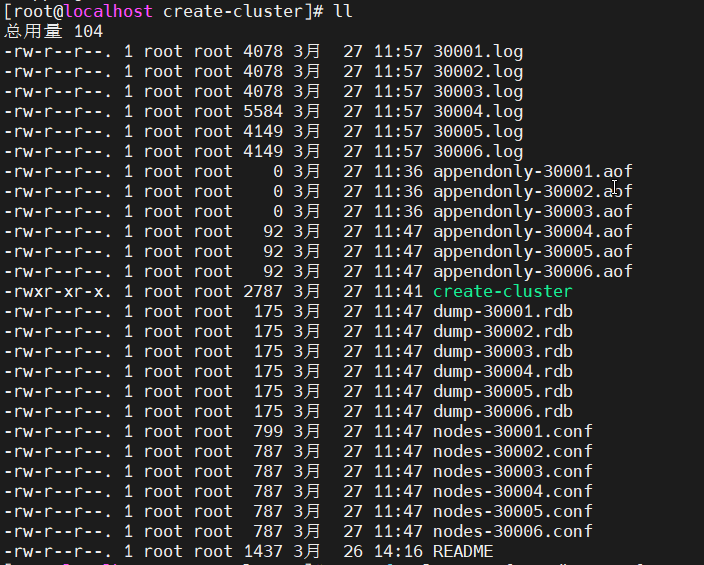
仍然使用 redis-cli -c
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli -c -p 30001
至此,集群搭建结束。
集群扩容
集群扩容时,先增加主节点,再给新增的主节点分配槽,然后增加从节点
在第一种集群的基础上,再增加两个节点,7007和7008,7007作为新增的主节点,7008作为7007的从节点。
添加配置把7001的配置文件,复制给7007和7008,并把配置文件里面的7001,全部替换成7007和7008。
[root@localhost conf]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3/conf
[root@localhost conf]# mkdir 7007 7008
[root@localhost conf]# cp 7001/redis.conf 7007/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# cp 7001/redis.conf 7008/redis.conf
[root@localhost conf]# ll
总用量 0
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7001
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7002
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7003
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7004
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7005
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 112 3月 27 12:01 7006
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 24 3月 27 12:05 7007
drwxr-xr-x. 2 root root 24 3月 27 12:05 7008
扩容时,先增加主节点,再增加从节点
先启动7007节点[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-server conf/7007/redis.conf
增加主节点之前的集群状态
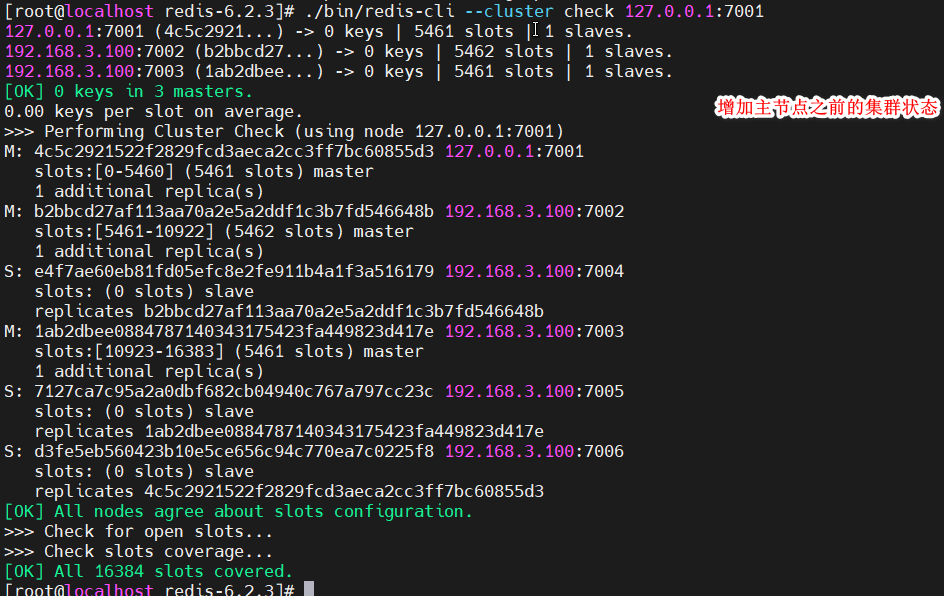
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster add-node 192.168.3.100:7007 192.168.3.100:7001
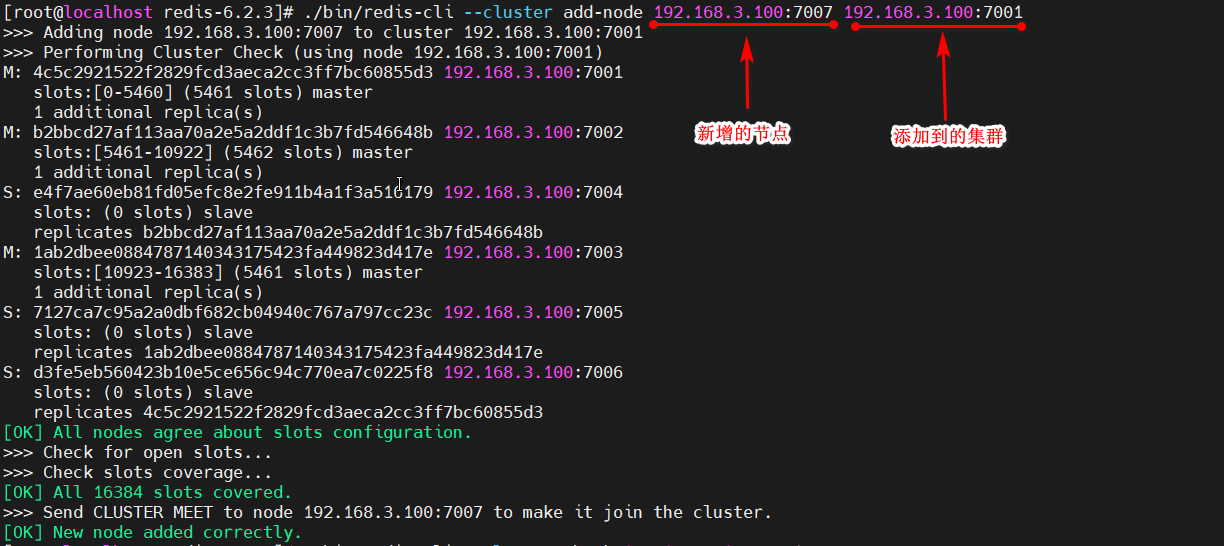
新增的节点,已成为集群中的主节点,但还没有给新主节点分配槽,0~16383(共16384个)这个范围的槽,全部被分配在了原来的三个主节点上,即使现在向集群中set数据,数据仍会被分配到原来的三个主节点上。
现在,为新增的主节点分配槽,执行以下命令:
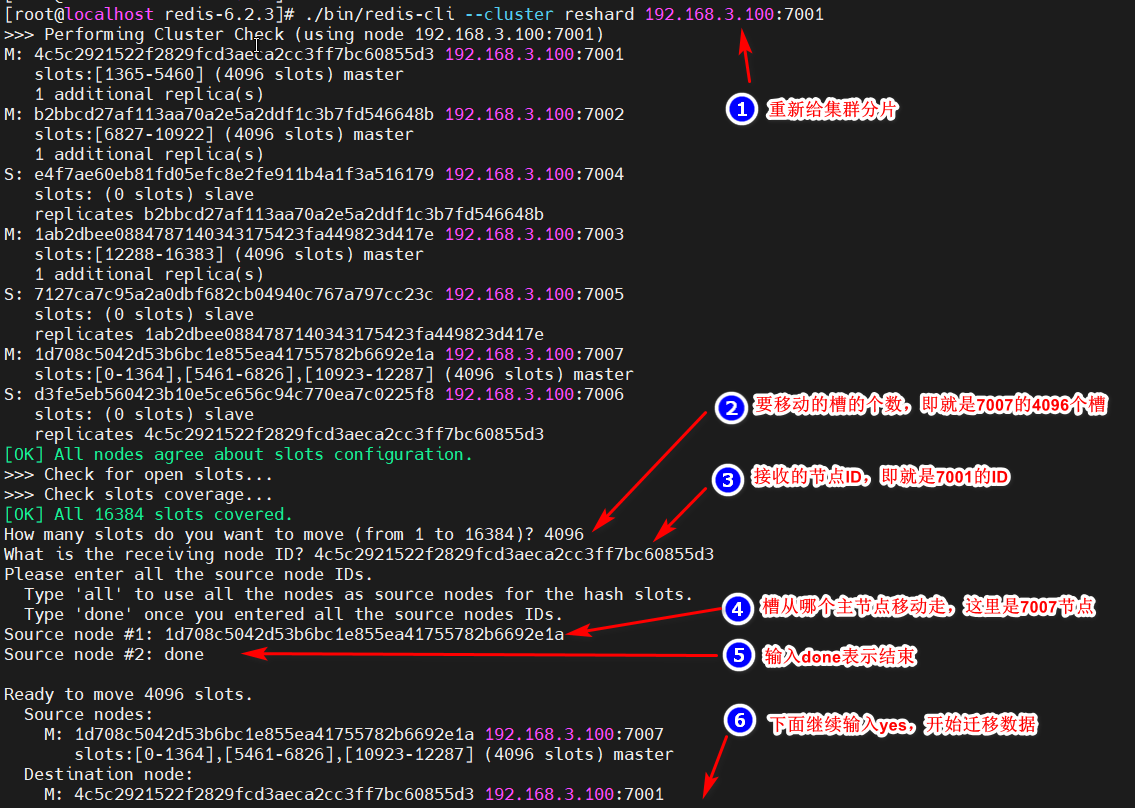
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster reshard 192.168.3.100:7001
此时会询问给新增master节点分配多少个槽,总共16384个,平均分配给4个主节点,每个节点分配4096,就输入4096
然后询问接收节点的ID,输入新增的master节点的ID
然后输入从哪几个节点来分,输入前三个主节点的ID,最后输入done表示结束。
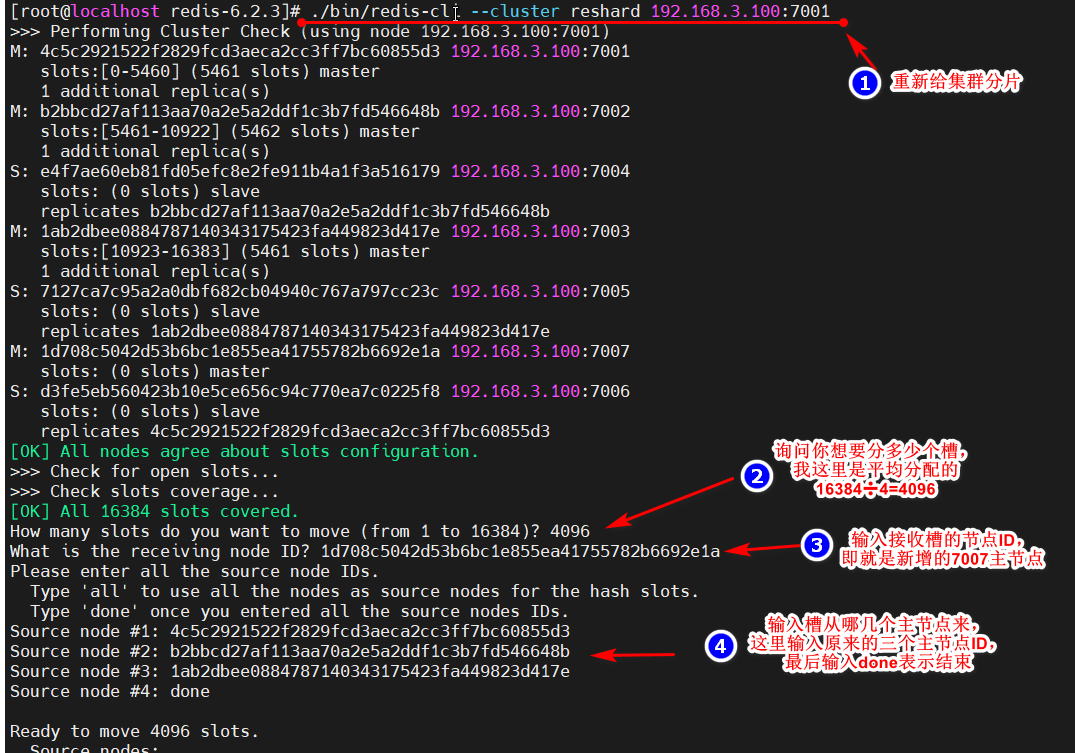
输入yes开始数据迁移,等待结束
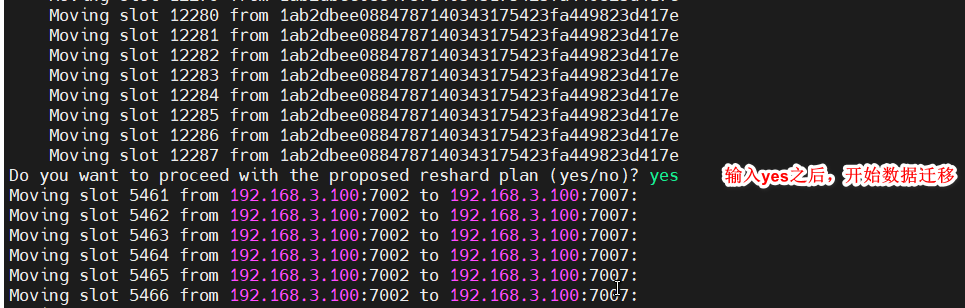
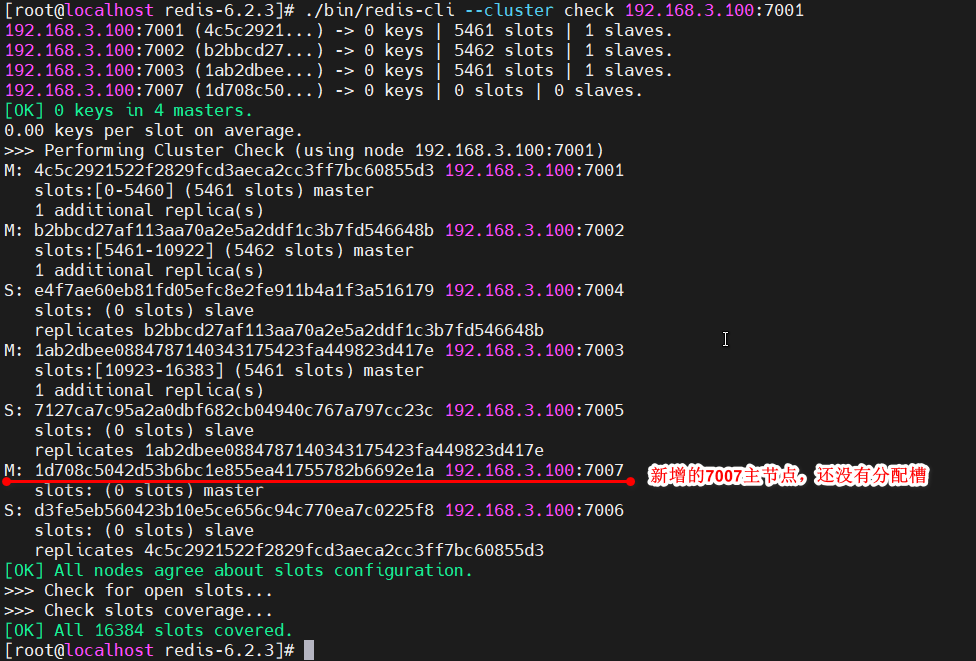
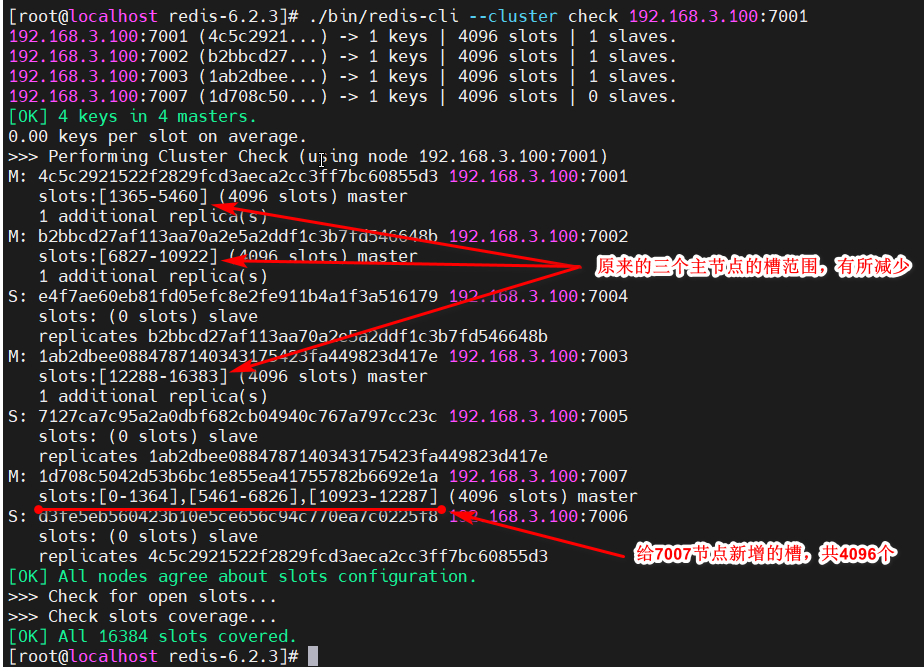
使用redis-cli --cluster check检查当前的集群状态,看槽是否已经分配完成
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster check 192.168.3.100:7001
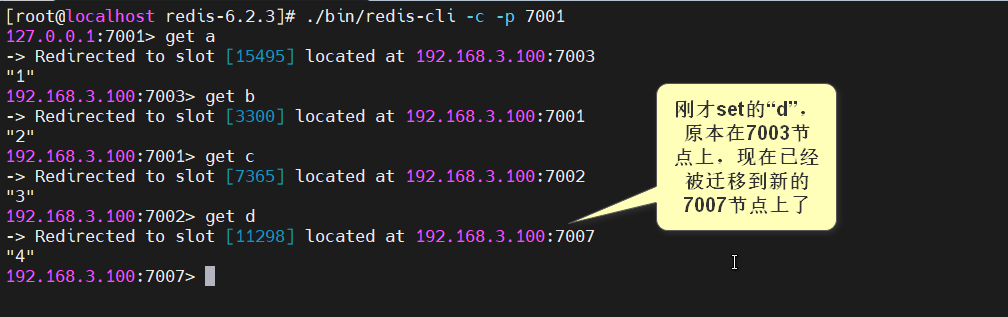
查看下面的数据所在的槽和所属的redis服务端口
至此,集群增加主节点结束。
增加从节点增加从节点有两个步骤:1、将新增节点7008加入到集群中,暂时作为主节点。2、将新增的节点7008挂接到从节点7007上去。
启动新增的从节点[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-server conf/7008/redis.conf
将新增的节点7008,加入到集群中,暂时作为主节点
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster add-node 192.168.3.100:7008 192.168.3.100:7001
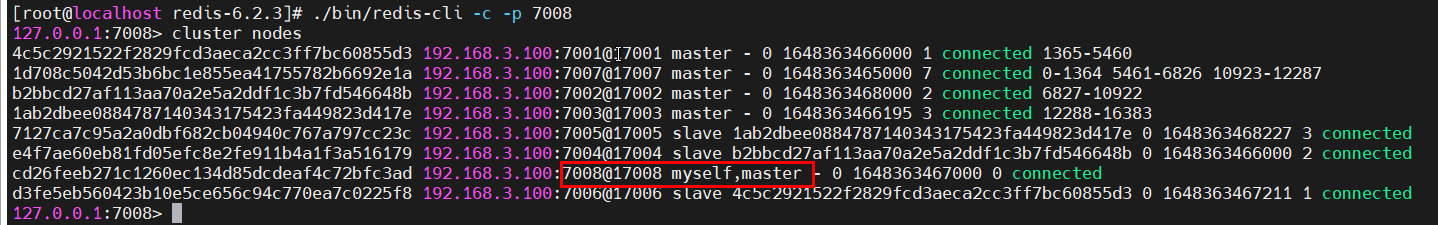
将新节点7008,挂接到集群的7007主节点上,作为其从节点。在7008的客户端里面执行以下命令,最后面的ID是主节点7007的ID:
127.0.0.1:7008> cluster replicate 1d708c5042d53b6bc1e855ea41755782b6692e1a

此时查看状态,7008已经成为7007的从节点,而且7008上的数据,和7007上的数据完全一样
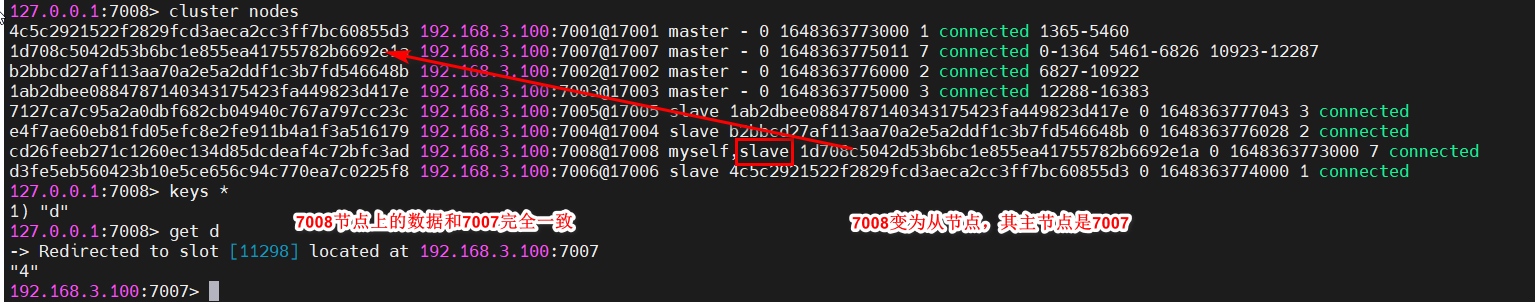
至此,集群扩容已完成。
集群缩容
删除从节点缩容的步骤,正好与扩容相反,先删除从节点,再将主节点的槽,分配给其他三个主节点的其中一个,然后删除主节点
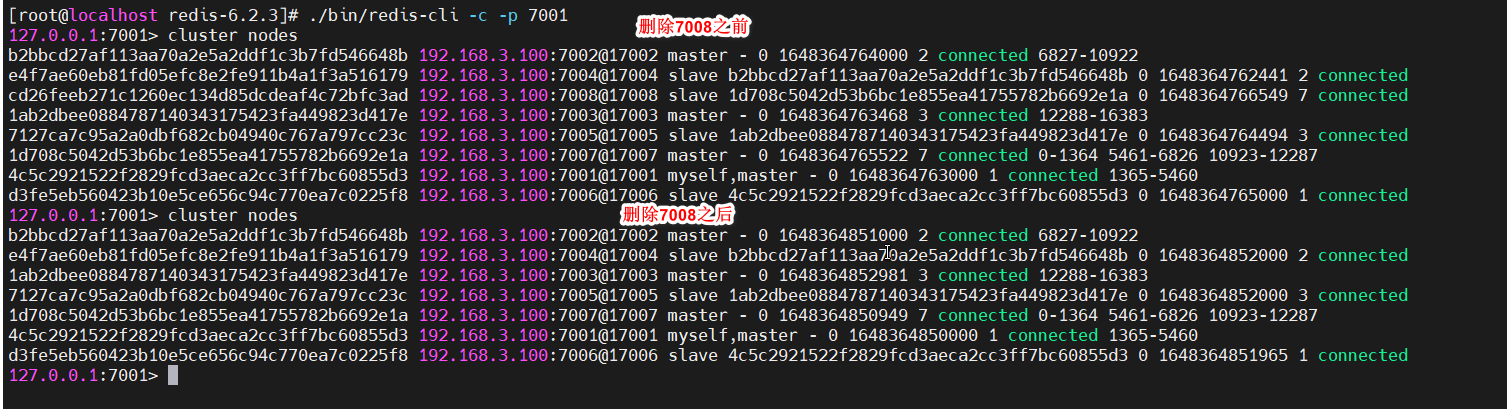
以删除7008从节点为例,使用redis-cli --cluster del-node命令删除从节点,192.168.3.100:7001 表示要从哪个集群删除(注意这并不是要删除的节点IP和端口),后面的cd26feeb271c1260ec134d85dcdeaf4c72bfc3ad才表示要删除的节点ID,也就是7008的ID
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster del-node 192.168.3.100:7001 cd26feeb271c1260ec134d85dcdeaf4c72bfc3ad
>>> Removing node cd26feeb271c1260ec134d85dcdeaf4c72bfc3ad from cluster 192.168.3.100:7001
>>> Sending CLUSTER FORGET messages to the cluster...
>>> Sending CLUSTER RESET SOFT to the deleted node.
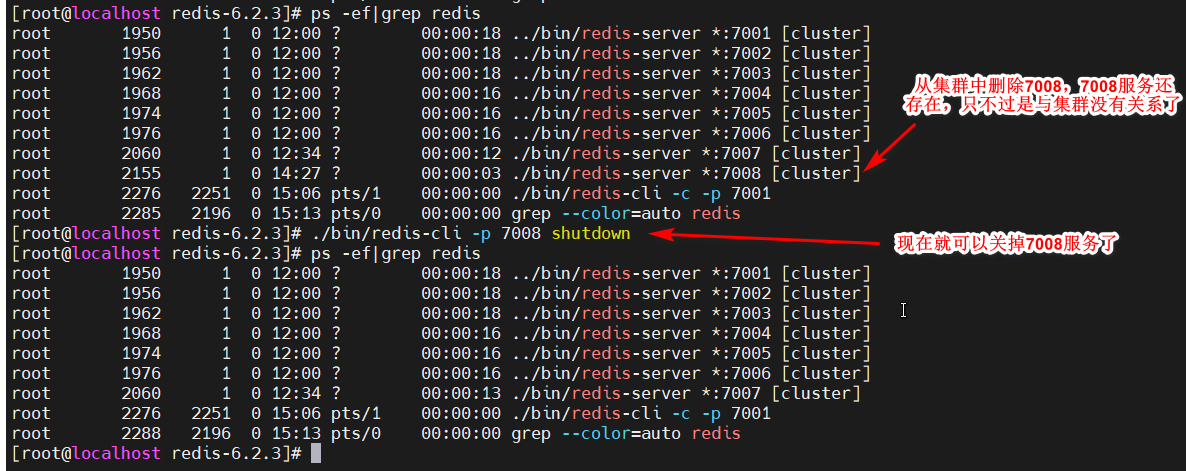
此时再查看集群状态,集群中已经没有7008节点了,但是7008的服务还启动着,现在就可以关掉了
关掉7008服务
在删除集群中的主节点7007之前,需要先将其槽分给其他的三个主节点中的某一个,这里以分配给7001节点为例:
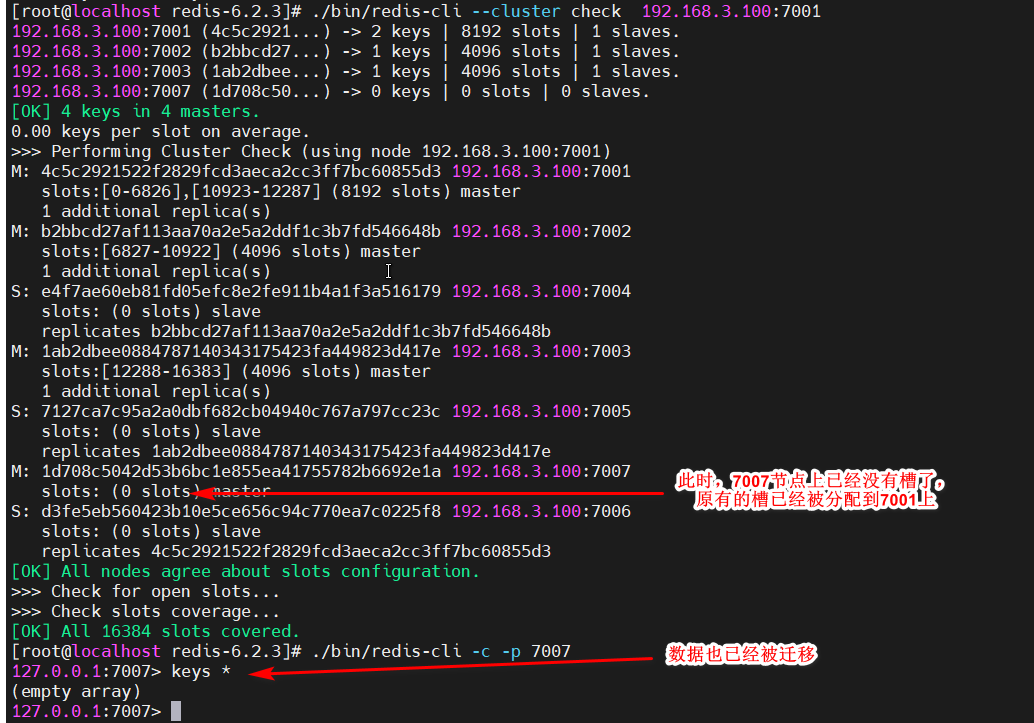
此时,7007上已经没有数据和槽了,可以从集群中删除7007节点了,删除方式和删除从节点一样,直接执行删除命令:
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# pwd
/opt/app/redis/cluster/redis-6.2.3
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]# ./bin/redis-cli --cluster del-node 192.168.3.100:7001 1d708c5042d53b6bc1e855ea41755782b6692e1a
>>> Removing node 1d708c5042d53b6bc1e855ea41755782b6692e1a from cluster 192.168.3.100:7001
>>> Sending CLUSTER FORGET messages to the cluster...
>>> Sending CLUSTER RESET SOFT to the deleted node.
[root@localhost redis-6.2.3]#
再查看集群状态,集群中已经没有7007节点了
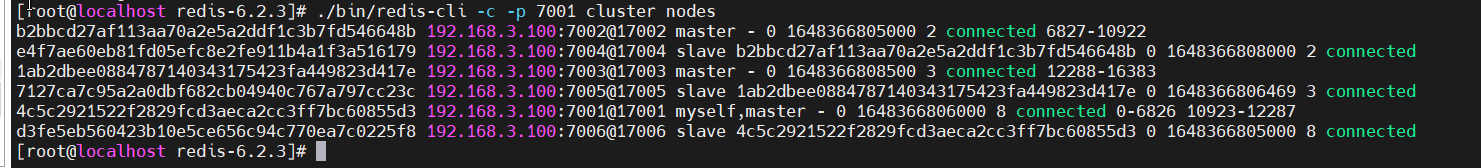
再关闭7007服务即可:
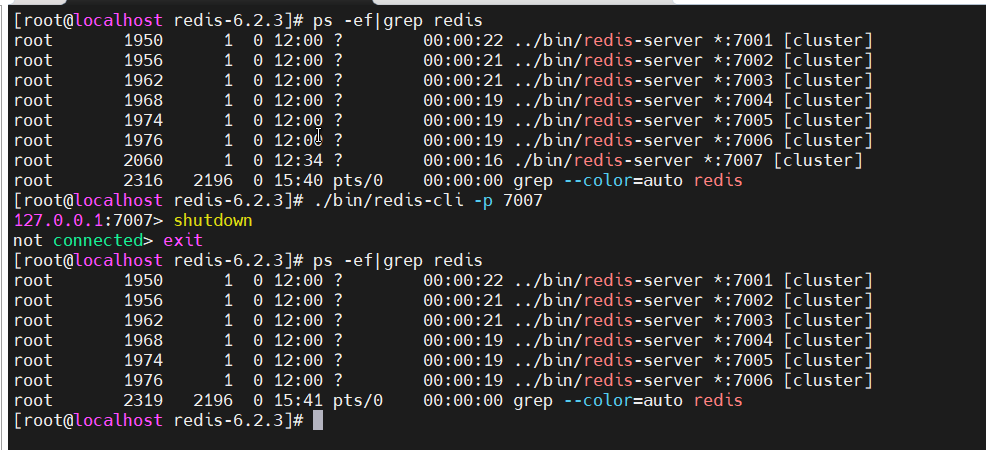
至此,redis集群缩容完成
Java连接cluster集群 使用Jedis连接Redis
新建一个简单的maven项目,在pom文件中引入jedis依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>4.1.1</version>
</dependency>
测试:
public class RedisClusterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<HostAndPort> nodes = new HashSet();
//集群的所有节点
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7001));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7002));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7003));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7004));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7005));
nodes.add(new HostAndPort("192.168.3.100", 7006));
//JedisCluster客户端
JedisCluster jedisCluster = new JedisCluster(nodes);
//set值
jedisCluster.set("a", "a");
jedisCluster.set("b", "b");
jedisCluster.set("c", "c");
jedisCluster.set("d", "d");
//get值
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("a"));
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("b"));
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("c"));
System.out.println(jedisCluster.get("d"));
//关闭jedisCluster
jedisCluster.close();
}
}
新建一个SpringBoot项目,在项目中引入以下依赖:
<!-- Spring web的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot项目pom文件中,加入redis依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.6.4</version>
</dependency>
<!-- test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.6.5</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- test -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- fastjson,设置序列化-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.79</version>
</dependency>
在application.properties配置文件中,加入集群的节点的配置信息(这里做了简化)
spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.3.100:7001,192.168.3.100:7002,192.168.3.100:7003,192.168.3.100:7004,192.168.3.100:7005,192.168.3.100:7006
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate = new RedisTemplate();
redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object> jsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<>(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
StringRedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setValueSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(jsonRedisSerializer);
redisTemplate.afterPropertiesSet();
return redisTemplate;
}
}
@SpringBootTest(classes = RedisBootApplication.class)
public class TestRedisClusterClient {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
@Test
public void test1() {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("a", 1);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("b", 2);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("c", 3);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("d", 4);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("a"));
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("b"));
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("c"));
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("d"));
}
}
在redis-cli中查看
127.0.0.1:7001> get a
-> Redirected to slot [15495] located at 192.168.3.100:7003
"1"
192.168.3.100:7003> get b
-> Redirected to slot [3300] located at 192.168.3.100:7001
"2"
192.168.3.100:7001> get c
-> Redirected to slot [7365] located at 192.168.3.100:7002
"3"
192.168.3.100:7003> get d
-> Redirected to slot [11298] located at 192.168.3.100:7001
"4"