今天我们来结合源码来探究一下ASP.NET CORE Web框架的运行原理。
可以先整体看一下下面这张基于源码分析过程的一个总结大纲,包含各环节完成的关键步骤:
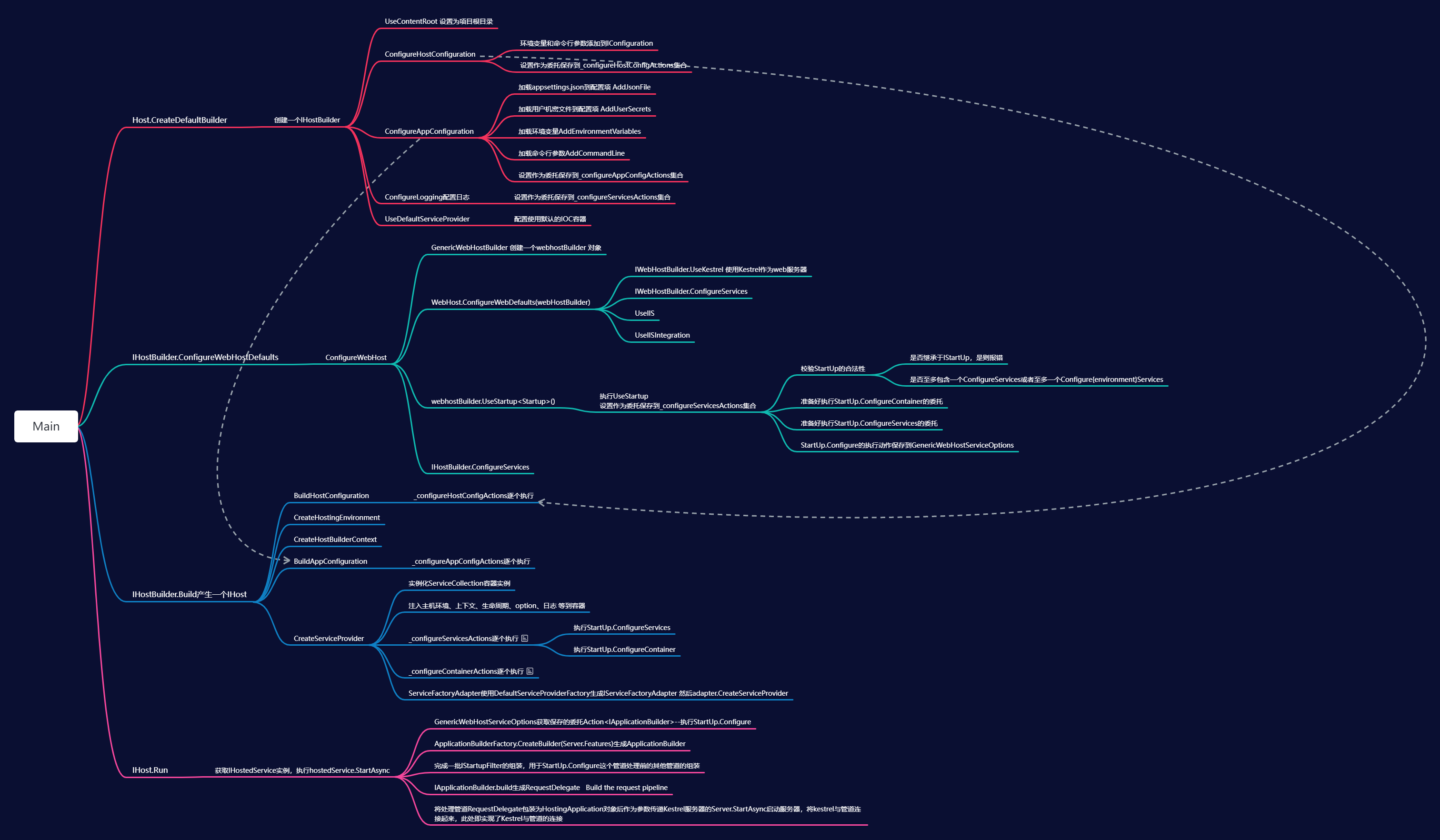
下面我们将一起来结合源码探索启动一个ASP.NET CORE的Web项目时框架是怎么运行起来的,以及各个环节框架底层的源码大致做了哪些事情!
一、初始化与框架配置
首先我们聚焦于Host.CreateDefaultBuilder
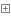
1 public static IHostBuilder CreateDefaultBuilder(string[] args) 2 { 3 //使用默认的配置初始化一个HostBuilder对象 4 var builder = new HostBuilder(); 5 6 builder.UseContentRoot(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()); 7 builder.ConfigureHostConfiguration(config => 8 { 9 config.AddEnvironmentVariables(prefix: "DOTNET_"); 10 if (args != null) 11 { 12 config.AddCommandLine(args); 13 } 14 }); 15 16 builder.ConfigureAppConfiguration((hostingContext, config) => 17 { 18 var env = hostingContext.HostingEnvironment; 19 20 config.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true) 21 .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true, reloadOnChange: true); 22 23 if (env.IsDevelopment() && !string.IsNullOrEmpty(env.ApplicationName)) 24 { 25 var appAssembly = Assembly.Load(new AssemblyName(env.ApplicationName)); 26 if (appAssembly != null) 27 { 28 config.AddUserSecrets(appAssembly, optional: true); 29 } 30 } 31 32 config.AddEnvironmentVariables(); 33 34 if (args != null) 35 { 36 config.AddCommandLine(args); 37 } 38 }) 39 .ConfigureLogging((hostingContext, logging) => 40 { 41 var isWindows = RuntimeInformation.IsOSPlatform(OSPlatform.Windows); 42 43 // IMPORTANT: This needs to be added *before* configuration is loaded, this lets 44 // the defaults be overridden by the configuration. 45 if (isWindows) 46 { 47 // Default the EventLogLoggerProvider to warning or above 48 logging.AddFilter<EventLogLoggerProvider>(level => level >= LogLevel.Warning); 49 } 50 51 logging.AddConfiguration(hostingContext.Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); 52 logging.AddConsole(); 53 logging.AddDebug(); 54 logging.AddEventSourceLogger(); 55 56 if (isWindows) 57 { 58 // Add the EventLogLoggerProvider on windows machines 59 logging.AddEventLog(); 60 } 61 }) 62 .UseDefaultServiceProvider((context, options) => 63 { 64 var isDevelopment = context.HostingEnvironment.IsDevelopment(); 65 options.ValidateScopes = isDevelopment; 66 options.ValidateOnBuild = isDevelopment; 67 }); 68 69 return builder; 70 }View Code
该方法首先会创建一个IHostBuilder,并使用一些默认的配置进行初始化:
UseContentRoot 设置主机项目根目录
ConfigureHostConfiguration配置环境变量和命令行参数添加到Configure对象,便于程序在以后的运行中可以从Configure对象获取到来源于环境变量和命令行的参数
ConfigureAppConfiguration设置对配置文件和用户机密文件的加载,并且可以再次使用该方法来定义App应用的配置信息,对于Configure的讲解可查看我的这篇文章《浅析.netcore中的Configuration》
ConfigureLogging用来配置系统的日志
UseDefaultServiceProvider用来配置框架使用默认的IOC容器
然后程序来到了ConfigureWebHostDefaults方法
程序会先使用GenericWebHostBuilder 创建和初始化一个IWebhostBuilder 对象,然后调用WebHost.ConfigureWebDefaults方法,在方法中通过调用UseKestrel告诉框架使用Kestrel作为web服务器用于接受请求,完成Kestrel服务器的相关配置。
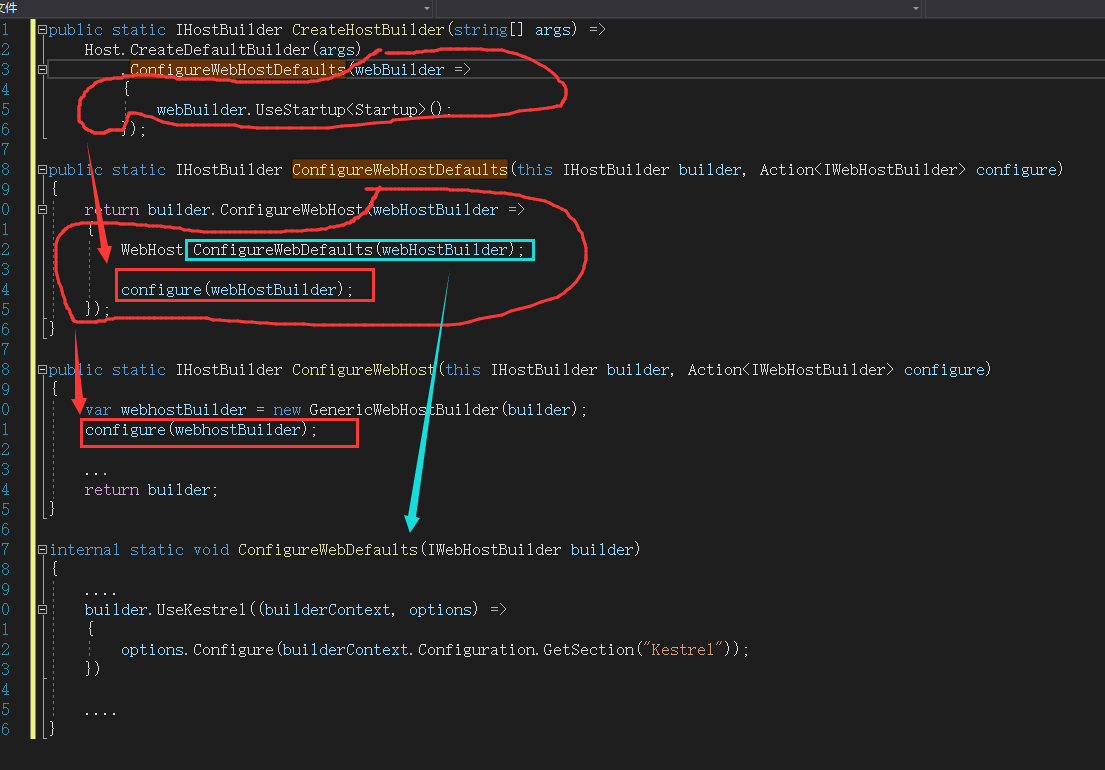
接着程序会调用webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>(),该方法会找出Startup中的ConfigureServices、ConfigureContainer和Configure方法,将其方法的实际执行动作调用IHostBuilder中的ConfigureServices方法以委托的形式保存起来。下面为UseStartUp执行的部分源代码

1 public IWebHostBuilder UseStartup(Type startupType) 2 { 3 // UseStartup can be called multiple times. Only run the last one. 4 _builder.Properties["UseStartup.StartupType"] = startupType; 5 _builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) => 6 { 7 if (_builder.Properties.TryGetValue("UseStartup.StartupType", out var cachedType) && (Type)cachedType == startupType) 8 { 9 UseStartup(startupType, context, services); 10 } 11 }); 12 13 return this; 14 } 15 16 private void UseStartup(Type startupType, HostBuilderContext context, IServiceCollection services) 17 { 18 var webHostBuilderContext = GetWebHostBuilderContext(context); 19 var webHostOptions = (WebHostOptions)context.Properties[typeof(WebHostOptions)]; 20 21 ... 22 try 23 { 24 //1.完成对StartUp类的合法性进行校验 25 // We cannot support methods that return IServiceProvider as that is terminal and we need ConfigureServices to compose 26 if (typeof(IStartup).IsAssignableFrom(startupType)) 27 { 28 throw new NotSupportedException($"{typeof(IStartup)} isn't supported"); 29 } 30 if (StartupLoader.HasConfigureServicesIServiceProviderDelegate(startupType, context.HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName)) 31 { 32 throw new NotSupportedException($"ConfigureServices returning an {typeof(IServiceProvider)} isn't supported."); 33 } 34 35 instance = ActivatorUtilities.CreateInstance(new HostServiceProvider(webHostBuilderContext), startupType); 36 context.Properties[_startupKey] = instance; 37 38 //2.查找并校验StartUp类中的ConfigureServices方法 39 // Startup.ConfigureServices 40 var configureServicesBuilder = StartupLoader.FindConfigureServicesDelegate(startupType, context.HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName); 41 var configureServices = configureServicesBuilder.Build(instance); 42 43 //3.执行StartUp类中的ConfigureServices 44 configureServices(services); 45 46 //4.查找并校验StartUp类中的ConfigureContainer方法 47 // REVIEW: We're doing this in the callback so that we have access to the hosting environment 48 // Startup.ConfigureContainer 49 var configureContainerBuilder = StartupLoader.FindConfigureContainerDelegate(startupType, context.HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName); 50 ... 51 52 //5.查找并校验StartUp类中的Configure方法 53 // Resolve Configure after calling ConfigureServices and ConfigureContainer 54 configureBuilder = StartupLoader.FindConfigureDelegate(startupType, context.HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName); 55 } 56 catch (Exception ex) when (webHostOptions.CaptureStartupErrors) 57 { 58 startupError = ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(ex); 59 } 60 61 ... 62 }View Code
有些同学可能已经发现,我们可以使用UseStartup的时候可以不指定具体的StartUp类,而是指定一个程序集便可实现通过定义不同的环境去加载不同的StartUp类。如下图我们定义了多个StartUp类

然后将webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>()改为webBuilder.UseStartup(typeof(Startup).GetTypeInfo().Assembly.FullName),通过设置不同的环境配置项便可执行对应的StartUp
这个又是怎么实现的呢?这便要说起前面我们使用GenericWebHostBuilder构造IWebHostBuilder对象的时候,构造函数中会拿到传递到程序集字符串集合当前的主机环境找到对应的StartUp类,最后的执行与直接使用webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>()最后调用的逻辑是一样的。所以看到源码之后,就会对于这样的写法和用途醍醐灌顶。

1 public GenericWebHostBuilder(IHostBuilder builder) 2 { 3 _builder = builder; 4 5 ... 6 7 _builder.ConfigureServices((context, services) => 8 { 9 var webhostContext = GetWebHostBuilderContext(context); 10 var webHostOptions = (WebHostOptions)context.Properties[typeof(WebHostOptions)]; 11 12 ... 13 14 // webHostOptions.StartupAssembly拿到的就是UseStartUp传递的程序集字符串 15 // Support UseStartup(assemblyName) 16 if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(webHostOptions.StartupAssembly)) 17 { 18 try 19 { 20 //根据Environment找到对应的StartUp类 21 var startupType = StartupLoader.FindStartupType(webHostOptions.StartupAssembly, webhostContext.HostingEnvironment.EnvironmentName); 22 //webBuilder.UseStartup<Startup>()调用过程中也会执行此方法,实现的作用在上面有进行说明 23 UseStartup(startupType, context, services); 24 } 25 catch (Exception ex) when (webHostOptions.CaptureStartupErrors) 26 { 27 } 28 } 29 }); 30 }View Code
二、IHostBuilder.Build()构建装载框架的处理能力
到此为止,前面的动作都是使用默认的配置完成了一些对象的初始化,并且将一些执行动作保存为委托,并没有实际执行,等到来到Build方法,会执行方法内部的三个核心动作。

1 public IHost Build() 2 { 3 ... 4 BuildHostConfiguration(); 5 ... 6 BuildAppConfiguration(); 7 CreateServiceProvider(); 8 9 ... 10 } 11 12 private void BuildHostConfiguration() 13 { 14 var configBuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder() 15 .AddInMemoryCollection(); // Make sure there's some default storage since there are no default providers 16 17 foreach (var buildAction in _configureHostConfigActions) 18 { 19 buildAction(configBuilder); 20 } 21 _hostConfiguration = configBuilder.Build(); 22 } 23 24 private void BuildAppConfiguration() 25 { 26 var configBuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder() 27 .SetBasePath(_hostingEnvironment.ContentRootPath) 28 .AddConfiguration(_hostConfiguration, shouldDisposeConfiguration: true); 29 30 foreach (var buildAction in _configureAppConfigActions) 31 { 32 buildAction(_hostBuilderContext, configBuilder); 33 } 34 _appConfiguration = configBuilder.Build(); 35 _hostBuilderContext.Configuration = _appConfiguration; 36 } 37 38 private void CreateServiceProvider() 39 { 40 var services = new ServiceCollection(); 41 .... //注册框架需要的服务实例到容器 42 43 foreach (var configureServicesAction in _configureServicesActions) 44 { 45 configureServicesAction(_hostBuilderContext, services); 46 } 47 48 var containerBuilder = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateBuilder(services); 49 50 foreach (var containerAction in _configureContainerActions) 51 { 52 containerAction.ConfigureContainer(_hostBuilderContext, containerBuilder); 53 } 54 55 _appServices = _serviceProviderFactory.CreateServiceProvider(containerBuilder); 56 57 if (_appServices == null) 58 { 59 throw new InvalidOperationException($"The IServiceProviderFactory returned a null IServiceProvider."); 60 } 61 62 // resolve configuration explicitly once to mark it as resolved within the 63 // service provider, ensuring it will be properly disposed with the provider 64 _ = _appServices.GetService<IConfiguration>(); 65 }View Code
BuildHostConfiguration会执行前面调用ConfigureHostConfiguration保存的委托方法完成对Host的配置
BuildAppConfiguration会执行前面调用ConfigureAppConfiguration保存的委托方法完成对App应用的配置
CreateServiceProvider首先会初始化ServiceCollection的容器实例,然后将部分框架需要的实例对象添加到容器中,完成主机环境、上下文、生命周期等相关对象的容器注册,随后会执行前面调用ConfigureServices保存的委托方法,所以StartUp类中的ConfigureServices其实就是在这个环节执行的。
三、IHost.Run()组装请求处理流程并启动服务器监听
最后来到IHost.Run去运行主机

1 //Run最终会调用该方法 2 public async Task StartAsync(CancellationToken cancellationToken) 3 { 4 ..... 5 6 RequestDelegate application = null; 7 8 try 9 { 10 //这边是前面拿到的StartUp中的Configure方法 11 Action<IApplicationBuilder> configure = Options.ConfigureApplication; 12 13 if (configure == null) 14 { 15 throw new InvalidOperationException($"No application configured. Please specify an application via IWebHostBuilder.UseStartup, IWebHostBuilder.Configure, or specifying the startup assembly via {nameof(WebHostDefaults.StartupAssemblyKey)} in the web host configuration."); 16 } 17 18 var builder = ApplicationBuilderFactory.CreateBuilder(Server.Features); 19 20 .... 21 22 configure(builder); 23 24 // Build the request pipeline 25 application = builder.Build(); 26 } 27 catch (Exception ex) 28 { 29 } 30 31 var httpApplication = new HostingApplication(application, Logger, DiagnosticListener, HttpContextFactory); 32 33 await Server.StartAsync(httpApplication, cancellationToken); 34 35 ... 36 }View Code
该过程中框架会拿到执行前面查询StartUp找到并保存起来的Configure方法,此方法会定义并添加对请求进行处理的管道中间件以及中间间的处理顺序,然后会通过ApplicationBuilderFactory创建一个IApplicationBuilder对象,使用IApplicationBuilder.build去组装管道处理流程,最后生成一个RequestDelegate,该对象就是我们的处理管道对象。
然后程序会把RequestDelegate进行包装后作为参数传递到Server.StartAsync方法中,Server对象即为Kestrel服务器,调用Server.StartAsync便会启动Kestrel服务器,实现站点对请求的监听,同时通过传递过来的RequestDelegate对象,便把Kestrel与管道中间件连接起来了,从而实现了从请求监听到请求处理的全过程。
今天的分享就到这里,后续会继续带来更多关于ASP.NET Core框架的解读,希望有收获的小伙伴推荐支持一下,有疑问可评论区留言讨论!