栈和队列一、栈和队列的基本概念 在数组中,我们可以通过索引(下标)访问随机元素。但是,在某些情况下,我们可能需要限制处理顺序,这就产生了栈和队列这两种功能受限的线性结
在数组中,我们可以通过索引(下标)访问随机元素。但是,在某些情况下,我们可能需要限制处理顺序,这就产生了栈和队列这两种功能受限的线性结构。
栈和队列是两种不同的处理顺序:先进后出和先进先出,以及两个相应的线性数据结构。
二、数据结构中的栈和队列 1、栈(stack)数据后进先出,先进后出 LIFO (last in first out)
栈只有一个开口,先进去的就到下面,后进来的就在上面(top),要是拿出去的话,肯定是从开口端拿出去,所以说先进后出,后进先出。
入栈 push 出栈 pop 获取栈顶元素 top判断栈是否已经是空
判断栈是否已经满了 is_full(如果是数组实现的)
2、队列(queue)先进先出,后进后出 FIFO (first in first out)
队列有队首(front) 和队尾(back), 数据从对尾进去队列,从队首出列,队头(front)指向队列的第一个数据,对尾(back)指向队列中最后一个数据。
入队 push 出队 pop 队头 front 队尾 back 三、栈和队列的基本结构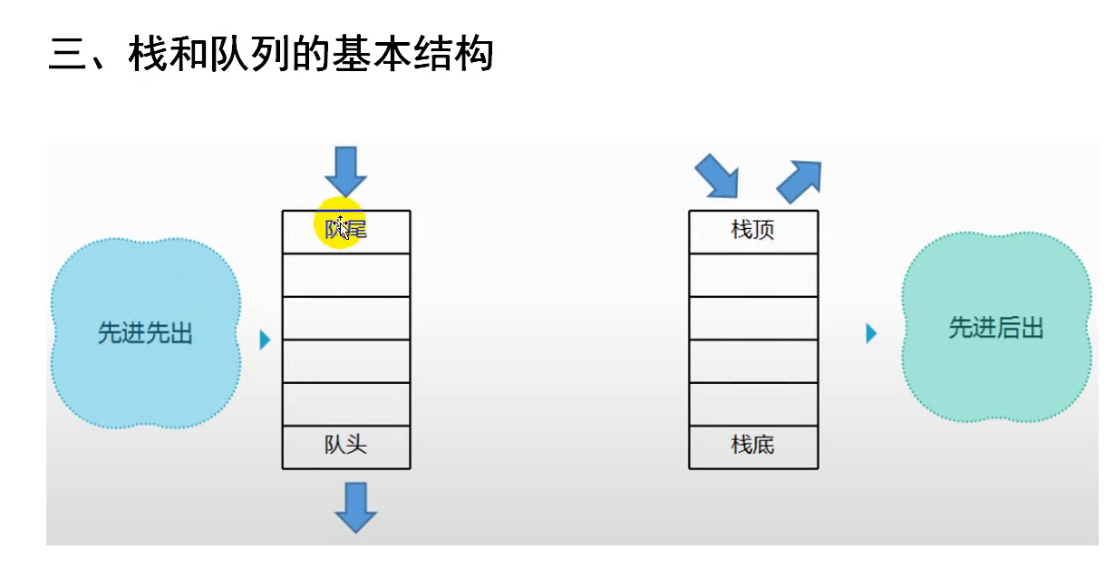
#define STACK_SIZE_MAX 10 //栈的最大大小
typedef struct Stack //栈的结构声明
{
Type data[STACK_SIZE_MAX]; //数据域
int top; //栈顶元素下标
}Stack;
//1 栈的初始化函数
Stack* stack_init();
//2 数据入栈函数
void stack_push(Stack* stack,Type val);
//3 数据出栈函数
Type stack_pop(Stack* stack);
//4 获取栈顶元素
Type stack_top(Stack* stack);
//5 判断栈是否为空
bool stack_empty(Stack* stack);
//6 判断栈是否满了
bool stack_full(Stack* stack);
//1 栈的初始化函数
Stack* stack_init()
{
Stack* temp = (Stack*)malloc(sizeof(Stack));
assert(temp);
temp->top = -1; //初始化栈顶元素下标为-1,表示栈中没有数据
return temp;
}
//2 数据入栈函数
void stack_push(Stack* stack, Type val)
{
assert(stack); //判断栈是否存在
assert(!stack_full(stack)); //判断栈是否满了
stack->data[++stack->top] = val; //栈顶插入元素
}
//3 数据出栈函数
Type stack_pop(Stack* stack)
{
assert(stack);
assert(!stack_empty(stack)); //判断栈是否为空
Type val = stack->data[stack->top]; //记录当前栈顶元素
stack->top--; //栈顶下标-1
return val;
}
//4 获取栈顶元素
Type stack_top(Stack* stack)
{
assert(stack);
assert(!stack_empty(stack)); //判断栈是否为空
return stack->data[stack->top];
}
//5 判断栈是否为空
bool stack_empty(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top == -1; //栈空了
}
//6 判断栈是否满了
bool stack_full(Stack* stack)
{
return stack->top >= STACK_SIZE_MAX - 1; //栈满了
}
对于队列来说,入队和出队比较频繁,所以如果用顺序表实现入队虽然简单,但是每次出队都要移动整个顺序表,效率不高,所以使用链表实现。
2.1 队列声明//队列节点的声明
typedef struct Node
{
Type data;
Node* next;
}Node;
typedef struct Queue
{
Node* front; //队首
Node* back; //队尾
}Queue;
//队列单例表的初始化
Queue* queue_init();
//队列单链表节点的初始化
Node* node_create(Type val);
//1 数据入队
void queue_push(Queue* q, Type val);
//2 数据出队
Type queue_pop(Queue* q);
//3 获取队首元素
Type queue_front(Queue* q);
//4 获取队尾元素
Type queue_back(Queue* q);
//5 判断队列是否为空
bool queue_isNull(Queue* q);
//1 队列单例表的初始化
Queue* queue_init()
{
Queue* queue = (Queue*)malloc(sizeof(Queue));//开辟空间
assert(queue); //断言:如果queue为空或者0,则会弹出报错窗口
queue->front = queue->back = nullptr;
return queue;
}
//2 队列单链表节点的初始化
Node* node_create(Type val)
{
Node* temp = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
assert(temp);
temp->data = val;
temp->next = nullptr;
return temp;
}
//3 数据入队
void queue_push(Queue* q, Type val) //尾插
{
assert(q);
if (q->front == nullptr) //队首为空
{
q->front = node_create(val);
q->back = q->front;
}
else
{
q->back->next = node_create(val);
q->back = q->back->next;
}
}
//4 数据出队
Type queue_pop(Queue* q) //头删
{
assert(q); //整个链表不存在
assert(q->front); //链表为空
Node* temp = q->front;
Type val = temp->data;
q->front = q->front->next; //当前队首的下一个节点成为新的队首
free(temp); //之前的队首出队,空间释放
temp = NULL; //避免temp是野指针
return val;
}
//5 获取队首元素
Type queue_front(Queue* q)
{
assert(q); //整个链表不存在
assert(q->front); //链表为空
return q->front->data;
}
//6 获取队尾元素
Type queue_back(Queue* q)
{
assert(q); //整个链表不存在
assert(q->front); //链表为空
return q->back->data;
}
//7 判断队列是否为空
bool queue_isNull(Queue* q)
{
assert(q); //整个链表不存在
if (q->front == NULL)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
//或者直接 return q->front == NULL;
}
