一.首先看布局层次 看这么几张图
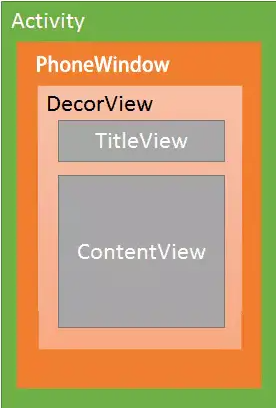
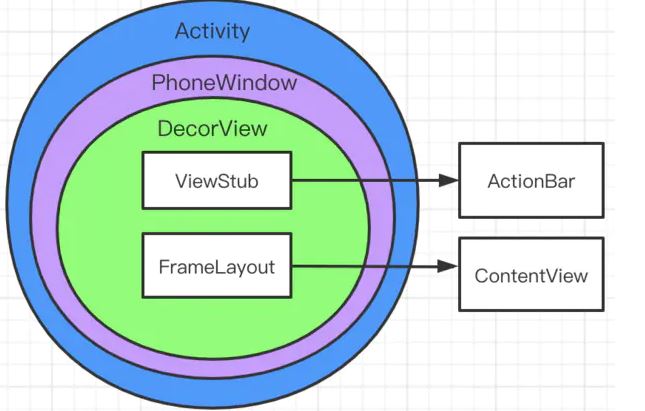
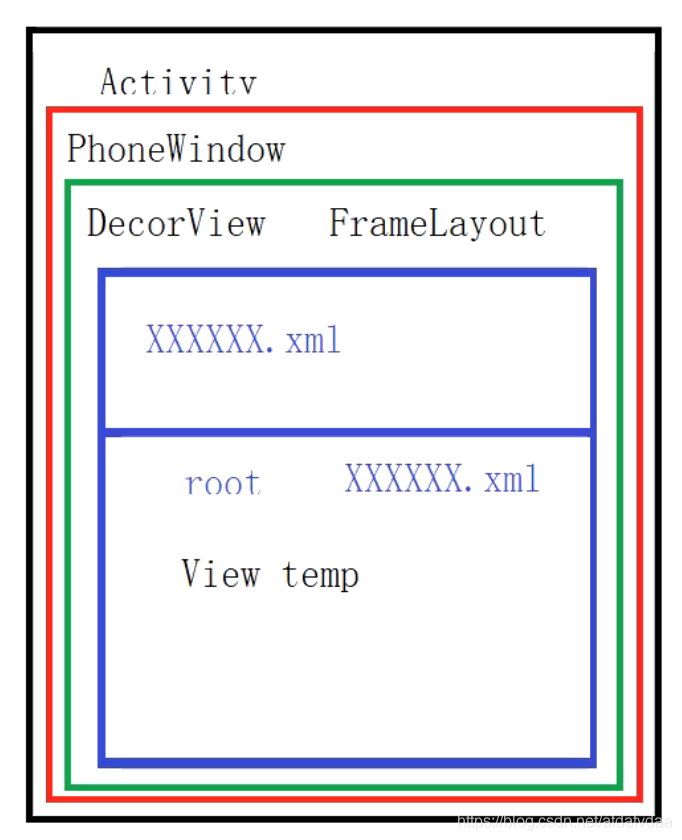
我们会发现DecorView里面包裹的内容可能会随着不同的情况而变化,但是在Decor之前的层次关系都是固定的。即Activity包裹PhoneWindow,PhoneWindow包裹DecorView。接下来我们首先看一下三者分别是如何创建的。
二.Activity是如何创建的
首先看到入口类ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity方法:
private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
ContextImpl appContext = createBaseContextForActivity(r);
Activity activity = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = appContext.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(
cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
StrictMode.incrementExpectedActivityCount(activity.getClass());
r.intent.setExtrasClassLoader(cl);
r.intent.prepareToEnterProcess();
if (r.state != null) {
r.state.setClassLoader(cl);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
...
}
有句特别关键的代码,即
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
所以activity是Instrumentation类的newActivity方法创建的,追踪过去,源码如下
public Activity newActivity(ClassLoader cl, String className,
Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException,
ClassNotFoundException {
String pkg = intent != null && intent.getComponent() != null
? intent.getComponent().getPackageName() : null;
return getFactory(pkg).instantiateActivity(cl, className, intent);
}
追踪源码,可知getFactory方法返回一个AppComponentFactory对象,然后调用AppComponentFactory的instantiateActivity方法,继续追踪
public @NonNull Activity instantiateActivity(@NonNull ClassLoader cl, @NonNull String className,
@Nullable Intent intent)
throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, ClassNotFoundException {
return (Activity) cl.loadClass(className).newInstance();
}
到这里就结束了,我们可以发现Activity是通过反射创建的。
三.PhoneWindow的创建
我们还是回到ActivityThread的performLaunchActivity方法,在刚刚展示的那一段的下面有如下部分代码
Window window = null;
if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {
window = r.mPendingRemoveWindow;
r.mPendingRemoveWindow = null;
r.mPendingRemoveWindowManager = null;
}
// Activity resources must be initialized with the same loaders as the
// application context.
appContext.getResources().addLoaders(
app.getResources().getLoaders().toArray(new ResourcesLoader[0]));
appContext.setOuterContext(activity);
activity.attach(appContext, this, getInstrumentation(), r.token,
r.ident, app, r.intent, r.activityInfo, title, r.parent,
r.embeddedID, r.lastNonConfigurationInstances, config,
r.referrer, r.voiceInteractor, window, r.configCallback,
r.assistToken);
在activity.attach这个方法中,传入了一个Window对象,追踪这个attach方法,里面有一句关键代码
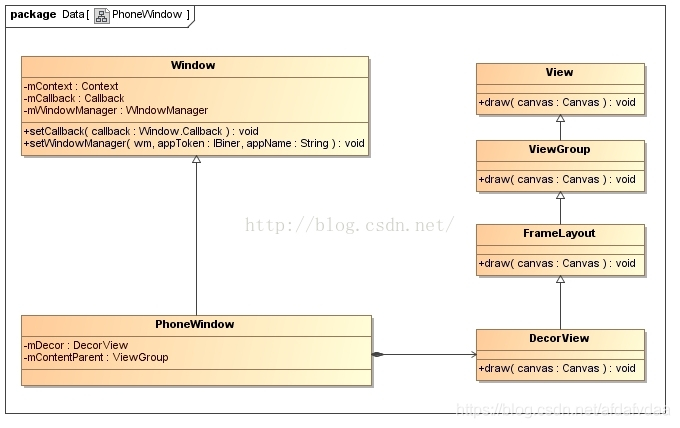
mWindow = new PhoneWindow(this, window, activityConfigCallback);
此时就创建了PhoneWindow。所以我们可以知道,在Activity创建完之后,会为当前的Activity创建一个PhoneWindow对象。
四.DecorView的创建
DecorView的创建就不是performLaunchActivity方法里面了,这次我们从Activity的setContentView的源码开始分析。下面的Activity的setContentView方法的内容。
public void setContentView(@LayoutRes int layoutResID) {
getWindow().setContentView(layoutResID);
initWindowDecorActionBar();
}
我们发现,Activity的setContentView实际是调用了PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,跟踪源码。我们会首先进入Window抽象类,然后我们找其子类PhoneWindow,在里面找到setContentView方法
public void setContentView(int layoutResID) {
if (mContentParent == null) {
installDecor();
} else if (!hasFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS)) {
mContentParent.removeAllViews();
}
...
当mContentParent为null时,会调用installDecor方法,追踪进入
private void installDecor() {
mForceDecorInstall = false;
if (mDecor == null) {
mDecor = generateDecor(-1);
mDecor.setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_AFTER_DESCENDANTS);
mDecor.setIsRootNamespace(true);
if (!mInvalidatePanelMenuPosted && mInvalidatePanelMenuFeatures != 0) {
mDecor.postOnAnimation(mInvalidatePanelMenuRunnable);
}
} else {
mDecor.setWindow(this);
}
...
它调用了generateDecor方法,追踪进入
protected DecorView generateDecor(int featureId) {
// System process doesn't have application context and in that case we need to directly use
// the context we have. Otherwise we want the application context, so we don't cling to the
// activity.
Context context;
if (mUseDecorContext) {
Context applicationContext = getContext().getApplicationContext();
if (applicationContext == null) {
context = getContext();
} else {
context = new DecorContext(applicationContext, this);
if (mTheme != -1) {
context.setTheme(mTheme);
}
}
} else {
context = getContext();
}
return new DecorView(context, featureId, this, getAttributes());
}
会发现generateDecor方法会创建一个DecorView对象,并且作为返回值返回。再追踪DecorView
public class DecorView extends FrameLayout implements RootViewSurfaceTaker, WindowCallbacks
会发现DecorView其实是一个FrameLayout 。到这就介绍完DecorView是如何创建的了
五.布局加载流程
我们回到PhoneWindow的installDecor方法,再刚刚看的部分的下面,有(2692行)
if (mContentParent == null) {mContentParent = generateLayout(mDecor);
追踪进入
protected ViewGroup generateLayout(DecorView decor) {
// Apply data from current theme.
TypedArray a = getWindowStyle();
if (false) {
System.out.println("From style:");
String s = "Attrs:";
for (int i = 0; i < R.styleable.Window.length; i++) {
s = s + " " + Integer.toHexString(R.styleable.Window[i]) + "="
+ a.getString(i);
}
System.out.println(s);
}
mIsFloating = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowIsFloating, false);
int flagsToUpdate = (FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR)
& (~getForcedWindowFlags());
if (mIsFloating) {
setLayout(WRAP_CONTENT, WRAP_CONTENT);
setFlags(0, flagsToUpdate);
} else {
setFlags(FLAG_LAYOUT_IN_SCREEN|FLAG_LAYOUT_INSET_DECOR, flagsToUpdate);
getAttributes().setFitInsetsSides(0);
getAttributes().setFitInsetsTypes(0);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowNoTitle, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
} else if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBar, false)) {
// Don't allow an action bar if there is no title.
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarOverlay, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR_OVERLAY);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActionModeOverlay, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowFullscreen, false)) {
setFlags(FLAG_FULLSCREEN, FLAG_FULLSCREEN & (~getForcedWindowFlags()));
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowTranslucentStatus,
false)) {
setFlags(FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS, FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_STATUS
& (~getForcedWindowFlags()));
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowTranslucentNavigation,
false)) {
setFlags(FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION, FLAG_TRANSLUCENT_NAVIGATION
& (~getForcedWindowFlags()));
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowShowWallpaper, false)) {
setFlags(FLAG_SHOW_WALLPAPER, FLAG_SHOW_WALLPAPER&(~getForcedWindowFlags()));
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowEnableSplitTouch,
getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
>= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB)) {
setFlags(FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH, FLAG_SPLIT_TOUCH&(~getForcedWindowFlags()));
}
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowMinWidthMajor, mMinWidthMajor);
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowMinWidthMinor, mMinWidthMinor);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Min width minor: " + mMinWidthMinor.coerceToString()
+ ", major: " + mMinWidthMajor.coerceToString());
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedWidthMajor)) {
if (mFixedWidthMajor == null) mFixedWidthMajor = new TypedValue();
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedWidthMajor,
mFixedWidthMajor);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedWidthMinor)) {
if (mFixedWidthMinor == null) mFixedWidthMinor = new TypedValue();
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedWidthMinor,
mFixedWidthMinor);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedHeightMajor)) {
if (mFixedHeightMajor == null) mFixedHeightMajor = new TypedValue();
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedHeightMajor,
mFixedHeightMajor);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedHeightMinor)) {
if (mFixedHeightMinor == null) mFixedHeightMinor = new TypedValue();
a.getValue(R.styleable.Window_windowFixedHeightMinor,
mFixedHeightMinor);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowContentTransitions, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_CONTENT_TRANSITIONS);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowActivityTransitions, false)) {
requestFeature(FEATURE_ACTIVITY_TRANSITIONS);
}
mIsTranslucent = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowIsTranslucent, false);
final Context context = getContext();
final int targetSdk = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
final boolean targetPreL = targetSdk < android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP;
final boolean targetPreQ = targetSdk < Build.VERSION_CODES.Q;
if (!mForcedStatusBarColor) {
mStatusBarColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.Window_statusBarColor, 0xFF000000);
}
if (!mForcedNavigationBarColor) {
mNavigationBarColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.Window_navigationBarColor, 0xFF000000);
mNavigationBarDividerColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.Window_navigationBarDividerColor,
0x00000000);
}
if (!targetPreQ) {
mEnsureStatusBarContrastWhenTransparent = a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.Window_enforceStatusBarContrast, false);
mEnsureNavigationBarContrastWhenTransparent = a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.Window_enforceNavigationBarContrast, true);
}
WindowManager.LayoutParams params = getAttributes();
// Non-floating windows on high end devices must put up decor beneath the system bars and
// therefore must know about visibility changes of those.
if (!mIsFloating) {
if (!targetPreL && a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.Window_windowDrawsSystemBarBackgrounds,
false)) {
setFlags(FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS,
FLAG_DRAWS_SYSTEM_BAR_BACKGROUNDS & ~getForcedWindowFlags());
}
if (mDecor.mForceWindowDrawsBarBackgrounds) {
params.privateFlags |= PRIVATE_FLAG_FORCE_DRAW_BAR_BACKGROUNDS;
}
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowLightStatusBar, false)) {
decor.setSystemUiVisibility(
decor.getSystemUiVisibility() | View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LIGHT_STATUS_BAR);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowLightNavigationBar, false)) {
decor.setSystemUiVisibility(
decor.getSystemUiVisibility() | View.SYSTEM_UI_FLAG_LIGHT_NAVIGATION_BAR);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowLayoutInDisplayCutoutMode)) {
int mode = a.getInt(R.styleable.Window_windowLayoutInDisplayCutoutMode, -1);
if (mode < LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_DEFAULT
|| mode > LAYOUT_IN_DISPLAY_CUTOUT_MODE_ALWAYS) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Unknown windowLayoutInDisplayCutoutMode: "
+ a.getString(R.styleable.Window_windowLayoutInDisplayCutoutMode));
}
params.layoutInDisplayCutoutMode = mode;
}
if (mAlwaysReadCloseOnTouchAttr || getContext().getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
>= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {
if (a.getBoolean(
R.styleable.Window_windowCloseOnTouchOutside,
false)) {
setCloseOnTouchOutsideIfNotSet(true);
}
}
if (!hasSoftInputMode()) {
params.softInputMode = a.getInt(
R.styleable.Window_windowSoftInputMode,
params.softInputMode);
}
if (a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_backgroundDimEnabled,
mIsFloating)) {
/* All dialogs should have the window dimmed */
if ((getForcedWindowFlags()&WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DIM_BEHIND) == 0) {
params.flags |= WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_DIM_BEHIND;
}
if (!haveDimAmount()) {
params.dimAmount = a.getFloat(
android.R.styleable.Window_backgroundDimAmount, 0.5f);
}
}
if (params.windowAnimations == 0) {
params.windowAnimations = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowAnimationStyle, 0);
}
// The rest are only done if this window is not embedded; otherwise,
// the values are inherited from our container.
if (getContainer() == null) {
if (mBackgroundDrawable == null) {
if (mFrameResource == 0) {
mFrameResource = a.getResourceId(R.styleable.Window_windowFrame, 0);
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowBackground)) {
mBackgroundDrawable = a.getDrawable(R.styleable.Window_windowBackground);
}
}
if (a.hasValue(R.styleable.Window_windowBackgroundFallback)) {
mBackgroundFallbackDrawable =
a.getDrawable(R.styleable.Window_windowBackgroundFallback);
}
if (mLoadElevation) {
mElevation = a.getDimension(R.styleable.Window_windowElevation, 0);
}
mClipToOutline = a.getBoolean(R.styleable.Window_windowClipToOutline, false);
mTextColor = a.getColor(R.styleable.Window_textColor, Color.TRANSPARENT);
}
// Inflate the window decor.
int layoutResource;
int features = getLocalFeatures();
// System.out.println("Features: 0x" + Integer.toHexString(features));
if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_LEFT_ICON) | (1 << FEATURE_RIGHT_ICON))) != 0) {
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleIconsDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title_icons;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
// System.out.println("Title Icons!");
} else if ((features & ((1 << FEATURE_PROGRESS) | (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS))) != 0
&& (features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) == 0) {
// Special case for a window with only a progress bar (and title).
// XXX Need to have a no-title version of embedded windows.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_progress;
// System.out.println("Progress!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_CUSTOM_TITLE)) != 0) {
// Special case for a window with a custom title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogCustomTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_custom_title;
}
// XXX Remove this once action bar supports these features.
removeFeature(FEATURE_ACTION_BAR);
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_NO_TITLE)) == 0) {
// If no other features and not embedded, only need a title.
// If the window is floating, we need a dialog layout
if (mIsFloating) {
TypedValue res = new TypedValue();
getContext().getTheme().resolveAttribute(
R.attr.dialogTitleDecorLayout, res, true);
layoutResource = res.resourceId;
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_BAR)) != 0) {
layoutResource = a.getResourceId(
R.styleable.Window_windowActionBarFullscreenDecorLayout,
R.layout.screen_action_bar);
} else {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_title;
}
// System.out.println("Title!");
} else if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_ACTION_MODE_OVERLAY)) != 0) {
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple_overlay_action_mode;
} else {
// Embedded, so no decoration is needed.
layoutResource = R.layout.screen_simple;
// System.out.println("Simple!");
}
mDecor.startChanging();
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
if (contentParent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Window couldn't find content container view");
}
if ((features & (1 << FEATURE_INDETERMINATE_PROGRESS)) != 0) {
ProgressBar progress = getCircularProgressBar(false);
if (progress != null) {
progress.setIndeterminate(true);
}
}
// Remaining setup -- of background and title -- that only applies
// to top-level windows.
if (getContainer() == null) {
mDecor.setWindowBackground(mBackgroundDrawable);
final Drawable frame;
if (mFrameResource != 0) {
frame = getContext().getDrawable(mFrameResource);
} else {
frame = null;
}
mDecor.setWindowFrame(frame);
mDecor.setElevation(mElevation);
mDecor.setClipToOutline(mClipToOutline);
if (mTitle != null) {
setTitle(mTitle);
}
if (mTitleColor == 0) {
mTitleColor = mTextColor;
}
setTitleColor(mTitleColor);
}
mDecor.finishChanging();
return contentParent;
}
分析源码和源码注释可以看出generateLayout方法的核心功能是完成DecorView的布局加载,而且根据不同的主题样式会加载不同的系统默认布局。那么比如有FrameLayout布局,它如何加载到DecorView中呢?
在generateLayout方法中,有这么一句
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
追踪进入
void onResourcesLoaded(LayoutInflater inflater, int layoutResource) {
if (mBackdropFrameRenderer != null) {
loadBackgroundDrawablesIfNeeded();
mBackdropFrameRenderer.onResourcesLoaded(
this, mResizingBackgroundDrawable, mCaptionBackgroundDrawable,
mUserCaptionBackgroundDrawable, getCurrentColor(mStatusColorViewState),
getCurrentColor(mNavigationColorViewState));
}
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
if (mDecorCaptionView.getParent() == null) {
addView(mDecorCaptionView,
new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
} else {
// Put it below the color views.
addView(root, 0, new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
mContentRoot = (ViewGroup) root;
initializeElevation();
}
关键在这里
mDecorCaptionView = createDecorCaptionView(inflater);
final View root = inflater.inflate(layoutResource, null);
if (mDecorCaptionView != null) {
...
mDecorCaptionView.addView(root,
new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
可以看到layoutResource作为参数,通过inflate方法进行解析加载。然后作为参数,传入addView方法,将布局挂载到上面。至此完成了DecorView的默认布局加载。如果是我们自己编写的布局是如何加载呢?再回到generateLayout的
mDecor.onResourcesLoaded(mLayoutInflater, layoutResource);
,在此之后,有这么一句
ViewGroup contentParent = (ViewGroup)findViewById(ID_ANDROID_CONTENT);
在DecorView执行onResourcesLoaded方法加载完默认布局后,会查找Id为ID_ANDROID_CONTENT的控件(默认布局中的FrameLayout控件)并作为generateLayout方法的返回值,我们回到setContentView方法中,可观察到以下代码:
mLayoutInflater.inflate(layoutResID, mContentParent);
所以,我们自己编写的布局是被加载到DecorView中Id为ID_ANDROID_CONTENT的控件上
六.总结
当Activity创建后会创建出一个PhoneWindow对象,当在Activity中调用setContentView时,实际上是调用了PhoneWindow的setContentView方法,此时PhoneWindow会创建根布局DecorView,并根据主题样式,为DecorView加载对应的默认系统布局,在默认的系统布局中包含了一个Id为ID_ANDROID_CONTENT的控件,而我们自己编写的布局就是加载到这个控件中的。
以上就是详解Android布局加载流程源码的详细内容,更多关于Android布局加载流程源码分析的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
