相关文章:
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(含实战)【一】
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(含实战)【二】
python处理Excel实现自动化办公教学(数据筛选、公式操作、单元格拆分合并、冻结窗口、图表绘制等)【三】
python入门之后须掌握的知识点(模块化编程、时间模块)【一】
python入门之后须掌握的知识点(excel文件处理+邮件发送+实战:批量化发工资条)【二】
1.基础温故【Pandas】
1.1 创建文件
import pandas as pddf = pd.DataFrame()
df.to_excel('001.xlsx') #可以指定路径
#df.to_excel('H:\\Anaconda\\001.xlsx')
df = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3],'name':['a','b','c']})
df.to_excel('001-data.xlsx')
df = pd.DataFrame({'id':[1,2,3],'name':['a','b','c']})
df = df.set_index('id')
df.to_excel('001-data-index.xlsx')
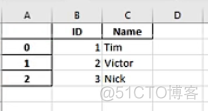
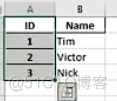
第一幅图索引默认在A列,通过set_index把ID设置为索引。
1.2 读取excel中的数据
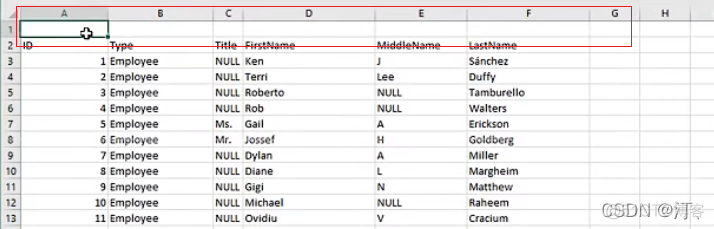
脏数据处理:第一行错误数据,或者没有数据
import pandas as pdpeople = pd.read_excel('people001.xlsx')
print(people.shape)
print(people.columns)
# 默认打印3行
print(people.head())
print(people.head(3))
# 默认打印5行
print(people.tail())
#脏数据处理:第一行错误数据,或者没有数据
#存在空行会自动识别并跳过,获取列名
people = pd.read_excel('people002.xlsx',header=1)
print(people.columns)
#脏数据处理:第一行没有列名,添加列名
people = pd.read_excel('people003.xlsx',header=None)
people.columns = ['ID', 'Type', 'Title', 'FirstName', 'MiddleName', 'LastName']
people = people.set_index('ID',inplace=True)
people.to_excel('output.xlsx')
其中在colums中是把列名和索引区别的,
people = people.set_index('ID',inplace=True)#设置完index后,
print(people.columns)
#显示
'Type', 'Title', 'FirstName', 'MiddleName', 'LastName'
再次读取时:id还是会当作列
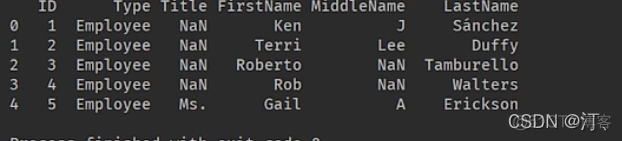
这时候在读取的时候需要设置index,即可。
import pandas as pdpeople = pd.read_excel('people001.xlsx',index_col="ID")
1.3 生成列、行、单元格(Series)
Series和python中的字典类似,下面是几种创建方法:
import pandas as pdd = {
'x':100,
'y':200,
'z':300,
}
print(d.values())
print(d.keys())
s1 = pd.Series(d)
print(s1.index)
L1 = [100,200,300]
L2 = ['x','y','z']
s2 = pd.Series(L1,index=L2)
print(s2.index)
s3 = pd.Series([100,200,300],index=['x','y','z'])
print(s3.index)
创建一个简单的列表:行列不同形式添加。
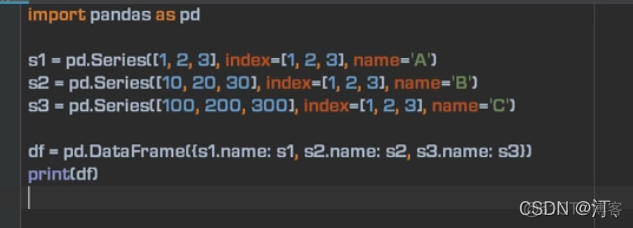
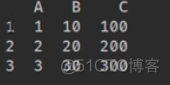
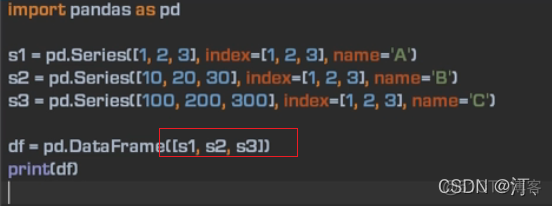
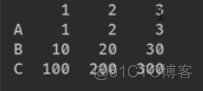
index是默认对齐的方式,如果不相同会用NaN填充。
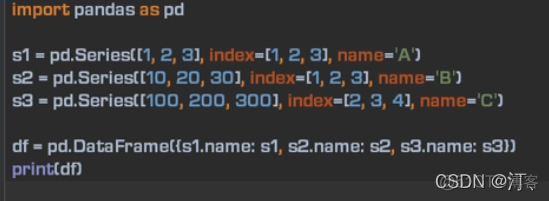
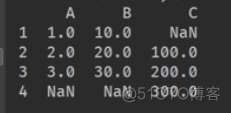
1.4 自动填充功能【数据区域读取填充数字】
1.4.1 数值填充
原始数据:只有name(书名)进行填充数据
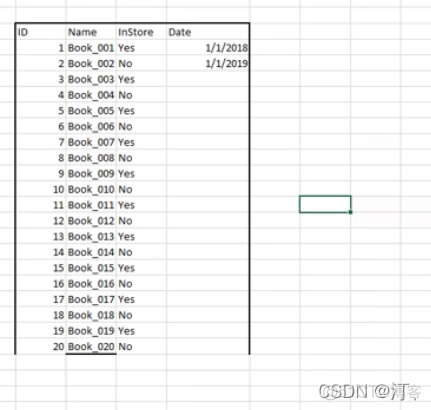
数据区域不是定格,无法自动识别
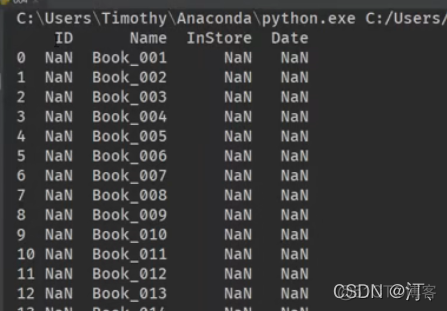
import pandas as pdbooks = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None)
#usecols='C,D,E,F',填充完再设置index_col
print(books)
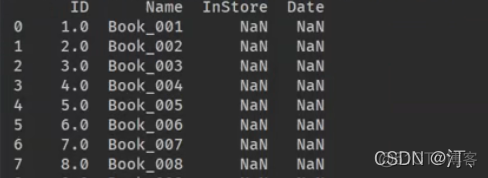
#NaN填充的dtype是float64
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
print(books)
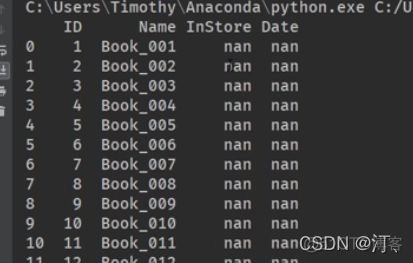
为了显示为整型,先把类型设置为str
import pandas as pdbooks = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
print(books)
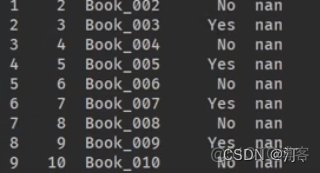
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
print(books)
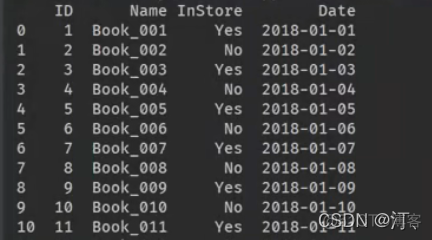
from datetime import date, timedelta
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
start=date(2018,1,1)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books["Date"].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
print(books)
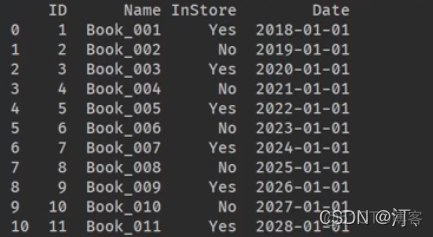
月份相加需要计算一下,定义个子函数
import pandas as pdfrom datetime import date, timedelta
def add_month[d, md):
yd=md/12
m=d.month+md%12
if m!= 12:
yd+=m/12
m=m%12
return date(d.year + yd,m, d.day)
books = pd.read_excel('books.xlsx',skiprows=4,usecols='C:F',index_col=None,dtype={"ID":str,"InStore":str,"Date":str})
start=date(2018,1,1)
for i in books.index:
books["ID"].at[i]=i+1
books["InStroe"].at[i]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books["Date"].at[i]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
#books["Date"].at[i]=add_month(start,i)
#print(books)
books.set_index("ID",inplace=True)
books.to_excel("output/xlsx")
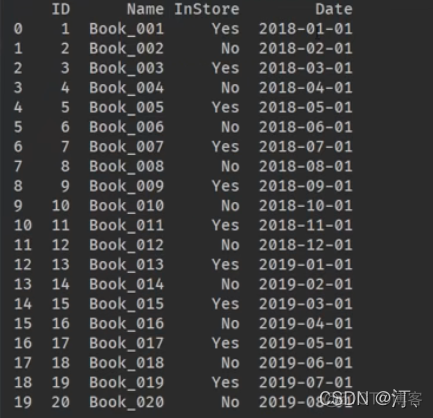
还有一种写法不改series直接改单元格写法如下:
for i in books.index:booksat[i,"ID"]]=i+1
books.at[i,"InStroe"]="yes" if i%2==0 else "no"
books.at[i,"Date"]=start+timedelta(days=i) #没有年月 month year; 时分秒有
#books["Date"].at[i]=date(start.year+i,start.month,start.day)
#books["Date"].at[i]=add_month(start,i)
#print(books)
1.4.2 计算填充(列操作)
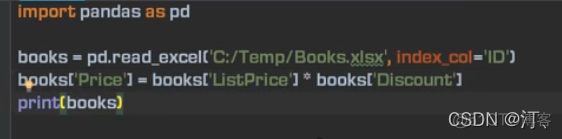
列相乘,操作符重载【不用循环计算更方便】
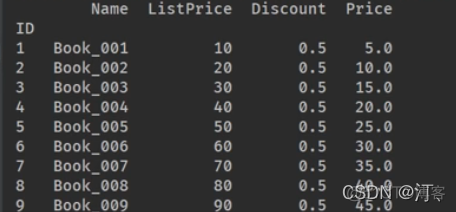
循环:【不从头到尾计算,部分区域计算采用单元格计算】
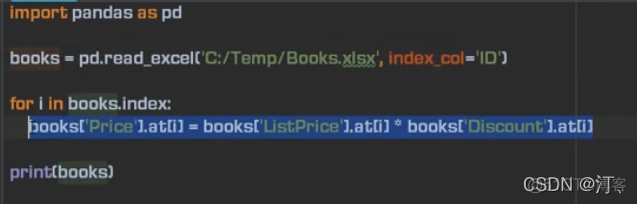
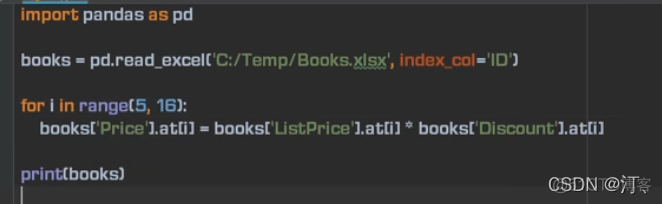
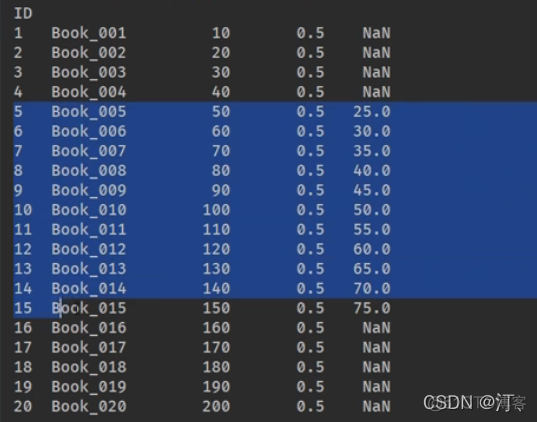
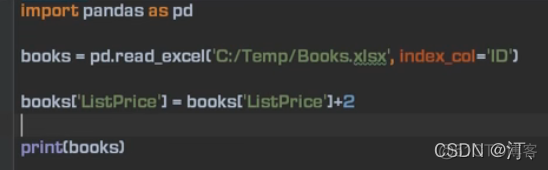
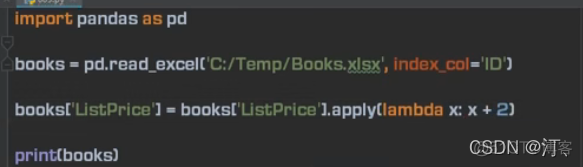
价格加2 使用apply
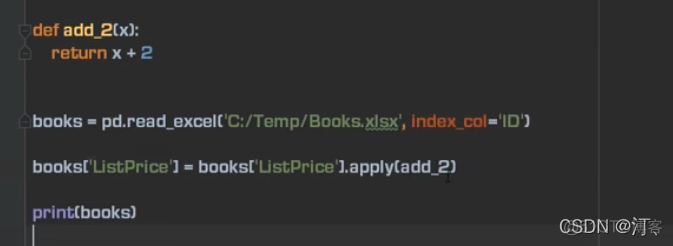
lambda:
1.5 排序,多重排序
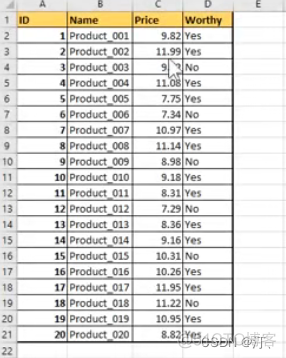
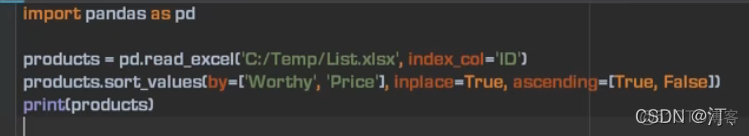
ascending默认从小到大排序:【true 从大到小 false从小到大】
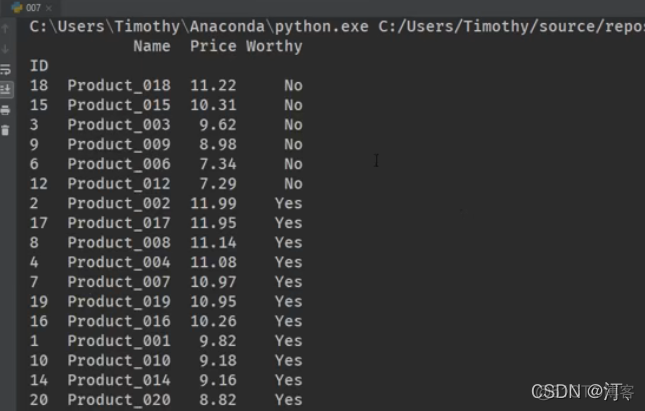
1.6 数据筛选、过滤
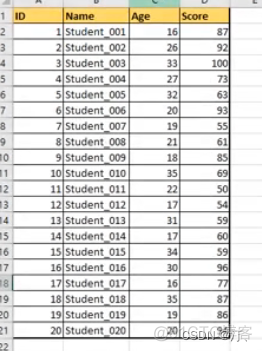
找出年龄【18,30】分数【60,90】之间的
import pandas as pddef validate_age(a):
return 18 <= a <= 30 #pandas特有写法
def level_b(s):
return 60 <= s < 90
students = pd.read_excel('Students.xlsx', index_col='ID')#id作为index
students = students.loc[students['Age'].apply(validate_age)].loc[students.Score.apply(level_b)] # 两
种语法
students = students.loc[students.Age.apply(validate_age)].loc[students.Score.apply(level_b)] # 两
种语法
print(students)
loc与iloc功能介绍:数据切片。通过索引来提取数据集中相应的行数据or列数据(可以是多行or多列)总结不同:
1. loc函数通过调用index名称的具体值来取数据
2. iloc函数通过行序号来取数据
3.取多行数据时iloc不包含末尾
4.对数据进行筛选使用loc函数,当使用loc函数时, 如果index不具有特定意义,而且重复,那么提取的数据需要进一步处理,可用.reset index()函数重置index相同: .
5.【】中无逗号时,默认取行
筛选出来的结果:
Name Age ScoreID
4 Student_004 27 73
8 Student_008 21 61
9 Student_009 18 85
19 Student_019 19 86
换一种写法:lambda
import pandas as pd# def validate_age(a):
# return 18 <= a <= 30
# def level_b(s):
# return 60 <= s < 90
students = pd.read_excel('Students.xlsx', index_col='ID')
students = students.loc[students['Age'].apply(
lambda a:18 <= a <= 30)] .loc[students.Score.apply(lambda s:60 <= s < 90)] # 两种语法
print(students)
2.数据可视化
2.1 柱状图
Field
Number
Agriculture
12,318
Business and Management
200,312
Education
19,483
Engineering
216,932
Fine and Applied Arts
59,736
Health Professions
33,947
Humanities
17,664
Mathematics and Computer Sciences
141,651
Other/Unspecified Subject Areas
185,107
Physical and Life Sciences
75,385
Social Sciences
81,304
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students1.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='Number', inplace=True, ascending=False)
students.index = range(0, len(students))
print(students)
plt.bar(students['Field'], students['Number'], color='orange', width=0.7)#
plt.xticks(students['Field'], rotation='90') #rotation旋转
plt.title('International Student by Field', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Field')
plt.ylabel('Number')
plt.tight_layout() #j紧凑型,避免下标显示不全
plt.show()
pandas中inplace参数在很多函数中都会有,它的作用是:是否在原对象基础上进行修改
inplace = True:不创建新的对象,直接对原始对象进行修改;
inplace = False:对数据进行修改,创建并返回新的对象承载其修改结果。
默认是False,即创建新的对象进行修改,原对象不变, 和深复制和浅复制有些类似。
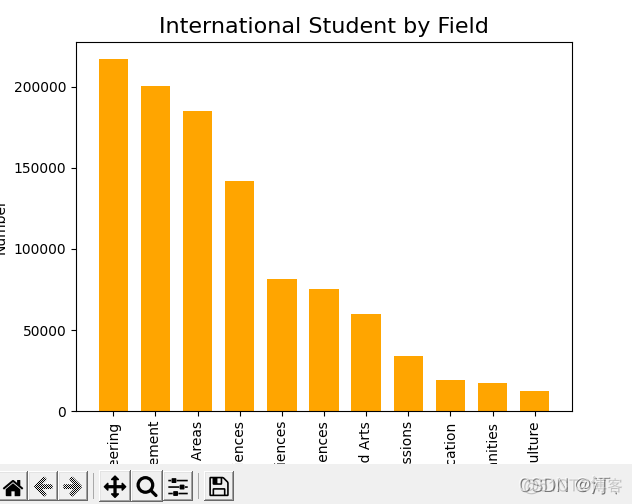
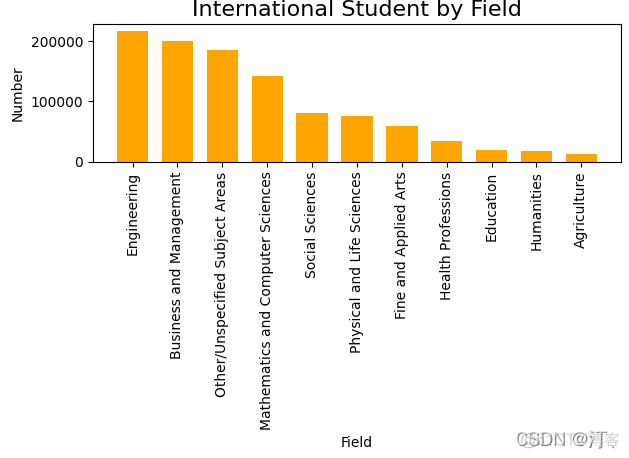
或者直接用pandas自带的:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('C:/Temp/Students.xlsx')
students.sort_values('Number', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(students)
students.plot.bar(x='Field', y='Number', color='blue', title='International Students by Field')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
2.2 分组柱图深度优化(比较图)
Field
2016
2017
Agriculture
12,318
12,602
Business and Management
200,312
200,754
Communications and Journalism
21,160
21,913
Education
19,483
17,993
Engineering
216,932
230,711
Fine and Applied Arts
59,736
61,506
Humanities
17,664
17,561
Intensive English
40,877
30,309
Legal Studies and Law Enforcement
15,077
15,306
Math and Computer Science
141,651
167,180
Physical and Life Sciences
75,385
76,838
Social Sciences
81,304
83,046
Other Fields of Study
81,318
87,577
Undeclared
26,675
21,131
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students2.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='2017', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(students)
students.plot.bar('Field', ['2016', '2017'], color=['orange', 'Red'])
plt.title('International Students by Field', fontsize=16,fontweight="bold")
plt.xlabel('Field', fontweight='bold')
plt.ylabel('Number', fontweight='bold')
plt.tight_layout()
ax = plt.gca() #坐标轴移动修改
ax.set_xticklabels(students['Field'], rotation=40, ha='right') #默认中心旋转
plt.gcf().subplots_adjust(left=0.2, bottom=0.42) #画布大小调整
plt.show()
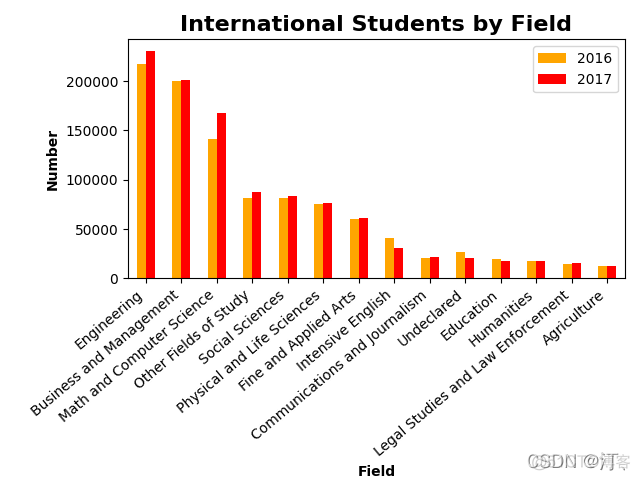
推荐第一个
import numpy as npimport pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students2.xlsx')
students.sort_values(by='2017', inplace=True, ascending=False)
students.index = range(0, len(students))
print(students)
bar_width = 0.7
x_pos = np.arange(len(students) * 2, step=2)
plt.bar(x_pos, students['2016'], color='green', width=bar_width)
plt.bar(x_pos + bar_width, students['2017'], color='blue', width=bar_width)
plt.legend()
plt.xticks(x_pos + bar_width / 2, students['Field'], rotation='90')
plt.title('International Student by Field', fontsize=16)
plt.xlabel('Field')
plt.ylabel('Number')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
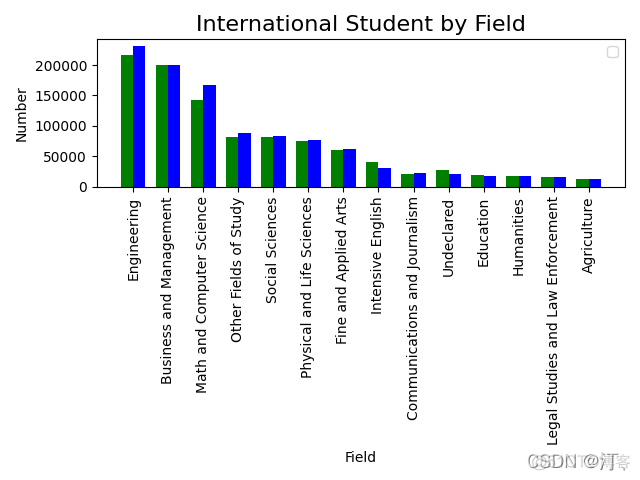
2.3 叠加柱状图
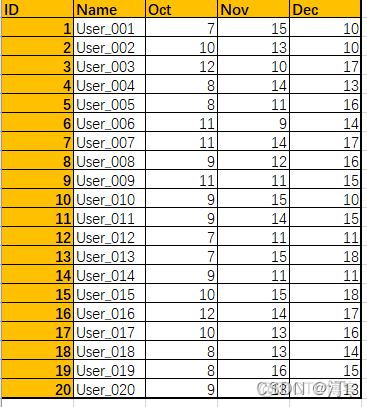
用户总量从大到小排序:
import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
users = pd.read_excel('Users.xlsx')
users['Total'] = users['Oct'] + users['Nov'] + users['Dec']
users.sort_values(by='Total', inplace=True, ascending=False)
print(users)
users.plot.bar(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)
# users.plot.barh(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)#水平柱状图堆积
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
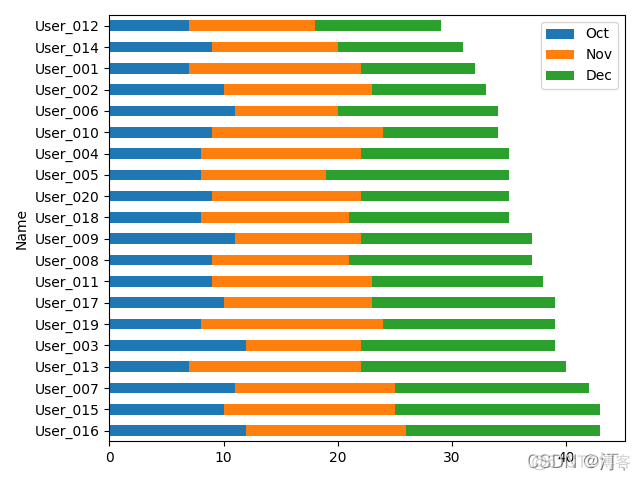
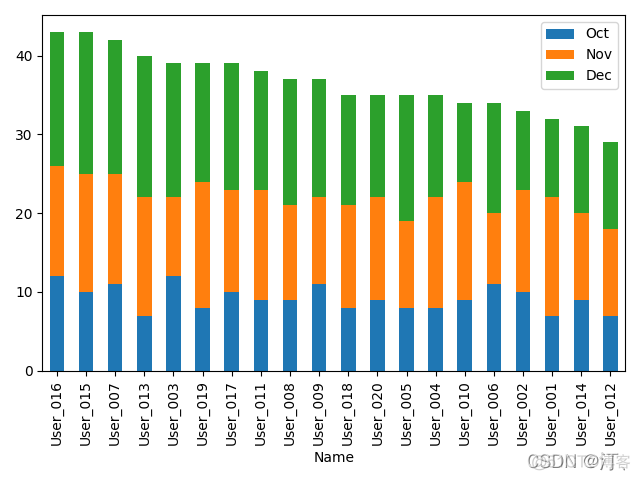
users.plot.barh(x='Name', y=['Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec'], stacked=True)#水平柱状图堆积
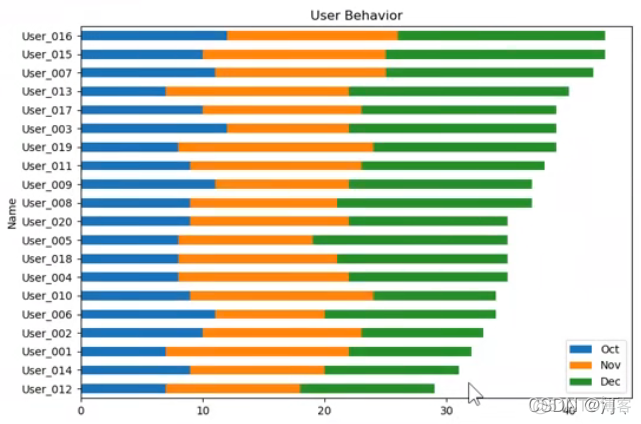
2.4 饼图
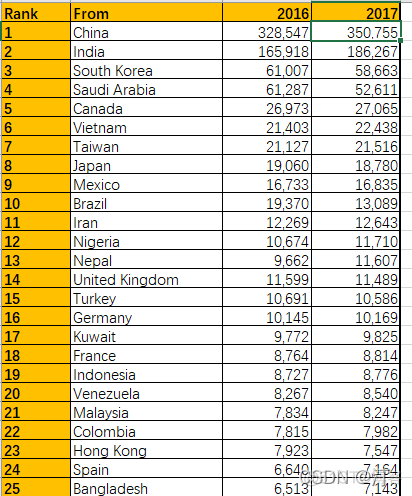
其中2016 2017是字符串,避免pandas误认为数字。
import pandas as pdimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
students = pd.read_excel('Students3.xlsx', index_col='From')
print(students)
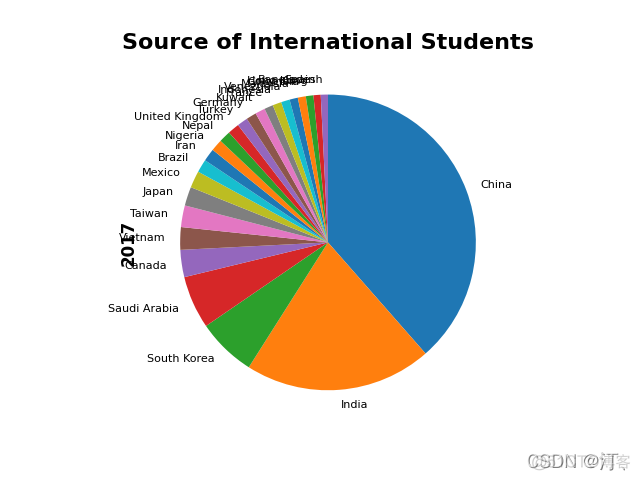
# counterclock顺逆时针,startangle开始点确认
students['2017'].plot.pie(fontsize=8, counterclock=False, startangle=-270)
plt.title('Source of International Students', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.ylabel('2017', fontsize=12, fontweight='bold')
plt.show()
2.5 折现趋势图,叠加区域图

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
weeks = pd.read_excel('Orders.xlsx', index_col='Week')
print(weeks)
weeks.plot(y=['Accessories', 'Bikes', 'Clothing', 'Components'])
weeks.plot.area(y=['Accessories', 'Bikes', 'Clothing', 'Components'])
plt.title('Sales Trends', fontsize=16, fontweight='bold')
plt.xticks(weeks.index, fontsize=8)
plt.show()
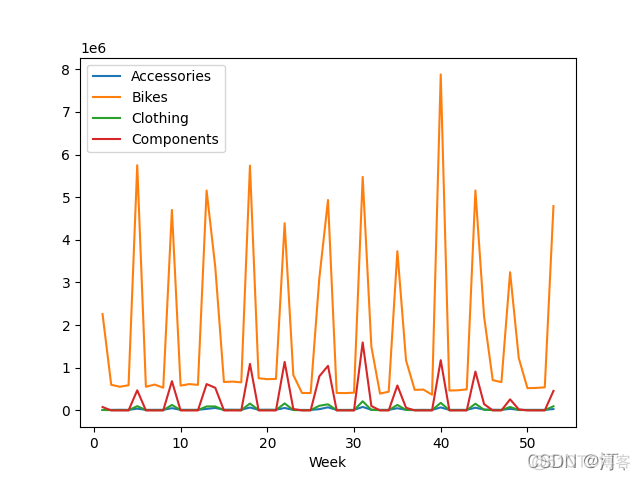
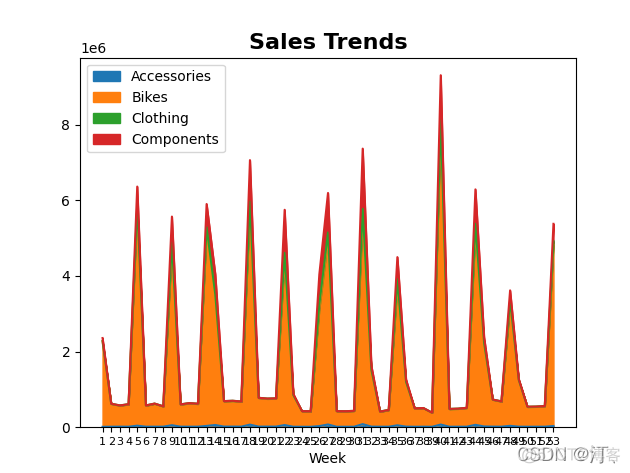
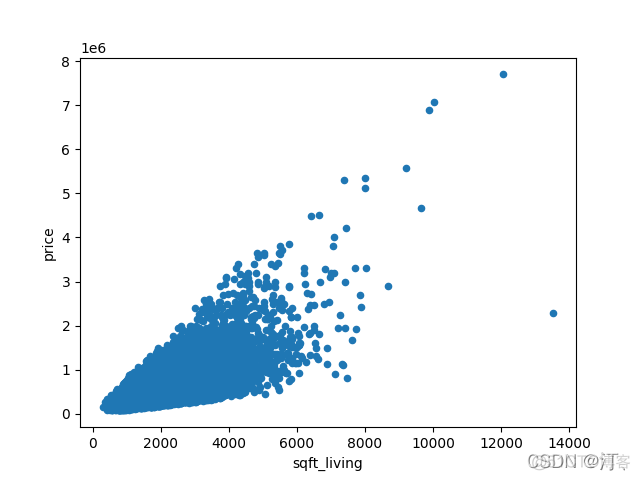
2.6 散点图直方图密度图
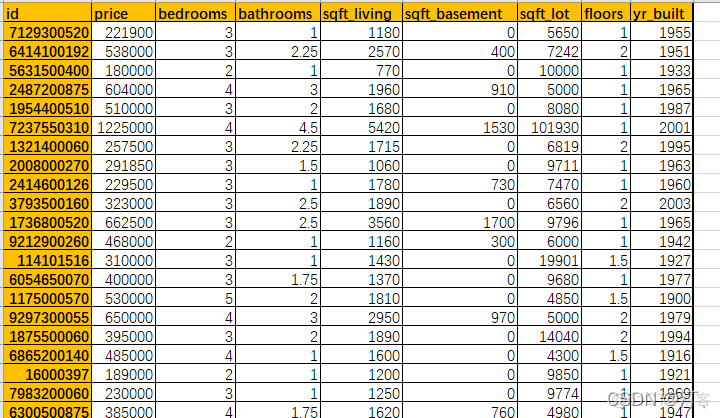
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
pd.options.display.max_columns = 999#所有列都会显示
homes = pd.read_excel('home_data.xlsx')
# print(homes.head())
print(homes.corr())#相关性
homes.plot.scatter(x='sqft_living', y='price')
plt.figure()
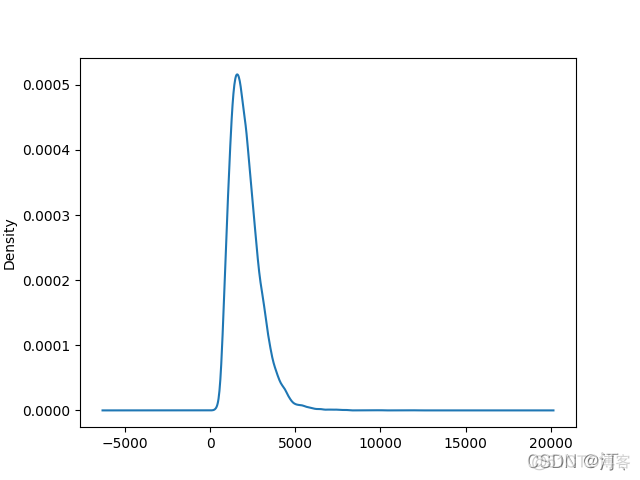
homes.sqft_living.plot.kde() #密度图
plt.figure()
homes.sqft_living.plot.hist(bins=100) #区间设置
plt.xticks(range(0, max(homes.sqft_living), 500), fontsize=8, rotation=90) #面积
# homes.price.plot.hist(bins=200)
# plt.xticks(range(0, max(homes.price), 100000), fontsize=8, rotation=90) #房价
plt.show()
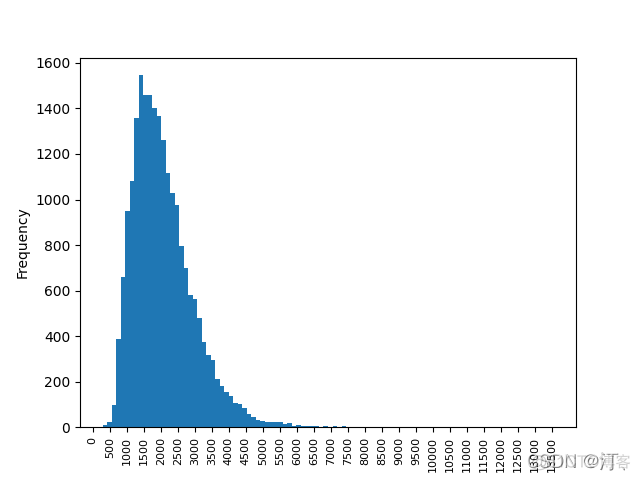
密度图:
相关性:corr()
id price bedrooms bathrooms sqft_living \id 1.000000 -0.016762 0.001286 0.005160 -0.012258
price -0.016762 1.000000 0.308350 0.525138 0.702035
bedrooms 0.001286 0.308350 1.000000 0.515884 0.576671
bathrooms 0.005160 0.525138 0.515884 1.000000 0.754665
sqft_living -0.012258 0.702035 0.576671 0.754665 1.000000
sqft_basement -0.005151 0.323816 0.303093 0.283770 0.435043
sqft_lot -0.132109 0.089661 0.031703 0.087740 0.172826
floors 0.018525 0.256794 0.175429 0.500653 0.353949
yr_built 0.021380 0.054012 0.154178 0.506019 0.318049
sqft_basement sqft_lot floors yr_built
id -0.005151 -0.132109 0.018525 0.021380
price 0.323816 0.089661 0.256794 0.054012
bedrooms 0.303093 0.031703 0.175429 0.154178
bathrooms 0.283770 0.087740 0.500653 0.506019
sqft_living 0.435043 0.172826 0.353949 0.318049
sqft_basement 1.000000 0.015286 -0.245705 -0.133124
sqft_lot 0.015286 1.000000 -0.005201 0.053080
floors -0.245705 -0.005201 1.000000 0.489319
yr_built -0.133124 0.053080 0.489319 1.000000
