1 简介 移动机器人的路径规划是移动机器人研究领域中的一个热点问题。 2 部分代码 % % PotentialFieldScript.m % %% Generate some points nrows = 400; ncols = 600; obstacle = false(nrows, ncols); [x, y] = meshg
1 简介
移动机器人的路径规划是移动机器人研究领域中的一个热点问题。


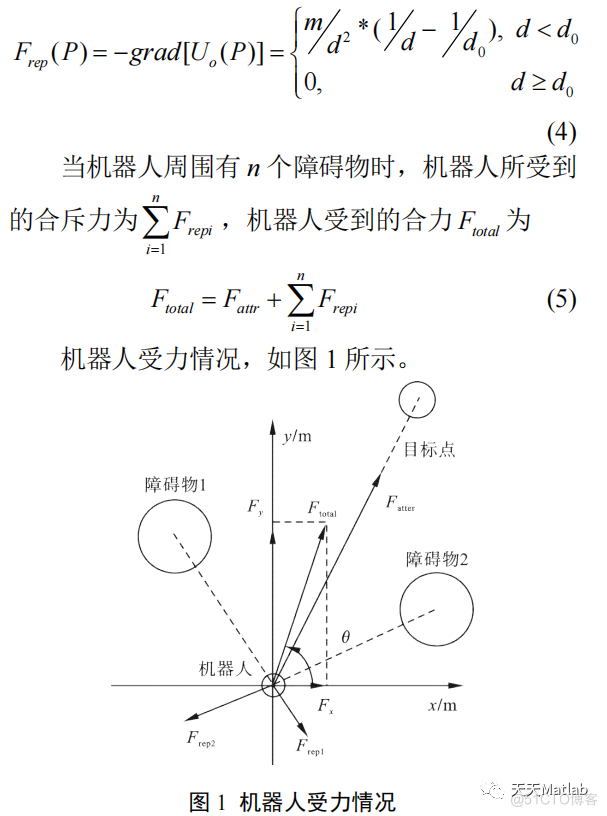


2 部分代码
%% PotentialFieldScript.m
%
%% Generate some points
nrows = 400;
ncols = 600;
obstacle = false(nrows, ncols);
[x, y] = meshgrid (1:ncols, 1:nrows);
%% Generate some obstacle
obstacle (300:end, 100:250) = true;
obstacle (150:200, 400:500) = true;
t = ((x - 200).^2 + (y - 50).^2) < 50^2;
obstacle(t) = true;
t = ((x - 400).^2 + (y - 300).^2) < 100^2;
obstacle(t) = true;
%% Compute distance transform
d = bwdist(obstacle);
% Rescale and transform distances
d2 = (d/100) + 1;
d0 = 2;
nu = 800;
repulsive = nu*((1./d2 - 1/d0).^2);
repulsive (d2 > d0) = 0;
%% Display repulsive potential
figure;
m = mesh (repulsive);
m.FaceLighting = 'phong';
axis equal;
title ('Repulsive Potential');
%% Compute attractive force
goal = [400, 50];
xi = 1/700;
attractive = xi * ( (x - goal(1)).^2 + (y - goal(2)).^2 );
figure;
m = mesh (attractive);
m.FaceLighting = 'phong';
axis equal;
title ('Attractive Potential');
%% Display 2D configuration space
figure;
imshow(~obstacle);
hold on;
plot (goal(1), goal(2), 'r.', 'MarkerSize', 25);
hold off;
axis ([0 ncols 0 nrows]);
axis xy;
axis on;
xlabel ('x');
ylabel ('y');
title ('Configuration Space');
%% Combine terms
f = attractive + repulsive;
figure;
m = mesh (f);
m.FaceLighting = 'phong';
axis equal;
title ('Total Potential');
%% Plan route
start = [50, 350];
route = GradientBasedPlanner (f, start, goal, 1000);
%% Plot the energy surface
figure;
m = mesh (f);
axis equal;
%% Plot ball sliding down hill
[sx, sy, sz] = sphere(20);
scale = 20;
sx = scale*sx;
sy = scale*sy;
sz = scale*(sz+1);
hold on;
p = mesh(sx, sy, sz);
p.FaceColor = 'red';
p.EdgeColor = 'none';
p.FaceLighting = 'phong';
hold off;
for i = 1:size(route,1)
P = round(route(i,:));
z = f(P(2), P(1));
p.XData = sx + P(1);
p.YData = sy + P(2);
p.ZData = sz + f(P(2), P(1));
drawnow;
drawnow;
end
%% quiver plot
[gx, gy] = gradient (-f);
skip = 20;
figure;
xidx = 1:skip:ncols;
yidx = 1:skip:nrows;
quiver (x(yidx,xidx), y(yidx,xidx), gx(yidx,xidx), gy(yidx,xidx), 0.4);
axis ([1 ncols 1 nrows]);
hold on;
ps = plot(start(1), start(2), 'r.', 'MarkerSize', 30);
pg = plot(goal(1), goal(2), 'g.', 'MarkerSize', 30);
p3 = plot (route(:,1), route(:,2), 'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
3 仿真结果
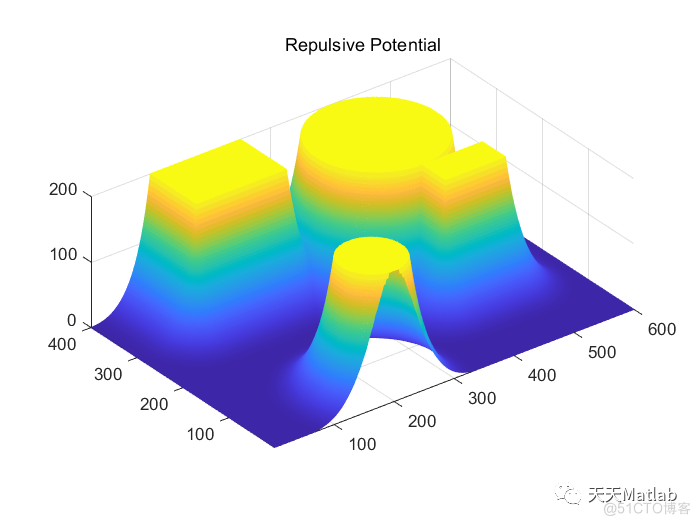
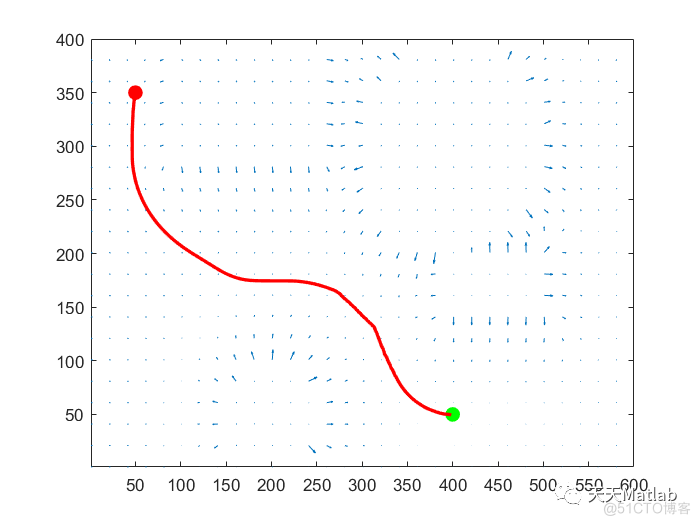
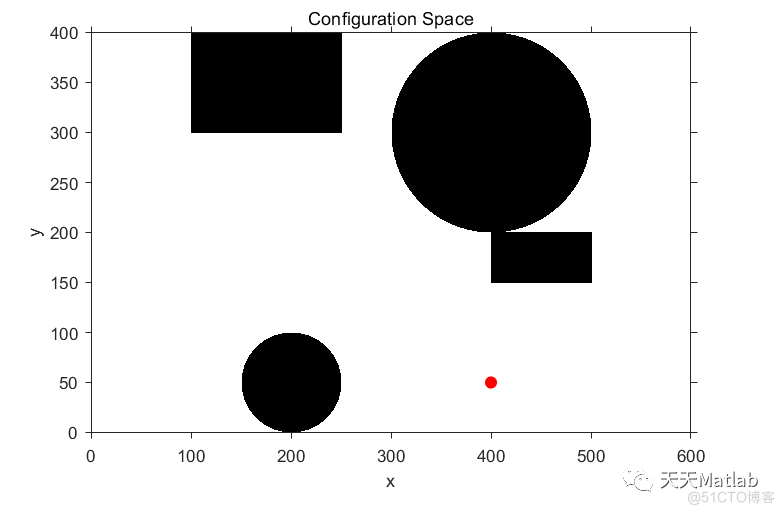
4 参考文献
[1]李欣, 朱大奇. 基于人工势场法的自治水下机器人路径规划[J]. 上海海事大学学报, 2010, 31(2):5.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。

