字符串
字符串常用方法
方法
使用说明
string[start: end :step]
字符串的切片
string.split
字符串分割
string.strip
删除首尾空白
string.rstrip
删除字符串右边空白
string.lstrip
删除字符串左边空白
string.index
返回子串首次出现的位置
string.replace
字符串替换
sep.join
将可迭代对象按sep分割符拼接为字符串
string.count
对字符串 的子串计数
string.find
返回子串首次出现位置
string.startwith
字符串是否以什么开头
string.endwith
字符串是否以什么结尾
使用字典对象
word_dict={}for word in sentence.split():
if word not in word_dict:
word_dict[word]=1
else:
word_dict[word]+=1
for word in sentence.split():
word_dict.setdefault(word,0)
word_dict[word]+=1
word_dict=defaultdict(int)
for word in sentence.split():
word_dict[word]+=1
print word_dict
defaultdict作用:defaultdict的作用是在于,当字典里的key不存在但被查找时,返回的不是keyError而是一个默认值
例如:作用是当key不存在时,返回的是工厂函数的默认值,比如list对应[ ],str对应的是空字符串,set对应set( ),int对应0
遍历字典
for key,value in word_dict.items():pirnt key,value
统计字典
from collections import Counter
使用字典的字典
from collections import defaultdictuser_movie_rating=defaultdict(lambda:defaultdict(int))
user_movie_rating[1][1]=4
user_movie_rating[1][2]=5
使用元组
元组是一种顺序容器对象,不可变,不允许插入操作
使用集合
Jaccard系数: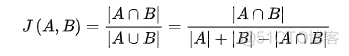
str_2=(dogs,hate,cats)
st_1_wrds=set(str_1.split())
st_2_wrds=set(str_2.split())
n1=len(st_1_wrds)
n2=len(st_2_wrds)
#找出集合共有词,并统计次数
cmn=st_1_wrds.intersection(st_2_wrds)
nocmn=len(st_1_wrds.intersection(st_2_wrds))
#找出集合不重复的词,并统计次数
unq=st_1_wrds.union(st_2_wrds)
nounq=len(st_1_wrds.union(st_2_wrds))
#计算相似度
similarity=nocmn/(1.0*nounq)
写一个列表
a.append(),a.pop()
from random import shuffle#shuffle 对生成的随机打乱顺序
a=range(1,20)
shuffle(a)
a.sort()
a.reverse()
从另一个列表创建–列表推导
a=[1,2,-1,-2,3,4,-3,-4]b=[pow(x,2) for x in a if x<0]
print b
使用迭代器
生成一个迭代器和生成器
使用可迭代对象
迭代器对象是从集合中第一个元素开始访问,知道所有元素被访问结束,迭代器只前不会后退,
基本方法:iter()和next()
it=iter(list) #创建迭代器对象
print(next(it)) #输出迭代器的下一个元素
out:1
print(next(it))
out:2
把一个类作为迭代器使用需要在类中实现两个方法_iter_()与_next_().
iter() 方法返回一个特殊的迭代器对象, 这个迭代器对象实现了 next() 方法并通过 StopIteration 异常标识迭代的完成
生成器:使用yield语句而不是return语句返回结果,yield语句一次返回一个结果,在每个结果中间,挂起函数状态,以便下次重它离开的地方继续执行
生成器表达式:类似于列表推导,但是,生成器返回按产生结果的一个对象,而不是一次构建一个结果列表
装饰器
装饰器:它是一种函数的函数,因为装饰器传入的参数就是一个函数,通过实现各种功能来对这个函数的功能进行增强。特点:简洁
代码实现有无装饰器区别:
无装饰器:
def fun_one():
start = time()
sleep(1)
end = time()
cost_time = end - start
print("func one run time {}".format(cost_time))
def fun_two():
start = time()
sleep(1)
end = time()
cost_time = end - start
print("func two run time {}".format(cost_time))
def fun_three():
start = time()
sleep(1)
end = time()
cost_time = end - start
print("func three run time {}".format(cost_time))
使用装饰器:
def run_time(func):def wrapper():
start = time()
func() # 函数在这里运行
end = time()
cost_time = end - start
print("func three run time {}".format(cost_time))
return wrapper
def fun_one():
sleep(1)
def fun_two():
sleep(1)
def fun_three():
sleep(1)
带参数的装饰器
def logger(msg=None):def run_time(func):
def wrapper(*args, **kwargs):
start = time()
func() # 函数在这里运行
end = time()
cost_time = end - start
print("[{}] func three run time {}".format(msg, cost_time))
return wrapper
return run_time
(msg="One")
def fun_one():
sleep(1)
(msg="Two")
def fun_two():
sleep(1)
(msg="Three")
def fun_three():
sleep(1)
fun_one()
fun_two()
fun_three()
lambad,map,filter,zip,izip
数据分析(探索)
用图表分析单变量数据
data为单维x,target为y
方法:散点图,百分位,消除异常值
from matplotlib.pylab import frange
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
fill_data=lambda x:int(x.strip() or 0)
data=np.genfromtxt("president.txt",dtype=(int),converters={1:fill_data}delimier=[,])
x=data[:,0]
y=data[:,1]
plt.figure(1)
plt.title("")
plt.plot(x,y)
#百分位
perc_25=np.percentile(y,25)
#消除异常值
y_masked=np.ma.masked_where(y==0,y)
科普 pandas ix,iloc,loc区别
data=pd.Series(np.nan,index=[49,48,47,46,45,1,2,3,4,5])data.iloc[:3]
49 nan
48 nan
47 nan
data.loc[:3]
data.ix[:3]
iloc[:3]读取前3行
loc[:3]读取索引为3之前的行
ix[:3]会先寻找索引为3的,如果没有再寻找位置为3行的
