MOEAD原理及Python实现,MOEAD,切比雪夫方法实现,python语言 确定某点附近的点 答:每个解对应的是一组权重,即子问题,红点附近的四个点,也就是它的邻居怎么确定呢?由权重来确定
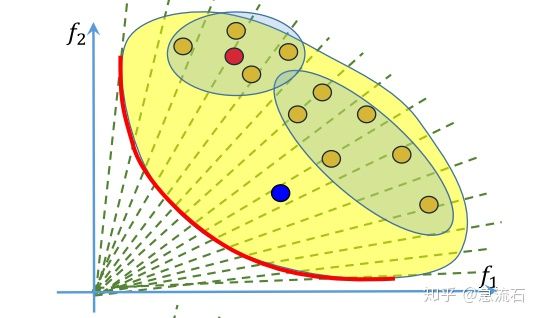
答:每个解对应的是一组权重,即子问题,红点附近的四个点,也就是它的邻居怎么确定呢?由权重来确定,算法初始化阶段就确定了每个权重对应的邻居,也就是每个子问题的邻居子问题。权重的邻居通过欧式距离来判断。取最近的几个。
取均匀分布向量https://www.cnblogs.com/Twobox/p/16408751.html
https://www.zhihu.com/question/263555181?sort=created
其中两个回答都挺好的
1. 输入N m # N表示取点密度 m表示问题维度 1.1 输入 T # 表示取最近的T个作为邻居 2. 生成均匀分布权重向量 2.1 计算每个权重向量之间的欧拉距离 3. 权重向量个数即为:初始种群个数 4. 初始化种群,每个个体一一对应权重 4.1 更具权重之间距离,取前T个作为邻居person 5. EP = 空 # 维护成最优前沿 6. 计算最初的全局最优Z # 把每个带入f1 f2中,取最小值 z1 z2 7. 开始循环N代 7.1对于每个个体,在领域中选取2个个体进行交叉变异,获得2个新个体 7.1.1更新全局解z 7.2在领域中随机选择2个个体,用新个与旧个体进行对比 # 新个体带入子目标问题,直接对比值即可 7.3如果更优,则替换旧个体dna 7.4更新EP # 如果有别接收的新解,将新解与EP每一个进行比较,删除被新解支配的,如果新解没有被旧解支配,那么加入EP
代码实现设计
# 分析 需要维护的数据结构: 某个体最近的T位邻居: 可以考虑采用对象列表即可 均匀分布的权重向量:一个二维ndarray数组即可 权重向量与个体对应关系:个体对象,直接保存权重向量数组 权重向量之间的距离矩阵:开局初始化,不变的 EP list,里面的个体是对象的引用 z list 目标函数集合,F list domain list # 接口设计 class Person attribute: dns:一维ndarray weight_vector: 一维ndarray neighbor: list<Person> o_func:Objective_Function 目标函数 function: mutation cross_get_two_new_dna:返回2段新dna compare#与子代比较 accept_new_dna choice_two_person:p1,p2 class Moead_Util attribute: N M T: o_func:Objective_Function pm:变异概率 EP:[dna1,dna2,..] weight_vectors:二维数组 Euler_distance:二维数组 pip_size Z:[] # 这里面元素为一维ndarray数组,即dna,即解 function: init_mean_vector:二维数组 init_Euler_distance:二维数组 init_population:[] init_Z:一维属猪 update_ep update_Z class Objective_Function: attribute: F:[] domain:[[0,1],[],[]] function: get_one_function:Objective_Function
Person.py
1 import numpy as np 2 3 4 class Person: 5 def __init__(self, dna): 6 self.dna = dna 7 self.weight_vector = None 8 self.neighbor = None 9 self.o_func = None # 目标函数 10 11 self.dns_len = len(dna) 12 13 def set_info(self, weight_vector, neighbor, o_func): 14 self.weight_vector = weight_vector 15 self.neighbor = neighbor 16 self.o_func = o_func# 目标函数 17 18 def mutation_dna(self, one_dna): 19 i = np.random.randint(0, self.dns_len) 20 low = self.o_func.domain[i][0] 21 high = self.o_func.domain[i][1] 22 new_v = np.random.rand() * (high - low) + low 23 one_dna[i] = new_v 24 return one_dna 25 26 def mutation(self): 27 i = np.random.randint(0, self.dns_len) 28 low = self.o_func.domain[i][0] 29 high = self.o_func.domain[i][1] 30 new_v = np.random.rand() * (high - low) + low 31 self.dna[i] = new_v 32 33 @staticmethod 34 def cross_get_two_new_dna(p1, p2): 35 # 单点交叉 36 cut_i = np.random.randint(1, p1.dns_len - 1) 37 dna1 = p1.dna.copy() 38 dna2 = p2.dna.copy() 39 temp = dna1[cut_i:].copy() 40 dna1[cut_i:] = dna2[cut_i:] 41 dna2[cut_i:] = temp 42 return dna1, dna2 43 44 def compare(self, son_dna): 45 F = self.o_func.f_funcs 46 f_x_son_dna = [] 47 f_x_self = [] 48 for f in F: 49 f_x_son_dna.append(f(son_dna)) 50 f_x_self.append(f(self.dna)) 51 fit_son_dna = np.array(f_x_son_dna) * self.weight_vector 52 fit_self = np.array(f_x_self) * self.weight_vector 53 return fit_son_dna.sum() - fit_self.sum() 54 55 def accept_new_dna(self, new_dna): 56 self.dna = new_dna 57 58 def choice_two_person(self): 59 neighbor = self.neighbor 60 neighbor_len = len(neighbor) 61 idx = np.random.randint(0, neighbor_len, size=2) 62 p1 = self.neighbor[idx[0]] 63 p2 = self.neighbor[idx[1]] 64 return p1, p2
1 from collections import defaultdict 2 3 import numpy as np 4 5 6 def zdt4_f1(x_list): 7 return x_list[0] 8 9 10 def zdt4_gx(x_list): 11 sum = 1 + 10 * (10 - 1) 12 for i in range(1, 10): 13 sum += x_list[i] ** 2 - 10 * np.cos(4 * np.pi * x_list[i]) 14 return sum 15 16 17 def zdt4_f2(x_list): 18 gx_ans = zdt4_gx(x_list) 19 if x_list[0] < 0: 20 print("????: x_list[0] < 0:", x_list[0]) 21 if gx_ans < 0: 22 print("gx_ans < 0", gx_ans) 23 if (x_list[0] / gx_ans) <= 0: 24 print("x_list[0] / gx_ans<0:", x_list[0] / gx_ans) 25 26 ans = 1 - np.sqrt(x_list[0] / gx_ans) 27 return ans 28 29 def zdt3_f1(x): 30 return x[0] 31 32 33 def zdt3_gx(x): 34 if x[:].sum() < 0: 35 print(x[1:].sum(), x[1:]) 36 ans = 1 + 9 / 29 * x[1:].sum() 37 return ans 38 39 40 def zdt3_f2(x): 41 g = zdt3_gx(x) 42 ans = 1 - np.sqrt(x[0] / g) - (x[0] / g) * np.sin(10 * np.pi * x[0]) 43 return ans 44 45 46 class Objective_Function: 47 function_dic = defaultdict(lambda: None) 48 49 def __init__(self, f_funcs, domain): 50 self.f_funcs = f_funcs 51 self.domain = domain 52 53 @staticmethod 54 def get_one_function(name): 55 if Objective_Function.function_dic[name] is not None: 56 return Objective_Function.function_dic[name] 57 58 if name == "zdt4": 59 f_funcs = [zdt4_f1, zdt4_f2] 60 domain = [[0, 1]] 61 for i in range(9): 62 domain.append([-5, 5]) 63 Objective_Function.function_dic[name] = Objective_Function(f_funcs, domain) 64 return Objective_Function.function_dic[name] 65 66 if name == "zdt3": 67 f_funcs = [zdt3_f1, zdt3_f2] 68 domain = [[0, 1] for i in range(30)] 69 Objective_Function.function_dic[name] = Objective_Function(f_funcs, domain) 70 return Objective_Function.function_dic[name]Moead_Util.py
1 import numpy as np 2 3 from GA.MOEAD.Person import Person 4 5 6 def distribution_number(sum, m): 7 # 取m个数,数的和为N 8 if m == 1: 9 return [[sum]] 10 vectors = [] 11 for i in range(1, sum - (m - 1) + 1): 12 right_vec = distribution_number(sum - i, m - 1) 13 a = [i] 14 for item in right_vec: 15 vectors.append(a + item) 16 return vectors 17 18 19 class Moead_Util: 20 def __init__(self, N, m, T, o_func, pm): 21 self.N = N 22 self.m = m 23 self.T = T # 邻居大小限制 24 self.o_func = o_func 25 self.pm = pm # 变异概率 26 27 self.Z = np.zeros(shape=m) 28 29 self.EP = [] # 前沿 30 self.EP_fx = [] # ep对应的目标值 31 self.weight_vectors = None # 均匀权重向量 32 self.Euler_distance = None # 欧拉距离矩阵 33 self.pip_size = -1 34 35 self.pop = None 36 # self.pop_dna = None 37 38 def init_mean_vector(self): 39 vectors = distribution_number(self.N + self.m, self.m) 40 vectors = (np.array(vectors) - 1) / self.N 41 self.weight_vectors = vectors 42 self.pip_size = len(vectors) 43 return vectors 44 45 def init_Euler_distance(self): 46 vectors = self.weight_vectors 47 v_len = len(vectors) 48 49 Euler_distance = np.zeros((v_len, v_len)) 50 for i in range(v_len): 51 for j in range(v_len): 52 distance = ((vectors[i] - vectors[j]) ** 2).sum() 53 Euler_distance[i][j] = distance 54 55 self.Euler_distance = Euler_distance 56 return Euler_distance 57 58 def init_population(self): 59 pop_size = self.pip_size 60 dna_len = len(self.o_func.domain) 61 pop = [] 62 pop_dna = np.random.random(size=(pop_size, dna_len)) 63 # 初始个体的 dna 64 for i in range(pop_size): 65 pop.append(Person(pop_dna[i])) 66 67 # 初始个体的 weight_vector, neighbor, o_func 68 for i in range(pop_size): 69 # weight_vector, neighbor, o_func 70 person = pop[i] 71 distance = self.Euler_distance[i] 72 sort_arg = np.argsort(distance) 73 weight_vector = self.weight_vectors[i] 74 # neighbor = pop[sort_arg][:self.T] 75 neighbor = [] 76 for i in range(self.T): 77 neighbor.append(pop[sort_arg[i]]) 78 79 o_func = self.o_func 80 person.set_info(weight_vector, neighbor, o_func) 81 self.pop = pop 82 # self.pop_dna = pop_dna 83 84 return pop 85 86 def init_Z(self): 87 Z = np.full(shape=self.m, fill_value=float("inf")) 88 for person in self.pop: 89 for i in range(len(self.o_func.f_funcs)): 90 f = self.o_func.f_funcs[i] 91 # f_x_i:某个体,在第i目标上的值 92 f_x_i = f(person.dna) 93 if f_x_i < Z[i]: 94 Z[i] = f_x_i 95 96 self.Z = Z 97 98 def get_fx(self, dna): 99 fx = [] 100 for f in self.o_func.f_funcs: 101 fx.append(f(dna)) 102 return fx 103 104 def update_ep(self, new_dna): 105 # 将新解与EP每一个进行比较,删除被新解支配的 106 # 如果新解没有被旧解支配,则保留 107 new_dna_fx = self.get_fx(new_dna) 108 accept_new = True # 是否将新解加入EP 109 # print(f"准备开始循环: EP长度{len(self.EP)}") 110 for i in range(len(self.EP) - 1, -1, -1): # 从后往前遍历 111 old_ep_item = self.EP[i] 112 old_fx = self.EP_fx[i] 113 # old_fx = self.get_fx(old_ep_item) 114 a_b = True # 老支配行 115 b_a = True # 新支配老 116 for j in range(len(self.o_func.f_funcs)): 117 if old_fx[j] < new_dna_fx[j]: 118 b_a = False 119 if old_fx[j] > new_dna_fx[j]: 120 a_b = False 121 # T T : fx相等 直接不改变EP 122 # T F :老支配新 留老,一定不要新,结束循环. 123 # F T :新支配老 留新,一定不要这个老,继续循环 124 # F F : 非支配关系 不操作,循环下一个 125 # TF为什么结束循环,FT为什么继续循环,你们可以琢磨下 126 if a_b: 127 accept_new = False 128 break 129 if not a_b and b_a: 130 if len(self.EP) <= i: 131 print(len(self.EP), i) 132 del self.EP[i] 133 del self.EP_fx[i] 134 continue 135 136 if accept_new: 137 self.EP.append(new_dna) 138 self.EP_fx.append(new_dna_fx) 139 return self.EP, self.EP_fx 140 141 def update_Z(self, new_dna): 142 new_dna_fx = self.get_fx(new_dna) 143 Z = self.Z 144 for i in range(len(self.o_func.f_funcs)): 145 if new_dna_fx[i] < Z[i]: 146 Z[i] = new_dna_fx[i] 147 return Z
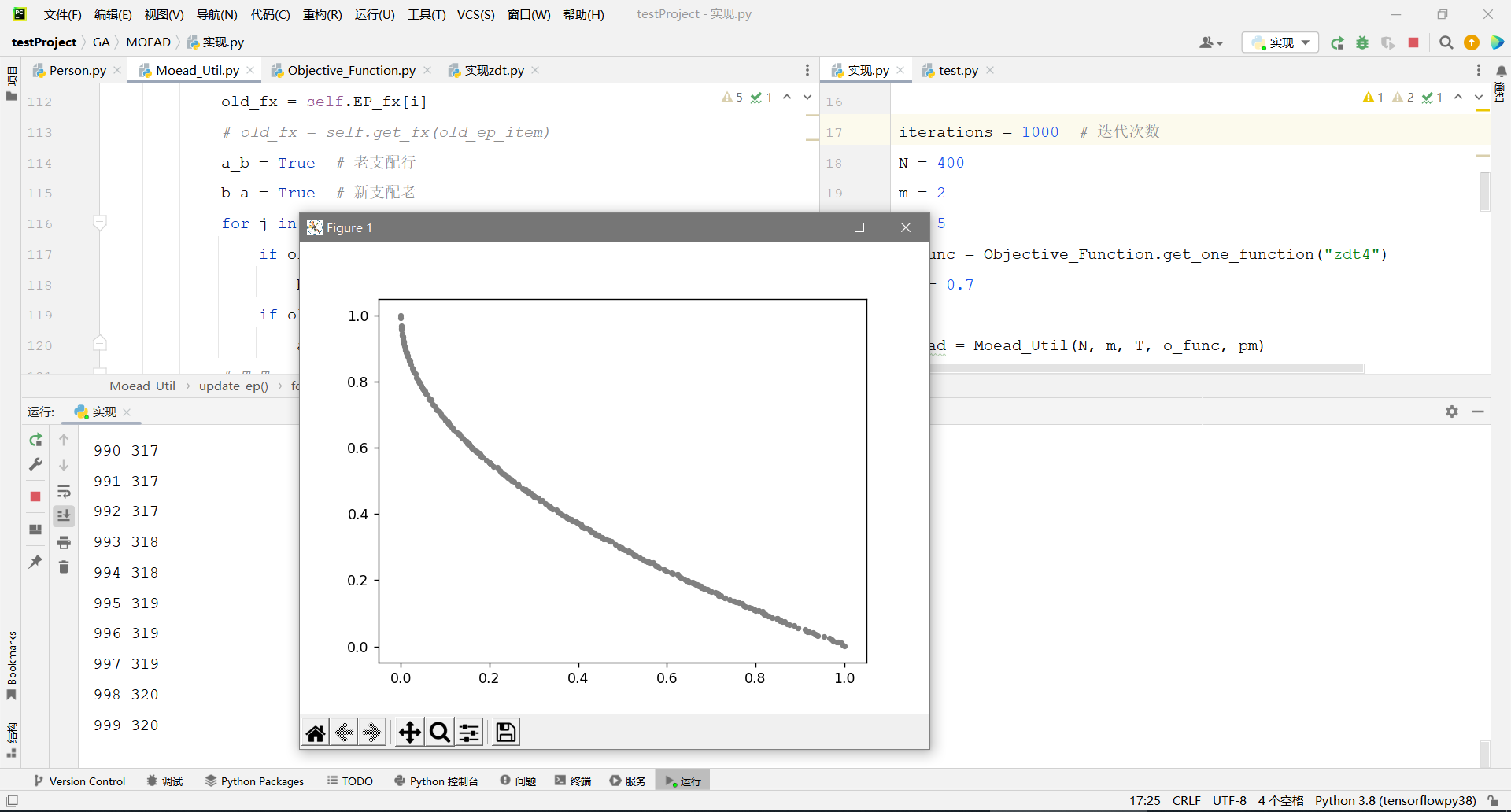
import random import numpy as np from GA.MOEAD.Moead_Util import Moead_Util from GA.MOEAD.Objective_Function import Objective_Function from GA.MOEAD.Person import Person import matplotlib.pyplot as plt def draw(x, y): plt.scatter(x, y, s=10, c="grey") # s 点的大小 c 点的颜色 alpha 透明度 plt.show() iterations = 1000 # 迭代次数 N = 400 m = 2 T = 5 o_func = Objective_Function.get_one_function("zdt4") pm = 0.7 moead = Moead_Util(N, m, T, o_func, pm) moead.init_mean_vector() moead.init_Euler_distance() pop = moead.init_population() moead.init_Z() for i in range(iterations): print(i, len(moead.EP)) for person in pop: p1, p2 = person.choice_two_person() d1, d2 = Person.cross_get_two_new_dna(p1, p2) if np.random.rand() < pm: p1.mutation_dna(d1) if np.random.rand() < pm: p1.mutation_dna(d2) moead.update_Z(d1) moead.update_Z(d2) t1, t2 = person.choice_two_person() if t1.compare(d1) < 0: t1.accept_new_dna(d1) moead.update_ep(d1) if t2.compare(d1) < 0: t2.accept_new_dna(d2) moead.update_ep(d1) # 输出结果画图 EP_fx = np.array(moead.EP_fx) x = EP_fx[:, 0] y = EP_fx[:, 1] draw(x, y)
本文原创