与spring和springboot相关的重要逻辑,如果想了解源头在哪,找refresh准没错 启动类,run @SpringBootApplication public class KafkaBootApplication { public static void main ( String [] args ) { SpringApplication . run
与spring和springboot相关的重要逻辑,如果想了解源头在哪,找refresh准没错
启动类,run
public class KafkaBootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KafkaBootApplication.class, args);
}
}

一路run
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}

return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}

直到refreshContext(context)
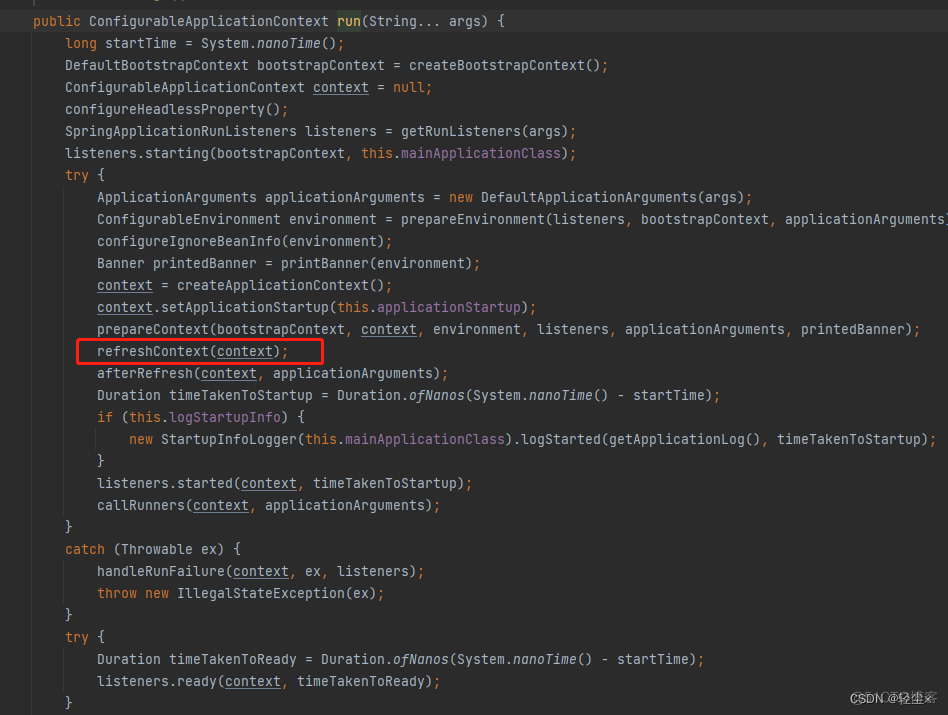

private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}

applicationContext.refresh();
}

public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw ex;
}
}

其实调用还是super.refresh(),也就是AbstractApplicationContext的refresh,再调用onRefresh()
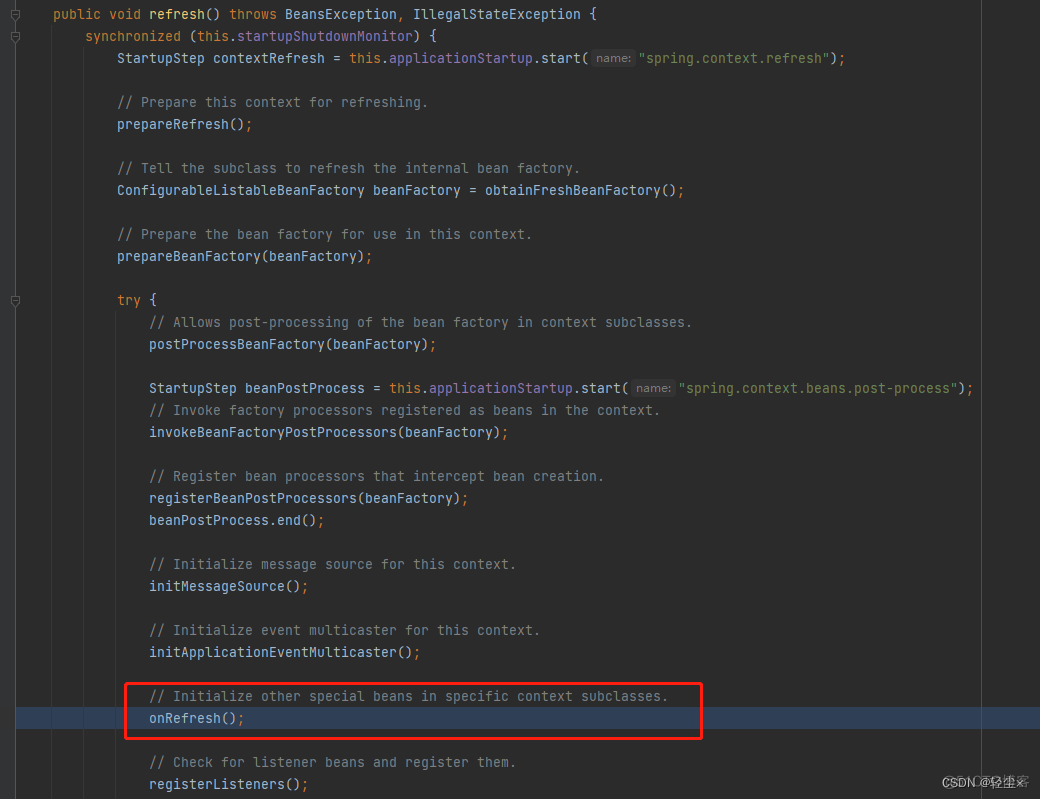

然后又回调回了ServletWebServerApplicationContext#onRefresh()
这里涉及到一个设计模式,模板方法设计模式,父类的onRefresh()是个空方法,留给子类实现。
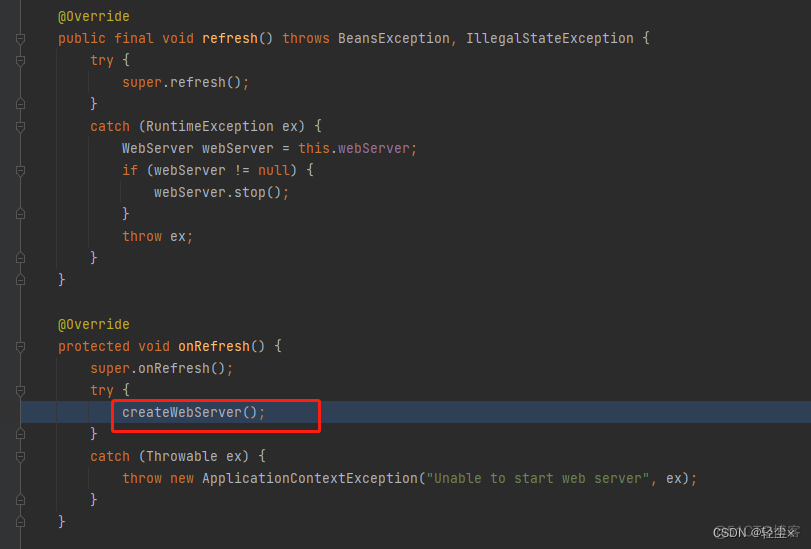

内置的tomcat就是在createWebServer()方法中
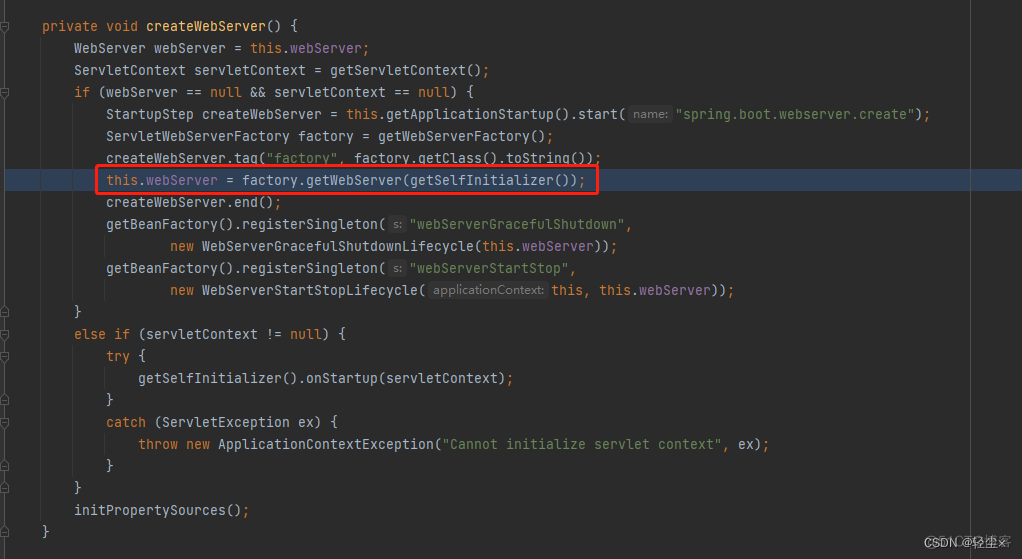

直接显示的new了一个Tomcat()
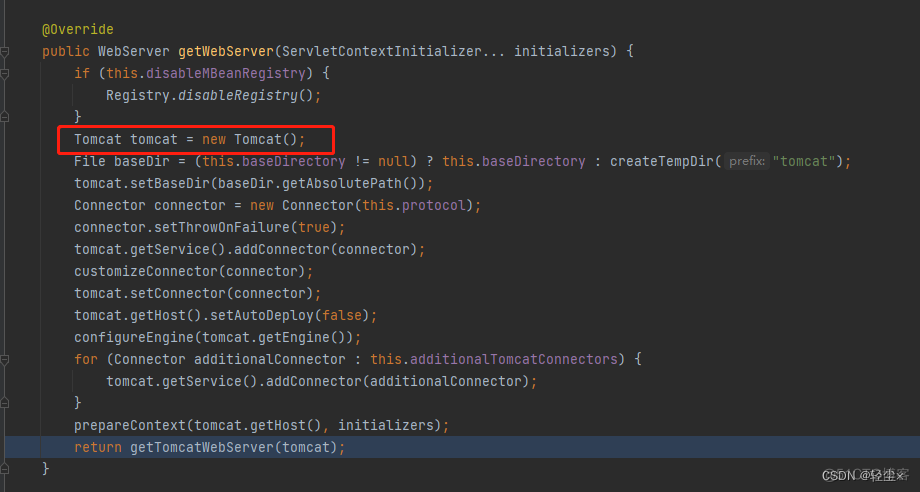

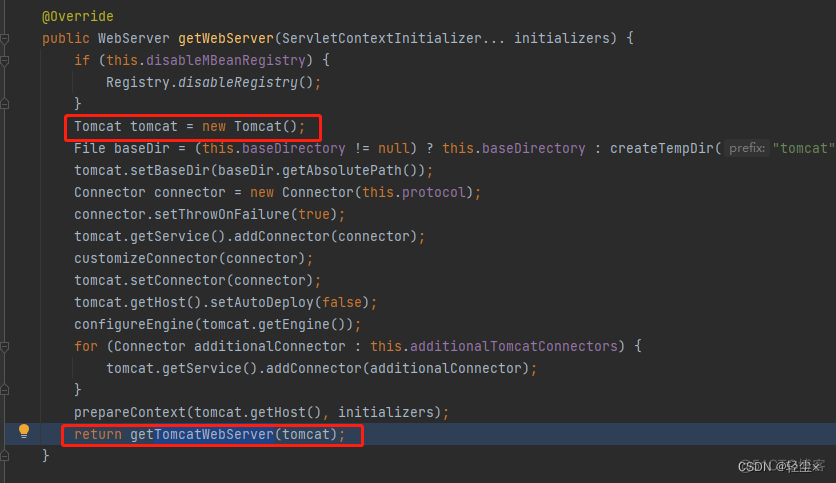
创建的只是一个Tomcat对象,需要返回的是 TomcatWebServer,也就是启动了的Tomcat
所以还需要启动Tomcat
 编辑
编辑
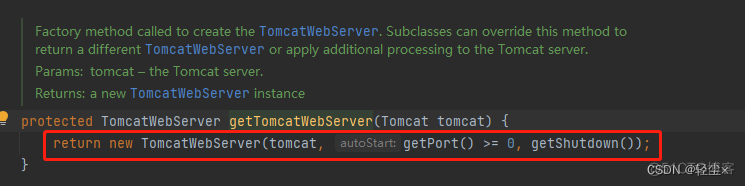
把Tomcat当作参数传过来,实例化一个TomcatWebServer对象
 编辑
编辑
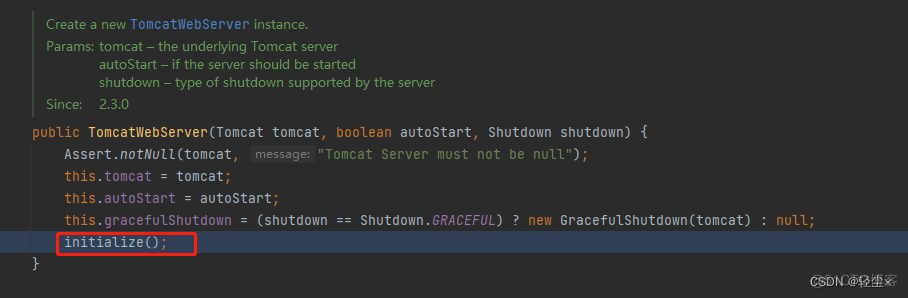
实例化过程中有个步骤叫初始化initialize()
 编辑
编辑
就是在这个初始化方法中完成了Tomcat的启动
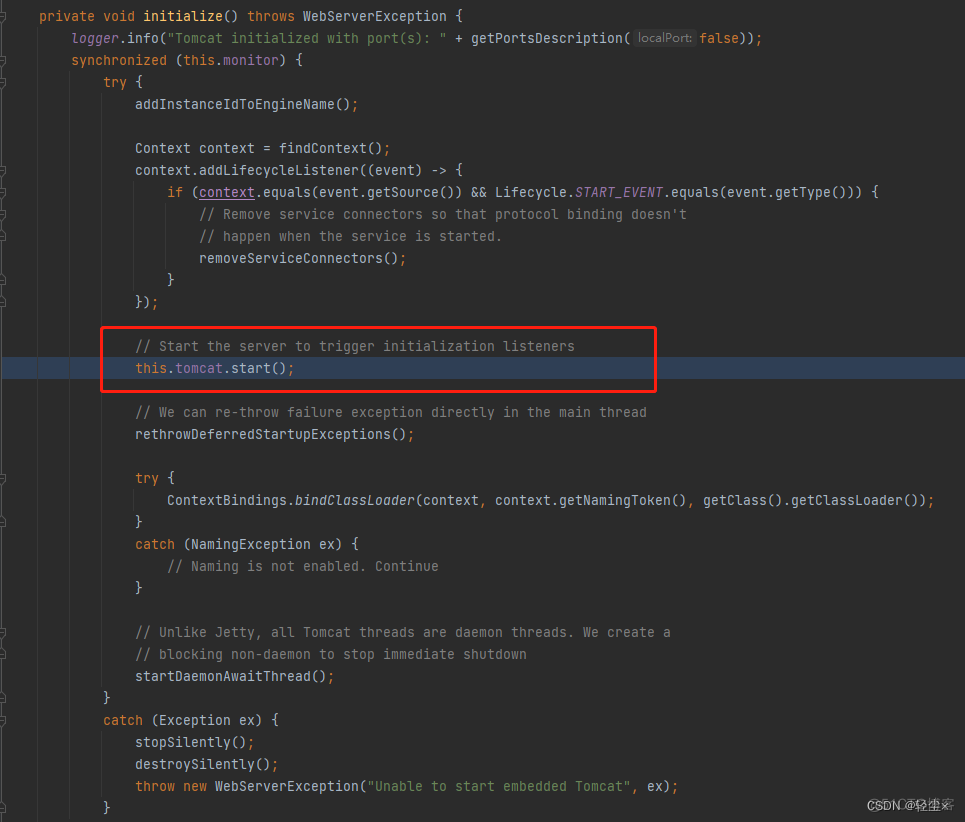

至此,springboot内置的tomcat就创建并启动完成了
