前文我们有了IOC的源码基础以及SpringMVC的基础,我们便可以进一步深入理解SpringMVC主要实现原理,包含DispatcherServlet的初始化过程和DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程的源码解析。本文是第二篇:DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程的源码解析。@pdai
- Spring框架系列(14) - SpringMVC实现原理之DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程
- DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程?
- 回顾整理处理流程
- doGet入口
- 请求分发
- 映射和适配器处理
- 视图渲染
- 更多文章
- DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程?
回顾整理处理流程一个请求发出,经过DispatcherServlet进行了什么样的处理,最后将内容返回的呢?
首先让我们整体看一下Spring Web MVC 处理请求的流程:

核心架构的具体流程步骤如下:
- 首先用户发送请求——>DispatcherServlet,前端控制器收到请求后自己不进行处理,而是委托给其他的解析器进行
处理,作为统一访问点,进行全局的流程控制; - DispatcherServlet——>HandlerMapping, HandlerMapping 将会把请求映射为 HandlerExecutionChain 对象(包含一
个Handler 处理器(页面控制器)对象、多个HandlerInterceptor 拦截器)对象,通过这种策略模式,很容易添加新
的映射策略; - DispatcherServlet——>HandlerAdapter,HandlerAdapter 将会把处理器包装为适配器,从而支持多种类型的处理器,
即适配器设计模式的应用,从而很容易支持很多类型的处理器; - HandlerAdapter——>处理器功能处理方法的调用,HandlerAdapter 将会根据适配的结果调用真正的处理器的功能处
理方法,完成功能处理;并返回一个ModelAndView 对象(包含模型数据、逻辑视图名); - ModelAndView 的逻辑视图名——> ViewResolver,ViewResolver 将把逻辑视图名解析为具体的View,通过这种策
略模式,很容易更换其他视图技术; - View——>渲染,View 会根据传进来的Model 模型数据进行渲染,此处的Model 实际是一个Map 数据结构,因此
很容易支持其他视图技术; - 返回控制权给DispatcherServlet,由DispatcherServlet 返回响应给用户,到此一个流程结束。
我们以上个demo中这个GET请求为例,请求URL是http://localhost:8080/011_spring_framework_demo_springmvc_war_exploded/user
我们知道servlet处理get请求是doGet方法,所以我们去找DispatcherServlet类结构中的doGet方法。
@Override
protected final void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
processRequest(request, response);
}
processRequest处理请求的方法如下:
/**
* Process this request, publishing an event regardless of the outcome.
* <p>The actual event handling is performed by the abstract
* {@link #doService} template method.
*/
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
// 计算处理请求的时间
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null;
LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request);
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor());
// 初始化context
initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
// 看这里
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException | IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
}
finally {
// 重置context
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
}
logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager);
publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
本质上就是调用doService方法,由DispatchServlet类实现
/**
* Exposes the DispatcherServlet-specific request attributes and delegates to {@link #doDispatch}
* for the actual dispatching.
*/
@Override
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
logRequest(request);
// 保存下请求之前的参数.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// 方便后续 handlers 和 view 要使用它们.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
if (this.flashMapManager != null) {
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
}
RequestPath previousRequestPath = null;
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
previousRequestPath = (RequestPath) request.getAttribute(ServletRequestPathUtils.PATH_ATTRIBUTE);
ServletRequestPathUtils.parseAndCache(request);
}
try {
// 看这里,终于将这个请求分发出去了
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
if (this.parseRequestPath) {
ServletRequestPathUtils.setParsedRequestPath(previousRequestPath, request);
}
}
}
doDispatch方法是真正处理请求的核心方法
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 判断是不是文件上传类型的request
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 根据request获取匹配的handler.
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// 根据handler获取匹配的handlerAdapter
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// 如果handler支持last-modified头处理
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = HttpMethod.GET.matches(method);
if (isGet || HttpMethod.HEAD.matches(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// 真正handle处理,并返回modelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 通过视图的prefix和postfix获取完整的视图名
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 应用后置的拦截器
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 处理handler处理的结果,显然就是对ModelAndView 或者 出现的Excpetion处理
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
对于真正的handle方法,我们看下其处理流程
/**
* This implementation expects the handler to be an {@link HandlerMethod}.
*/
@Override
@Nullable
public final ModelAndView handle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
return handleInternal(request, response, (HandlerMethod) handler);
}
交给handleInternal方法处理,以RequestMappingHandlerAdapter这个HandlerAdapter中的处理方法为例
@Override
protected ModelAndView handleInternal(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ModelAndView mav;
checkRequest(request);
// Execute invokeHandlerMethod in synchronized block if required.
if (this.synchronizeOnSession) {
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
Object mutex = WebUtils.getSessionMutex(session);
synchronized (mutex) {
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No HttpSession available -> no mutex necessary
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
}
else {
// No synchronization on session demanded at all...
mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
}
if (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) {
if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) {
applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers);
}
else {
prepareResponse(response);
}
}
return mav;
}
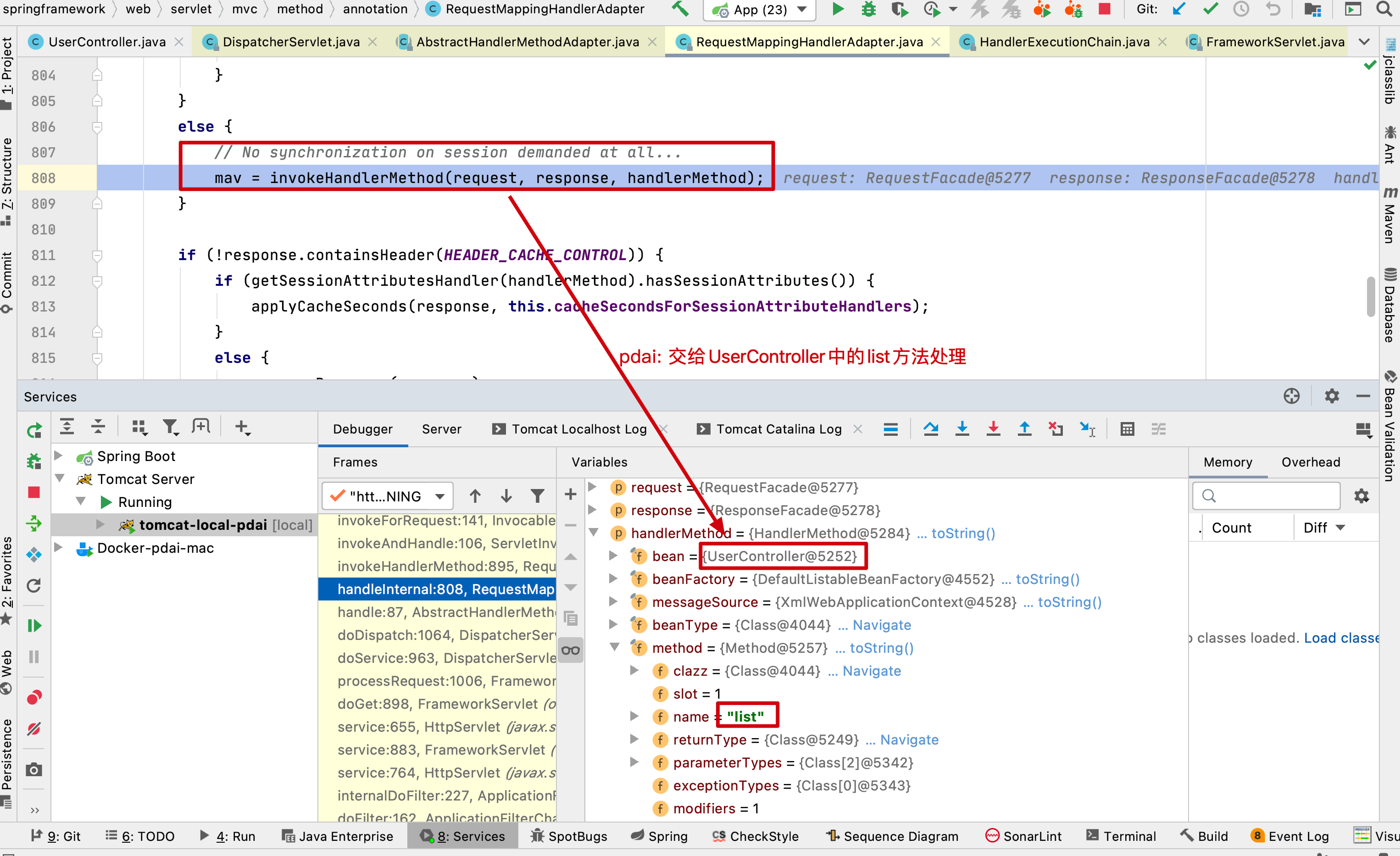
然后执行invokeHandlerMethod这个方法,用来对RequestMapping(usercontroller中的list方法)进行处理
/**
* Invoke the {@link RequestMapping} handler method preparing a {@link ModelAndView}
* if view resolution is required.
* @since 4.2
* @see #createInvocableHandlerMethod(HandlerMethod)
*/
@Nullable
protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request,
HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception {
ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response);
try {
WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod);
ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory);
// 重要:设置handler(controller#list)方法上的参数,返回值处理,绑定databinder等
ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod);
if (this.argumentResolvers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers);
}
if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) {
invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers);
}
invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory);
invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);
ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer();
mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request));
modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod);
mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect);
AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response);
asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor);
asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors);
asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors);
if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) {
Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult();
mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0];
asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult();
LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> {
String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn);
return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]";
});
invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result);
}
// 执行controller中方法
invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer);
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return null;
}
return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest);
}
finally {
webRequest.requestCompleted();
}
}
invokeAndHandle交给UserController中具体执行list方法执行
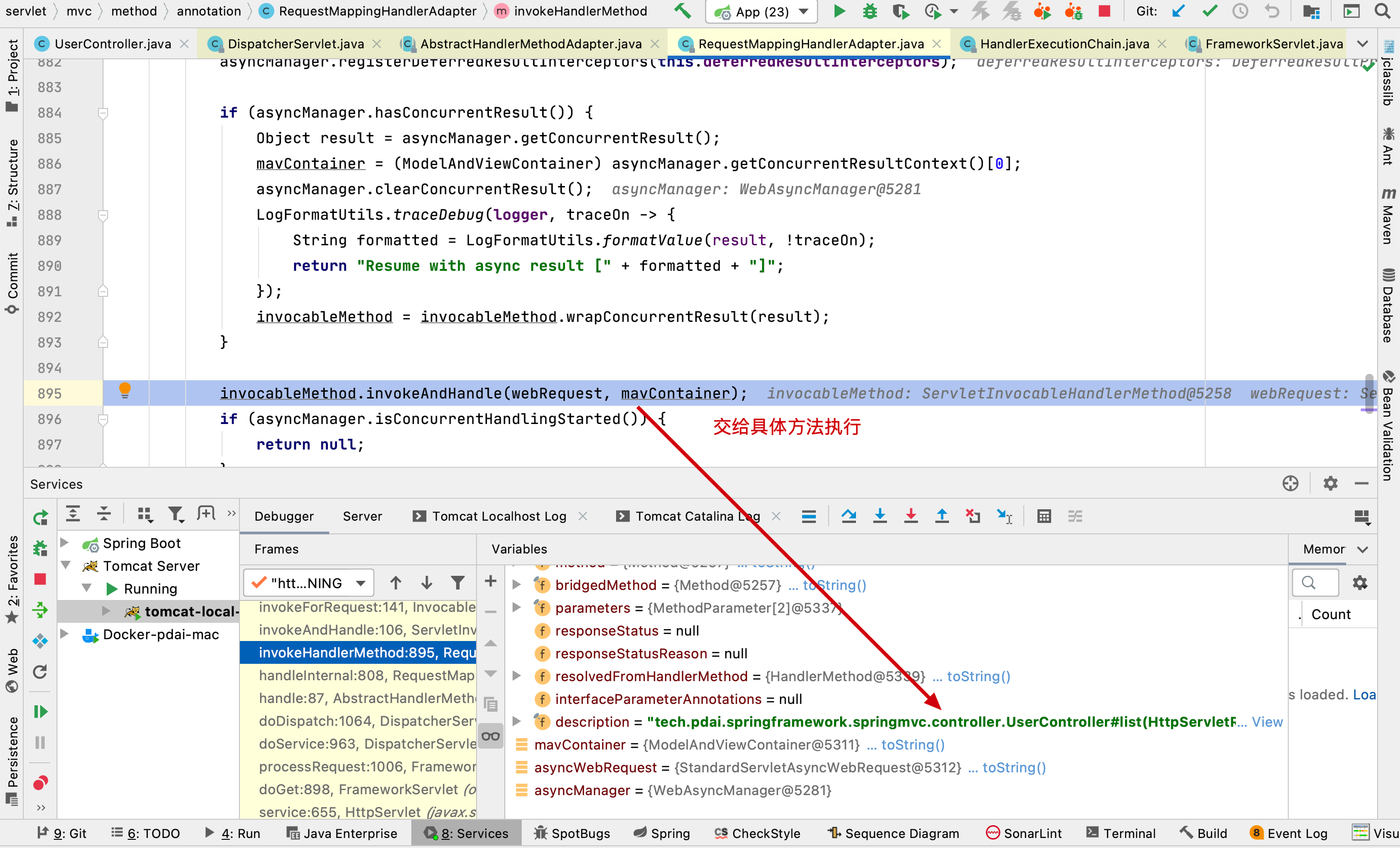
后续invoke执行的方法,直接看整个请求流程的调用链即可
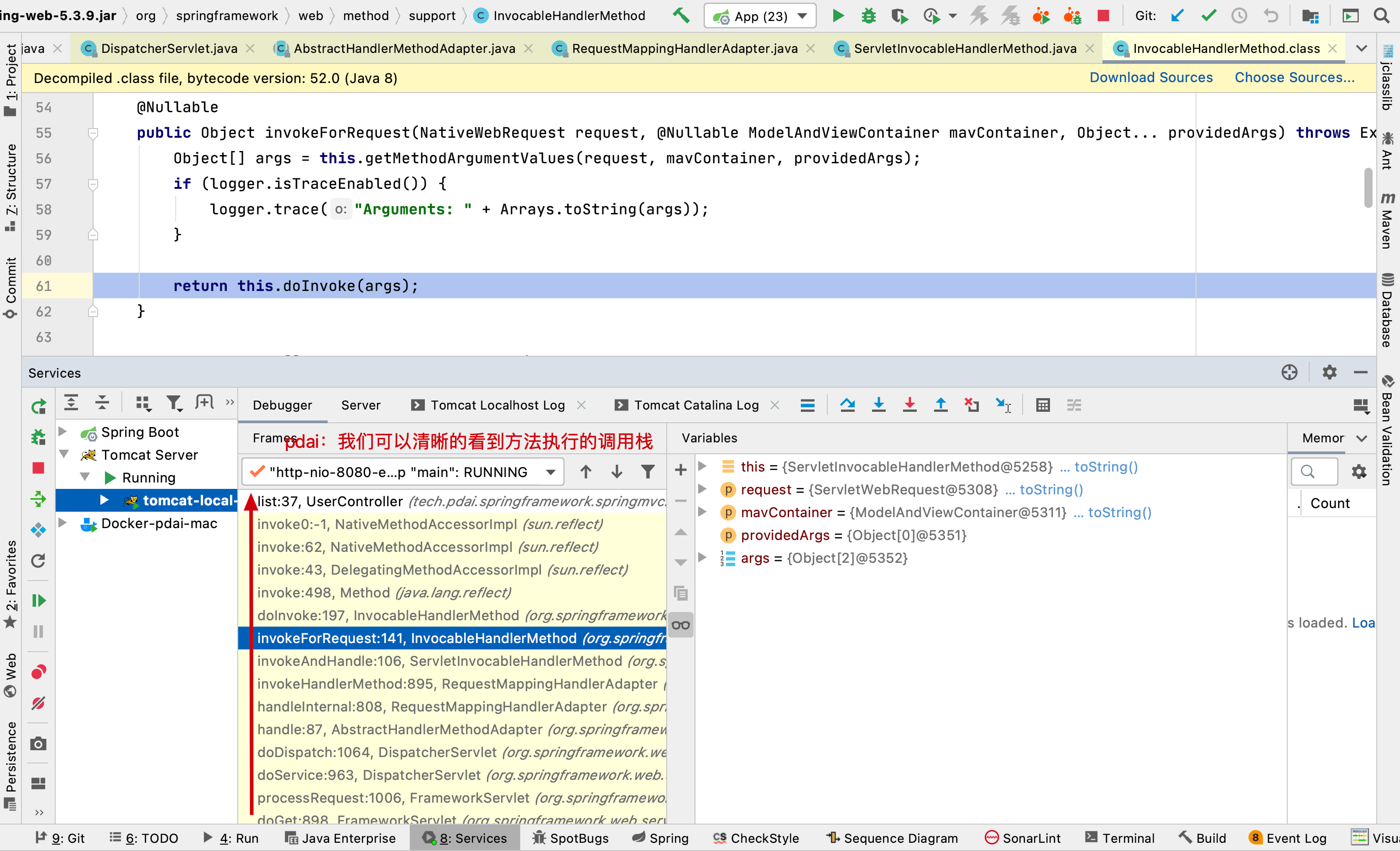
执行后获得视图和Model
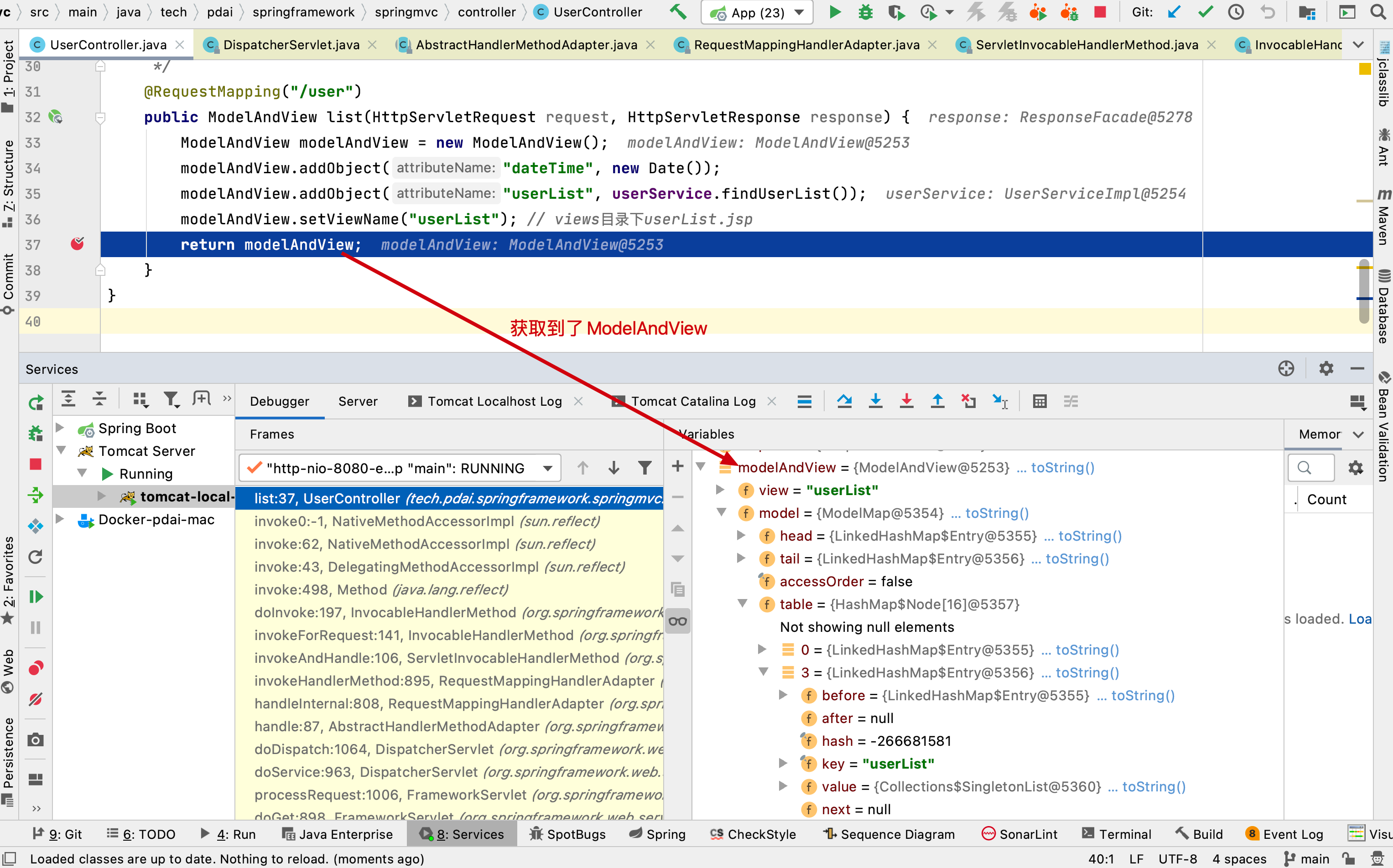
接下来继续执行processDispatchResult方法,对视图和model(如果有异常则对异常处理)进行处理(显然就是渲染页面了)
/**
* Handle the result of handler selection and handler invocation, which is
* either a ModelAndView or an Exception to be resolved to a ModelAndView.
*/
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv,
@Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception {
boolean errorView = false;
// 如果处理过程有异常,则异常处理
if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
}
// 是否需要渲染视图
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
render(mv, request, response); // 渲染视图
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned.");
}
}
if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
}
if (mappedHandler != null) {
// Exception (if any) is already handled..
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
接下来显然就是渲染视图了, spring在initStrategies方法中初始化的组件(LocaleResovler等)就派上用场了。
/**
* Render the given ModelAndView.
* <p>This is the last stage in handling a request. It may involve resolving the view by name.
* @param mv the ModelAndView to render
* @param request current HTTP servlet request
* @param response current HTTP servlet response
* @throws ServletException if view is missing or cannot be resolved
* @throws Exception if there's a problem rendering the view
*/
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale =
(this.localeResolver != null ? this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request) : request.getLocale());
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
String viewName = mv.getViewName();
if (viewName != null) {
// We need to resolve the view name.
view = resolveViewName(viewName, mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Rendering view [" + view + "] ");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "]", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
后续就是通过viewResolver进行解析了,这里就不再继续看代码了,上述流程基本上够帮助你构建相关的认知了。
最后无非是返回控制权给DispatcherServlet,由DispatcherServlet 返回响应给用户。
最后的最后我们看下请求的日志:
21:45:53.390 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet - GET "/011_spring_framework_demo_springmvc_war_exploded/user", parameters={}
21:45:53.400 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping - Mapped to tech.pdai.springframework.springmvc.controller.UserController#list(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse)
22:51:14.504 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView - View name 'userList', model {dateTime=Fri Apr 22 21:45:53 CST 2022, userList=[tech.pdai.springframework.springmvc.entity.User@7b8c8dc]}
22:51:14.550 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView - Forwarding to [/WEB-INF/views/userList.jsp]
22:51:44.395 [http-nio-8080-exec-6] DEBUG org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet - Completed 200 OK
首先, 从Spring框架的整体架构和组成对整体框架有个认知。
- Spring基础 - Spring和Spring框架组成
- Spring是什么?它是怎么诞生的?有哪些主要的组件和核心功能呢? 本文通过这几个问题帮助你构筑Spring和Spring Framework的整体认知。
其次,通过案例引出Spring的核心(IoC和AOP),同时对IoC和AOP进行案例使用分析。
- Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心
- 上文中我们简单介绍了Spring和Spring Framework的组件,那么这些Spring Framework组件是如何配合工作的呢?本文主要承接上文,向你展示Spring Framework组件的典型应用场景和基于这个场景设计出的简单案例,并以此引出Spring的核心要点,比如IOC和AOP等;在此基础上还引入了不同的配置方式, 如XML,Java配置和注解方式的差异。
- Spring基础 - Spring核心之控制反转(IOC)
- 在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了IoC的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些IoC相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读IOC的含义以及IOC的使用方式
- Spring基础 - Spring核心之面向切面编程(AOP)
- 在Spring基础 - Spring简单例子引入Spring的核心中向你展示了AOP的基础含义,同时以此发散了一些AOP相关知识点; 本节将在此基础上进一步解读AOP的含义以及AOP的使用方式。
基于Spring框架和IOC,AOP的基础,为构建上层web应用,需要进一步学习SpringMVC。
- Spring基础 - SpringMVC请求流程和案例
- 前文我们介绍了Spring框架和Spring框架中最为重要的两个技术点(IOC和AOP),那我们如何更好的构建上层的应用呢(比如web 应用),这便是SpringMVC;Spring MVC是Spring在Spring Container Core和AOP等技术基础上,遵循上述Web MVC的规范推出的web开发框架,目的是为了简化Java栈的web开发。 本文主要介绍SpringMVC的请求流程和基础案例的编写和运行。
Spring进阶 - IoC,AOP以及SpringMVC的源码分析
- Spring进阶 - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC体系结构设计
- 在对IoC有了初步的认知后,我们开始对IOC的实现原理进行深入理解。本文将帮助你站在设计者的角度去看IOC最顶层的结构设计
- Spring进阶 - Spring IOC实现原理详解之IOC初始化流程
- 上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构;紧接着这篇,我们可以看下源码的实现了:Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的
- Spring进阶 - Spring IOC实现原理详解之Bean实例化(生命周期,循环依赖等)
- 上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构;以及Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的;容器中存放的是Bean的定义即BeanDefinition放到beanDefinitionMap中,本质上是一个
ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>;并且BeanDefinition接口中包含了这个类的Class信息以及是否是单例等。那么如何从BeanDefinition中实例化Bean对象呢,这是本文主要研究的内容?
- 上文,我们看了IOC设计要点和设计结构;以及Spring如何实现将资源配置(以xml配置为例)通过加载,解析,生成BeanDefination并注册到IoC容器中的;容器中存放的是Bean的定义即BeanDefinition放到beanDefinitionMap中,本质上是一个
- Spring进阶 - Spring AOP实现原理详解之切面实现
- 前文,我们分析了Spring IOC的初始化过程和Bean的生命周期等,而Spring AOP也是基于IOC的Bean加载来实现的。本文主要介绍Spring AOP原理解析的切面实现过程(将切面类的所有切面方法根据使用的注解生成对应Advice,并将Advice连同切入点匹配器和切面类等信息一并封装到Advisor,为后续交给代理增强实现做准备的过程)。
- Spring进阶 - Spring AOP实现原理详解之AOP代理
- 上文我们介绍了Spring AOP原理解析的切面实现过程(将切面类的所有切面方法根据使用的注解生成对应Advice,并将Advice连同切入点匹配器和切面类等信息一并封装到Advisor)。本文在此基础上继续介绍,代理(cglib代理和JDK代理)的实现过程。
- Spring进阶 - Spring AOP实现原理详解之Cglib代理实现
- 我们在前文中已经介绍了SpringAOP的切面实现和创建动态代理的过程,那么动态代理是如何工作的呢?本文主要介绍Cglib动态代理的案例和SpringAOP实现的原理。
- Spring进阶 - Spring AOP实现原理详解之JDK代理实现
- 上文我们学习了SpringAOP Cglib动态代理的实现,本文主要是SpringAOP JDK动态代理的案例和实现部分。
- Spring进阶 - SpringMVC实现原理之DispatcherServlet初始化的过程
- 前文我们有了IOC的源码基础以及SpringMVC的基础,我们便可以进一步深入理解SpringMVC主要实现原理,包含DispatcherServlet的初始化过程和DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程的源码解析。本文是第一篇:DispatcherServlet的初始化过程的源码解析。
- Spring进阶 - SpringMVC实现原理之DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程
- 前文我们有了IOC的源码基础以及SpringMVC的基础,我们便可以进一步深入理解SpringMVC主要实现原理,包含DispatcherServlet的初始化过程和DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程的源码解析。本文是第二篇:DispatcherServlet处理请求的过程的源码解析。
