最近遇到读者提问:Python爬虫如何加速? 这个问题涉及到一个爬虫里,甚至是整个Python编程里都非常重要的问题: 如果同时下载1w张图片,如何有效地加速程序运行,缩短下载时间?

最近遇到读者提问:Python爬虫如何加速?
这个问题涉及到一个爬虫里,甚至是整个Python编程里都非常重要的问题:
如果同时下载1w张图片,如何有效地加速程序运行,缩短下载时间?
今天我们一起来看一下常用的解决方案。
1、为什么慢?
首先我们先看一下,原来的代码里,是什么原因导致程序慢的?下面是代码和运行结果:
import office for i in range(1, 18): url = 'https://www.python-office.com/api/img-cdn/test/spider/{}.jpg'.format(str(i)) office.image.down4img(url, output_name=str(i))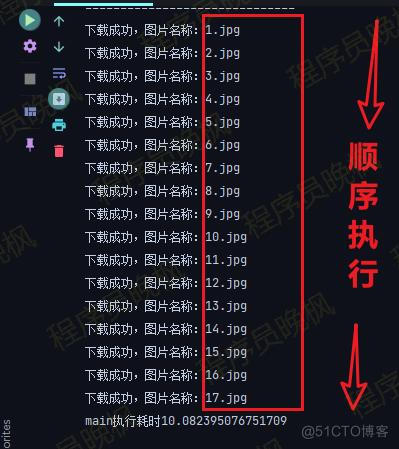
顺序执行看起来很完美,但是完美的背后是不是有陷阱呢?
为了更好的理解这个代码,我们先举一个例子:你面前有10台洗衣机编号是从1到10,里面转满了衣服需要你清洗,有的脏可能要强力洗洗的久,有的干净只需要速洗洗的快。
清洗以后,需要你记录下他们的清理顺序,有下列2种方案供你选择:
哪种方式最快呢?毫无疑问是第2种,因为可以让所有的洗衣机同时工作,时间资源可以复用。
回到我们的程序,我们下载一张图片也是分为2步:请求图片资源,保存到本地。
上面的代码之所以慢,就是因为它是请求到第1张的资源,保存到本地之后,再去请求第2张的资源。看起来很完美,但其实问题很大。
如何加快速度呢?我们如果可以先请求到所有的图片资源(打开所有的洗衣机),然后再统一保存图片(哪台洗完衣服,就先记录哪台),这样是不是就会快很多呢?
下面我们按照第2种思路,在Python里的实现实现一下。
2、解决代码
Talk is cheap,show me the code.先上代码和运行结果。
import asyncio from aiohttp import ClientSession tasks = [] url = "https://www.python-office.com/api/img-cdn/test/spider/{}.jpg" async def hello(url, i='wanfeng', type='jpg'): async with ClientSession() as session: async with session.get(url) as response: if response.status==200: response = await response.read() # print(response) async with aiofiles.open('.'.join((str(i), type)), 'wb') as output_img: # for chunk in response: await output_img.write(response) output_img.close() print(f"下载成功,图片名称:{'.'.join((str(i), type))}") def run(): for i in range(1, 18): task = asyncio.ensure_future(hello(url.format(i), i)) tasks.append(task) def main(): loop = asyncio.get_event_loop() run() loop.run_until_complete(asyncio.wait(tasks)) if __name__ == '__main__': main()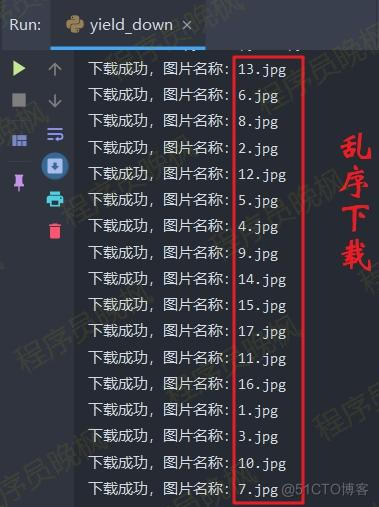 主要使用的库是:
主要使用的库是:
- asyncio:协程,让图片下载不按顺序,可以加快速度
- aiohttp:替代requests,用来异步发送请求。
- aiofiles:异步写入文件内容
3、还有其它方法吗?
还有多进程也可以试试,但是多进程更大的优势体现在计算密集型的场景下。爬虫获取网络请求属于I/O密集型操作,多进程的优势不大。
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import multiprocessing import os, time from multiprocessing import Pool import requests url = "https://www.python-office.com/api/img-cdn/test/spider/{}.jpg" def down4img(url, output_name, type): """ 下载指定url的一张图片,支持所有格式:jpg\png\gif .etc """ # print("子进程开始执行>>> pid={},ppid={},编号{}".format(os.getpid(), os.getppid(), output_name)) response = requests.get(url, stream=True) with open('.'.join((output_name, type)), 'wb') as output_img: for chunk in response: output_img.write(chunk) output_img.close() print(f"下载成功,图片名称:{'.'.join((output_name, type))}") # print("子进程终止>>> pid={},ppid={},编号{}".format(os.getpid(), os.getppid(), output_name)) def main(): print("主进程开始执行>>> pid={}".format(os.getpid())) ps = Pool(multiprocessing.cpu_count()) ps = Pool(3) for i in range(1, 18): # ps.apply(worker,args=(i,)) # 同步执行 output_name = str(i) type = 'jpg' ps.apply_async(down4img, args=(url.format(str(i)), output_name, type,)) # 异步执行 # ps.apply(down4img, args=(url.format(str(i)), output_name[0], type,)) # 同步执行 # 关闭进程池,停止接受其它进程 ps.close() # 阻塞进程 ps.join() print("主进程终止") if __name__ == '__main__': main()主要使用的库是:
- multiprocessing:创建进程池
4、写在最后
希望能给你带来帮助。
