运算符 a += 20 # a = a+20 逻辑运算: and 并且的意思. 左右两端的值必须都是真. 运算结果才是真 or 或者的意思. 左右两端有一个是真的. 结果就是真. 全部是假. 结果才能是假 not 非的意思.
运算符
a += 20 # a = a+20逻辑运算:
- and 并且的意思. 左右两端的值必须都是真. 运算结果才是真
- or 或者的意思. 左右两端有一个是真的. 结果就是真. 全部是假. 结果才能是假
- not 非的意思. 原来是假. 现在是真. 非真即假, 非假既真
- 先算括号,然后算not, 然后算and ,最后算or
print(1 < 2 and 3 < 4 or 1 > 2) # True
print(2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 < 1) # True
print(1 > 2 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 or 9 < 8) # False
print(1 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # False
print(not 2 > 1 and 3 < 4 or 4 > 5 and 2 > 1 and 9 > 8 or 7 < 6) # False
x or y 如果x==0 那么就是y, 否则是x
x and y, x为真,值是y,x为假,值是x
false相当于0
print(1 or 2) # 1print(2 or 3) # 2
print(0 or 3) # 3
print(0 or 4) # 4
print(0 or 1 or 3 or 0 or 5) # 1
print(1 and 2) # 2
print(2 and 0) # 0
print(0 and 3) # 0
print(0 and 4) # 0
print(0 or 4 and 3 or 7 or 9 and 6) # 3
print(2 > 3 and 3) # False false相当于0
print(2 < 1 and 4 > 6 or 3 and 4 > 5 or 6) # 6
字符编码
a = "你好"a_new = a.decode("utf-8").encode("gbk") # 第一个里填原来字符串的编码格式(原来的为utf-8),第二个填要转为的格式
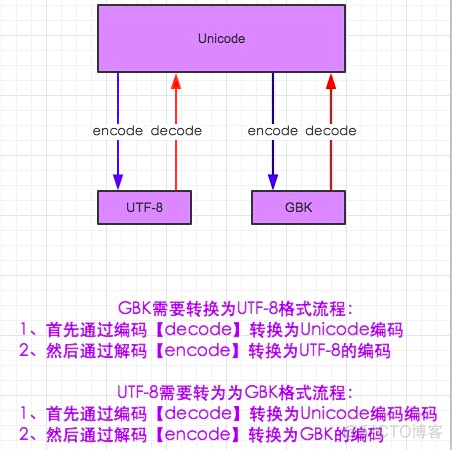
decode 解码 encode 编码
abc = '西安'print(abc.encode('utf-8'))
print('邹邹'.encode('utf-8')) # 转换为二进制
print(b'\xe4\xbd\xa0\xe5\xa5\xbd'.decode('utf-8')) # 转换为字符串
结果:
b'\xe8\xa5\xbf\xe5\xae\x89'b'\xe9\x82\xb9\xe9\x82\xb9'
你好
如果将字符串赋给了abc,则输出时不用引号,没赋值时需要引号。Utf-8必须有引号。二进制转换为字符串不要引号。
