1 内容介绍
强度不均匀性给图像分割带来了很大的困难。乘法偏置场校正模型部分解决了这个问题。但也存在分割速度慢、应用领域狭窄等问题。在本文中,提出了一种基于强度不均匀性的加性偏差校正(ABC)模型。该模型将观察到的图像分为三部分:加性偏置函数、反射边缘结构函数和高斯噪声。首先,定义了强度不均匀性的局部区域和局部聚类准则。其次,通过引入水平集函数,将局部聚类准则转化为基于水平集模型的能量函数。最后,估计的偏置场和反射边缘的结构是通过在图像分割时最小化能量函数的过程来计算的。为了提高系统的稳定性,设计了去参数化正则化函数和自适应数据驱动项函数。与传统的乘法模型相比,加法模型的计算速度更快。该模型对于强度不均匀的图像可以获得理想的分割效果。实验结果表明,与传统的分段和乘法模型相比,该方法更稳健、更快、更准确。与传统的乘法模型相比,加法模型的计算速度更快。该模型对于强度不均匀的图像可以获得理想的分割效果。实验结果表明,与传统的分段和乘法模型相比,该方法更稳健、更快、更准确。与传统的乘法模型相比,加法模型的计算速度更快。该模型对于强度不均匀的图像可以获得理想的分割效果。实验结果表明,与传统的分段和乘法模型相比,该方法更稳健、更快、更准确。
2 部分代码
%% A Level Set Method Based on Additive Bias Correction for Image Segmentation
% Author:Guirong Weng
% (School of Mechanical and Electric Engineering, Soochow University, Suzhou 215021, China)
% All rights researved by Guirong Weng, who formulated the model, designed
% and implemented the algorithm in the above paper.
% E-mail:wgr@suda.edu.cn, 2020.2.12
% Expert Systems With Applications,185(2021)115633
%% Model theory:
% Image observed I(x),i(x)=log(I): i(x)=b(x)+r(x)+n(x);
% A: the bias field b is supposed to be varying smoothly,
% B: the spatial derivatives of the observed intensity are mostly due to edges in the reflectance r.
% C: n is additive noise, The additive noise n can be assumed to be zero-mean Gaussian noise.
% D: b is therefore assumed to be piecewise (approximately)constant in a local region.
%%
close all; clear; clc
imgID = 9 ; % image ID = 1 ~15
Img1 = imread([num2str(imgID),'.bmp']);
c0 = 1; initialLSF = ones(size(Img1(:,:,1))).*c0;
% Three parameter settings, iteration, initial contour
[sigma,alfa,iterNum,k,initialLSF] = ABC_Switch(imgID,c0,initialLSF);
Img = double(Img1(:,:,1));
Img = log(1+Img/255); % rescale the image intensities
fmin = min(Img(:));
fmax = max(Img(:));
Img = 255*(Img-fmin)/(fmax-fmin); % Normalize Img to the range [0,255]
timestep = 1; % constant 1
epsilon = 1; % constant 1
G = fspecial('average',k); % Create predefined filter
u = initialLSF;
r = zeros(size(Img)); % Initial the reflection image
Ksigma = fspecial('gaussian',round(2*sigma)*2+1,sigma); % Gaussian kernel
KONE = conv2(ones(size(Img)),Ksigma,'same'); % G*1, in Eq. (20)
beta = std2(Img); % Standard deviation of image in Eq.(25)
figure;imagesc(Img1); colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal
hold on; contour(initialLSF,[0 0],'g','LineWidth',2);
figure;imagesc(Img1); colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal
% -----start level set evolution-----
for n = 1:iterNum
[u,r,b1,b2] = ABC_2D(Img,u,Ksigma,KONE,r,beta,alfa,epsilon,timestep);
u = tanh(7*u); % constant 7,in Eq.(26)
u = imfilter(u,G,'symmetric'); % in Eq.(27)
if mod(n,10) == 0
pause(0.01);
colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal;
hold on; contour(u,[0 0],'c');title(n);
% hold off;
end
end
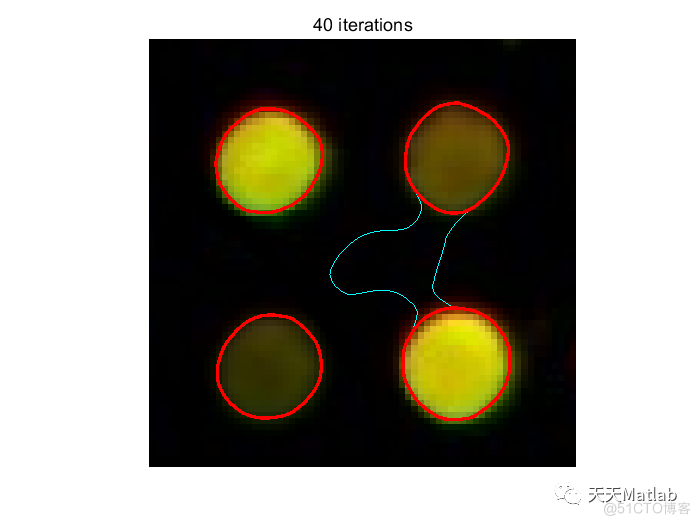
hold on;contour(u,[0 0],'r','LineWidth',2);
iterNumN = [num2str(n), ' iterations']; title(iterNumN);
Hu = 0.5*(1+(2/pi)*atan(u./epsilon));
b = b1.*Hu+b2.*(1-Hu); % Bias field image
figure; imagesc(b); colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal;
title('Bias image');
Ib = Img-b; % Bias correction image
figure; imagesc(Ib); colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal;
title('Bias correction image');
figure; imagesc(r); colormap(gray); axis off; axis equal;
title('ireflectance image');
3 运行结果
4 参考文献
[1]迪娜·加尔肯. 基于MATLAB的图像分割算法研究及实现[J]. 科学技术创新, 2021(26):3.
[2] Weng G , Dong B , Lei Y . A level set method based on additive bias correction for image segmentation[J]. Expert Systems with Application, 2021(185-Dec.).
