Pytorch学习笔记 张量Tensor 张量是一个统称,其中包含很多类型: 0阶张量:标量、常数,0-D Tensor 1阶张量:向量,1-D Tensor 2阶张量:矩阵,2-D Tensor 3阶张量 Pytorch中创建张量 使用python中
Pytorch学习笔记
张量Tensor
张量是一个统称,其中包含很多类型:
Pytorch中创建张量
使用python中的列表或者序列创建tensor
torch.tensor([[1., -1.], [1., -1.]])tensor([[ 1.0000, -1.0000],
[ 1.0000, -1.0000]])
使用numpy中的数组创建tensor
torch.tensor(np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]))tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 6]])
使用torch的api创建tensor
tensor([[ 0.8237, 0.5781, 0.6879],
[ 0.3816, 0.7249, 0.0998]])
tensor([[4, 5],
[6, 7]])
torch.randn([3,4])随机数的tensor,随机值的分布式均值为0,方差为1
Pytorch中tensor的常用方法
获取tensor中的数据(当tensor中只有一个元素可用):tensor.item()
In [10]: a = torch.tensor(np.arange(1))
In [11]: a
Out[11]: tensor([0])
In [12]: a.item()
Out[12]: 0
转化为numpy数组
In [55]: z.numpy()Out[55]:
array([[-2.5871205],
[ 7.3690367],
[-2.4918075]], dtype=float32)
获取形状:tensor.size()
xOut[72]:
tensor([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 10]], dtype=torch.int32)
In [73]: x.size()
Out[73]: torch.Size([3, 2])
形状改变:tensor.view((3,4))。类似numpy中的reshape,是一种浅拷贝,仅仅是形状发生改变
In [76]: x.view(2,3)Out[76]:
tensor([[ 1, 2, 3],
[ 4, 5, 10]], dtype=torch.int32)
获取阶数:tensor.dim()
获取最大值:tensor.max()
转置:tensor.t()
tensor的数据类型
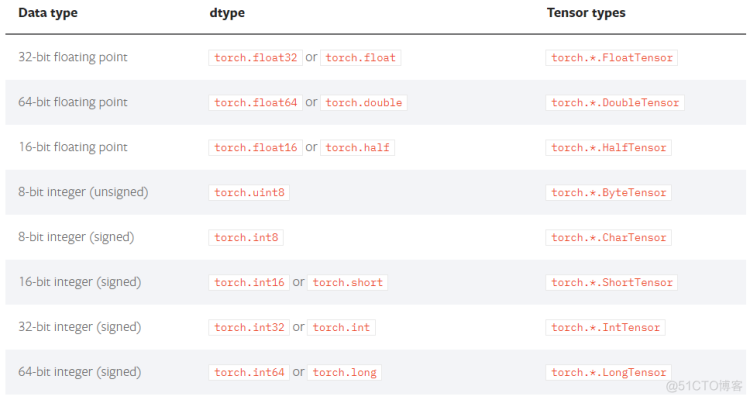
类型的修改
In [17]: aOut[17]: tensor([1, 2], dtype=torch.int32)
In [18]: a.type(torch.float)
Out[18]: tensor([1., 2.])
In [19]: a.double()
Out[19]: tensor([1., 2.], dtype=torch.float64)
tensor的其他操作
tensor和tensor相加
In [94]: x = x.new_ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.float)In [95]: y = torch.rand(5, 3)
In [96]: x+y
Out[96]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
In [98]: torch.add(x,y)
Out[98]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
In [99]: x.add(y)
Out[99]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
In [100]: x.add_(y) #带下划线的方法会对x进行就地修改
Out[100]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
In [101]: x #x发生改变
Out[101]:
tensor([[1.6437, 1.9439, 1.5393],
[1.3491, 1.9575, 1.0552],
[1.5106, 1.0123, 1.0961],
[1.4382, 1.5939, 1.5012],
[1.5267, 1.4858, 1.4007]])
带下划线的方法(比如:add_)会对tensor进行就地修改
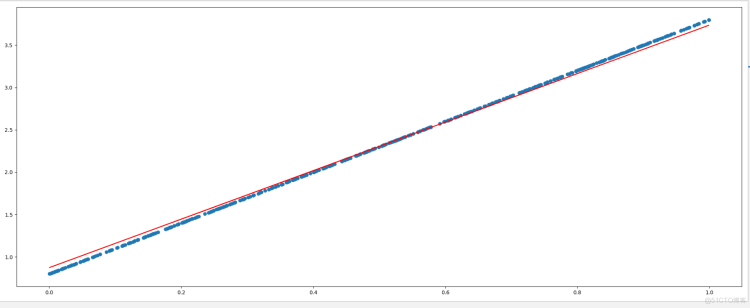
手写线性回归
import torchimport matplotlib.pyplot as plt
learning_rate=0.01
#1.准备数据
#y=3x+0.8
x=torch.rand([500,1])
y_true=3*x+0.8
#2.通过模型计算y_predict
w = torch.rand([1,1],requires_grad=True)
b = torch.tensor(0,requires_grad=True,dtype=torch.float32)
#4.通过循环,反向传播,更新参数
for i in range(2000):
y_predict = torch.matmul(x, w) + b
# 3.计算loss
loss = (y_true - y_predict).pow(2).mean()
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.data.zero_()
loss.backward() #反向传播
w.data = w.data - learning_rate * w.grad
b.data = b.data - learning_rate * b.grad
if i % 50==0:
print("w ,b ,loss",w.item(),b.item(),loss.item())
plt.figure(figsize=(20,8))
plt.scatter(x.numpy().reshape(-1),y_true.numpy().reshape(-1))
y_predict = torch.matmul(x, w) + b
plt.plot(x.numpy().reshape(-1),y_predict.detach().numpy().reshape(-1),c='r')
plt.show()
结果: