(一) 什么是反射?

反射就是把Java类中的各个成分映射成一个个的Java对象。即在运行状态中,对于任意一个类,都能够获取这个类的所有属性和方法;对于任意一个对象,都能调用其任意一个方法和属性。这种动态获取信息及动态调用对象方法的功能叫Java的反射机制。
说明:加载完类之后,在堆内存的方法区中就产生了一个Class类型的对象(一个 类只有一个Class对象),这个对象就包含了完整的类的结构信息。可以通过这个对象查看到所对应类的所有信息。
(二) 反射能做什么?
(1)在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类
(2)在运行时构造任意一个类的对象
(3)在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法
(4)在运行时获取泛型信息
(5)在运行时调用任意一个对象的成员变量和方法
(6)在运行时处理注解
(7)生成动态代理
(三) Class类
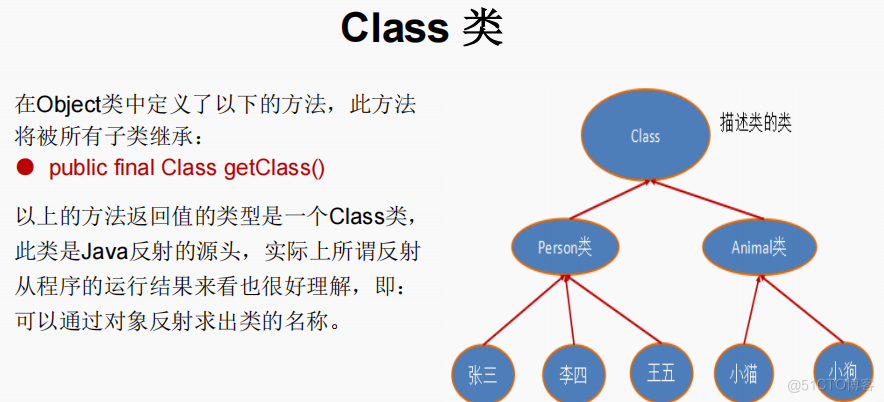
通过对象可以得到的信息:某个类的属性、方法和构造器、某个类到底实现了哪些接 口。对于每个类而言,JRE 都为其保留一个不变的 Class 类型的对象。一个 Class 对象包含 了特定某个结构(class/interface/enum/annotation/primitive type/void/[])的有关信息。
(1) Class本身也是一个类
(2) Class 对象只能由系统建立
(3) 一个加载的类在 JVM 中只会有一个Class实例
(4)一个Class对象对应的是一个加载到JVM中的一个.class文件
(5) 每个类的实例都会记得自己是由哪个 Class 实例所生成
(6)通过Class可以完整地得到一个类中的所有被加载的结构
(7)Class类是Reflection的根源,针对任何你想动态加载、运行的类,唯有先获得 相应的 Class对象
(四) 实际应用
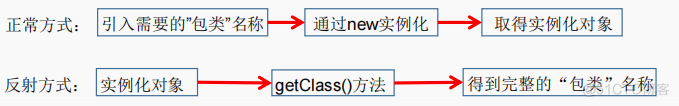
I.获取Class类的实例
方式一:调用运行时类的属性
方式二:通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()
方式三:调用Class的静态方法:formatName(String classPath)
方式四:使用类的加载器:ClassLoader
@Testpublic void test3() throws ClassNotFoundException {//获取运行时类的方式(前三种为重点)
//方式一:调用运行时类的属性
Class clazz = Person.class;
System.out.println(clazz);
//方式二: 通过运行时类的对象,调用getClass()
Person p1 = new Person();
Class clazz2 = p1.getClass();
System.out.println(clazz2);
//方式三:调用Class的静态方法:formatName(String classPath)
Class clazz3 = Class.forName("practice.Person");
System.out.println(clazz3);
//判断是否相等
System.out.println(clazz == clazz2);
System.out.println(clazz2 == clazz3);
//说明:更好地体现了动态性,在编译时无法判断出错误一旦运行,如果错误就直接报错
//方式四;使用类的加载器:ClassLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = ReflectionTest.class.getClassLoader();
Class clazz4 = classLoader.loadClass("practice.Person");
System.out.println(clazz4);
System.out.println(clazz3 == clazz4);
}
补充:
(1)哪些对象可以有Class实例?
① class: 外部类,成员(成员内部类,静态内部类),局部内部类,匿名内部类
② interface:接口
③ []:数组
④ enum:枚举
⑤ annotation:注解@interface
⑥ primitive type:基本数据类型
⑦ void
(2)类的加载器(ClassLoader)
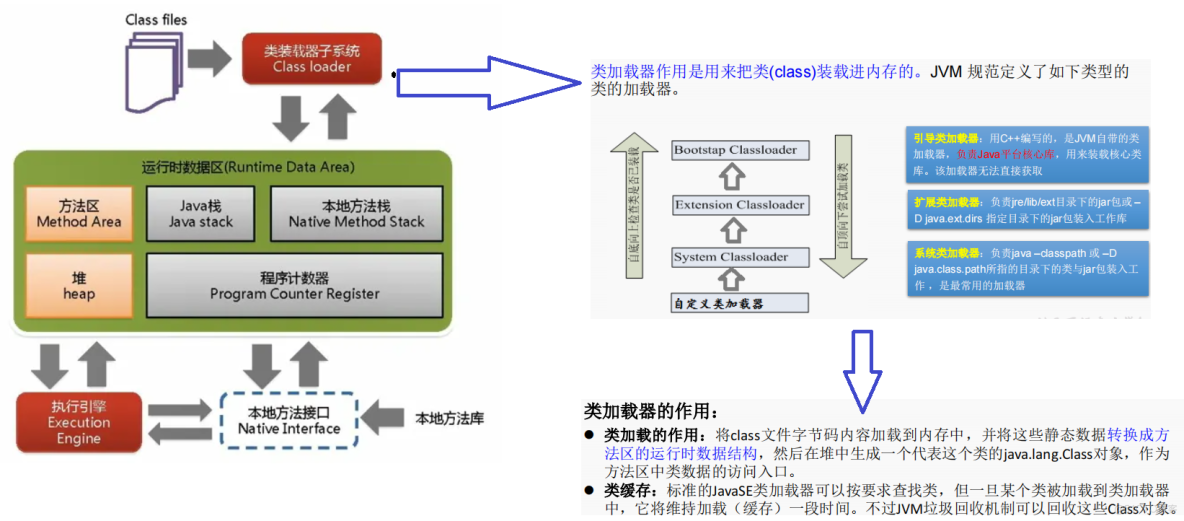
II.读取配置文件(properties)
基本介绍:
Java中的properties文件是一种配置文件,主要用于表达配置信息,文件类型为*.properties,格式为文本文件,文件的内容是格式是"键=值"的格式.
@Testpublic void test1() throws Exception {
Properties pros=new Properties();
//此时的文件默认路径为当前的module下
//也可以使用完整路径来寻找特定位置的properties文件
// FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("src\\practice\\jdbc1.properties");
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties");
pros.load(fis);
String user=pros.getProperty("user");
String password=pros.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("user = "+ user +"\npassword ="+ password);
}
/**
* 读取配置文件(方式二)
* */
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception {
Properties pros3=new Properties();
ClassLoader classLoader=ClassLoaderTest.class.getClassLoader();
//使用绝对路径
InputStream is=classLoader.getResourceAsStream("src\\practice\\jdbc1.properties");
pros3.load(is);
String name = pros3.getProperty("user");
String password=pros3.getProperty("password");
System.out.println("user= "+name+ ",password ="+password);
}
III.创建运行时类的对象
- newInstance():调用此方法,创建运行时类的对象,内部调用了运行时类的空参构造器
- 此方法使用前提:
- (1)运行时类必须提供空参构造器
- (2)空参构造器的访问权限必须要够,通常为public
-
- 在javabean中要求提供一个public的空参构造器
- 原因如下:
- (1) 便于通过反射,创建运行时类的对象
- (2) 便于子类继承此运行时类的对象,默认调用super()时,保证父类由此构造器
@Test
public void test2() throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//(1)获取运行时类
Class<Person> clazz=Person.class;
//(2)方法1--->newInstance() :调用此方法,创建对应的运行时类的对象(调用了运行时类的空参构造器)
Object obj=clazz.newInstance();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
IV.获取运行时类的完整结构
①. 实现的全部接口
public Class<?>[] getInterfaces()
说明:确定此对象所表示的类或接口实现的接口。
具体代码:
@Testpublic void test3(){
Class clazz= Person1.class;
Class[] interfaces=clazz.getInterfaces();
for(Class f:interfaces){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println();
//获取运行时类父类的接口
Class[]interfaces1=clazz.getSuperclass().getInterfaces();
for(Class m:interfaces1){
System.out.println(m);
}
}
②. 所继承的父类
public Class<? Super T> getSuperclass()
说明:返回表示此 Class 所表示的实体(类、接口、基本类型)的父类的 Class。
/*** 获取运行时类的父类
* */
@Test
public void test7(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
Class superclass=clazz.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(superclass);
}
/**
* 通过反射获取带泛型的父类
* */
@Test
public void test8(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
Type generiSuperclass=clazz.getGenericSuperclass();
ParameterizedType parameterizedType=(ParameterizedType) generiSuperclass;
//获取泛型类型
Type[] actualArguments=parameterizedType.getActualTypeArguments();
System.out.println(actualArguments[0].getTypeName());
}
③. 全部的构造器
public Constructor<T>[] getConstructors()
说明:返回此 Class 对象所表示的类的所有public构造方法。
public Constructor<T>[] getDeclaredConstructors()
说明:返回此 Class 对象表示的类声明的所有构造方法。
Constructor类中
public int getModifiers(); ----->说明 :取得修饰符
public String getName(); ------>说明:取得方法名称
public Class<?>[] getParameterTypes();--->说明: 取得参数的类型
代码实现:
@Testpublic void test1() throws NoSuchMethodException {
Class clazz=Person1.class;
//getConstructors():获取当前运行时类中声明为public 的方法
Constructor[]constructors=clazz.getConstructors();
for (Constructor e:constructors) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println();
//getDeclaredConstructor():获取当前类中所有声明的构造器
Constructor[]declareConstructors=clazz.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor e:declareConstructors) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
④. 全部的方法
public Method[] getDeclaredMethods()
说明:返回此Class对象所表示的类或接口的全部方法
public Method[] getMethods()
说明:返回此Class对象所表示的类或接口的public的方法
Method类中:
public Class<?>getReturnType()
说明:取得全部的返回值
public Class<?>[]getParameterTypes()
说明:取得全部的参数
public int getModifiers() ; --->取得修饰符
public Class<?>[]getExceptionTypes()取得异常信息
具体代码:
/*** 权限修饰符 数据类型 变量名
* */
@Test
public void test2(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
Field[]declareFields=clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f :declareFields){
System.out.println();
System.out.println(f);
//权限修饰符
int modifier=f.getModifiers();
//输出对应属性的权限及权限修饰符的等级
System.out.println(Modifier.toString(modifier));
System.out.println(modifier);
//数据类型
Class type=f.getType();
System.out.println(type+"\t");
//变量名
String name=f.getName();
System.out.println(name);
}
}
⑤.全部的Field
public Field[] getFields() ;
说明:返回此Class对象所表示的类或接口的public的Field。
public Field[] getDeclaredFields() ;
说明:返回此Class对象所表示的类或接口的全部Field。
Field方法
public int getModifiers() ;
说明:以整数形式返回此Field的修饰符。
public Class<?> getType() ;
说明:得到Field的属性类型
public String getName()
说明:返回Field的名称
具体代码
@Testpublic void test1(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
//获取属性结构
//getFields():获取当前运行时类及父类中声明为public访问权限的属性
Field[]field=clazz.getFields();
for(Field f:field){
System.out.println(f);
}
System.out.println();
//getDeclareFields():获取当前运行时类中声明的所有属性。(不包含父类中声明的属性)
Field[]declareFields=clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f: declareFields){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
⑥. Annotation相关
get Annotation(Class<T> annotationClass)
getDeclaredAnnotations()
代码实现:
@Testpublic void test9(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
Annotation[]annotations=clazz.getAnnotations();
for(Annotation s:annotations){
System.out.println(s);
}
}
⑦.泛型相关
Type getGenericSuperclass()
说明:获取父类泛型类型
ParameterizedType
说明:泛型类型
getActualTypeArguments()
说明:获取实际的泛型类型参数数组
⑧.类所在的包
Package getPackage()
代码实现
@Testpublic void test5(){
Class clazz=Person1.class;
Package pack=clazz.getPackage();
System.out.println(pack);
}
