在有限的手机屏幕空间内,当要浏览的内容较多,无法在一个屏幕空间内全部显示时,可以使用滚动视图来延长屏幕的空间。 当浏览的内容具有很强的类别性质时,更合适的方法是将不
当浏览的内容具有很强的类别性质时,更合适的方法是将不同类别的内容集中到各自的面板中,这时就需要使用面板标签(Tab)组件了。
Tab 组件利用面板标签把不同的面板内容切换到屏幕上,以显示不同类别的内容。
下面通过一个实例来了解一下 Tab 组件的使用方法。在工程 WidgetDemo 的布局文件 main.xml 中添加一个名为 TabDemo 的 Button,用以启动 TabActivity。
在 main.xml 中添加代码如下:
<Button
android:id="@+id/button13"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="TabDemo"/>
单击 Button 并启动 GridViewActivity 的代码如下:
Button tabbtn = (Button)this.findViewById(R.id.button13);
tabbtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener(){
@Override
public void onClick(View v){
Intent intent;
intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,TabActivity .class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
同时在 AndroidManifest.xml 文件中声明该 Activity:
<activity android:name=".TabActivity"/>
TabActivity 的运行效果如图 1 所示。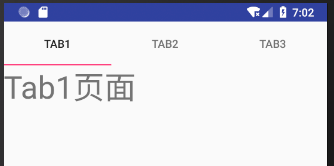
图 1 TabActivity 的运行结果
要使用 Tab 必然涉及它的容器 TabHost,TabHost 包括 TabWigget 和 FrameLayout 两部分。TabWidget 就是每个 Tab 的标签,FrameLayout 是 Tab 的内容。
TabActivity 使用的布局文件是 tab.xml。在 tab.xml 中定义了每个 Tab 中要显示的内容,代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/tabhost"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TabWidget
android:id="@android:id/tabs"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<FrameLayout
android:id="@android:id/tabcontent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tab1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tab1页面"
android:textSize="40dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tab2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tab2页面"
android:textSize="40dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tab3"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tab3页面"
android:textSize="40dp" />
</FrameLayout>
</LinearLayout>
</TabHost>
在 FrameLayout 中我们放置了三个 TextView 组件,分别对应三个 Tab 所显示的内容,当切换不同的 Tab 时会自动显示不同的 TextView 内容。在主程序 TabActivity 的 OnCreate() 方法中,首先获得 TabHost 的对象,并调用 setup() 方法进行初始化,然后通过 TabHost.TabSpec 增加 Tab 页,通过 setContent() 增加当前 Tab 页显示的内容,通过 setIndicator 增加页的标签,最后设定当前要显示的 Tab 页。
TabActivity 的代码如下:
package introduction.android.widgetdemo;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TabHost;
public class TabActivity extends Activity {
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.tab);
// 步骤1:获得TabHost的对象,并进行初始化setup()
TabHost tabs = (TabHost) findViewById(R.id.tabhost);
tabs.setup();
//步骤2:获得TabHost.TabSpec增加tab的一页,通过setContent()增加内容,通过setIndicator增加页的标签
/*增加第一个Tab */
TabHost.TabSpec spec = tabs.newTabSpec("Tag1");
//单击Tab要显示的内容
spec.setContent(R.id.tab1);
/* 显示Tabl内容*/
spec.setIndicator("Tab1");
tabs.addTab(spec);
/* 增加第二个Tab*/
spec = tabs.newTabSpec("Tag2");
spec.setContent(R.id.tab2);//单击Tab要显示的内容
/* 显示Tab2内容 */
spec.setIndicator("Tab2");
tabs.addTab(spec);
/*增加第三个Tab */
spec = tabs.newTabSpec("Tag3");
spec.setContent(R.id.tab3);//单击Tab要显示的内容
/* 显示Tab3内容*/
spec.setIndicator("Tab3");
tabs.addTab(spec);
/* 步骤3:可通过setCurrentTab(index)指定显示的页,从0开始计算*/
tabs.setCurrentTab(0);
}
}
除了使用上述方法设置 Tab 页面的显示内容外,还可以使用 setContent(Intent)方法启动某个 Activity,并将该 Activity 的视图作为 Tab 页面的内容。例如:
Intent intent = new Intent().setClass(this,AlbumsActivity .class);
spec = tabHost.newTabSpec("albums")
.setIndicator("Albums",res.getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_tab_albums)).setContent(intent);
tabHost.addTab(spec);
