对话框是人机交互过程中十分常见的组件,一般用于在特定条件下对用户显示一些信息,可以增强应用的友好性。 Dialog 类是对话框的基类。对话框虽然可以在界面上显示,但是 Dialog 不
Dialog 类是对话框的基类。对话框虽然可以在界面上显示,但是 Dialog 不是 View 类的子类,而是直接继承自 java.lang.Object 类。
Dialog 对象也有自己的生命周期,其生命周期由创建它的 Activity 进行管理。
Activity 可以调用 showDialog(int id) 将不同 ID 的对话框显示出来,也可以调用 dismissDialog(int id)方法将 ID 标识的对话框从用户界面中关闭掉。
当 Activity 调用了 showDialog(ID)方法,对应 ID 的对话框没有被创建时,Android 系统会回调 OnCreateDialog(ID) 方法来创建具有该 ID 的对话框。
在 Activity 中创建的对话框都会被 Activity 保存,下次 showDialog(ID) 方法被调用时,若该 ID 的对话框已经被创建,则系统不会再次调用 OnCreateDialog(ID) 方法创建该对话框,而是会回调 onPrepareDialog(int id, Dialog dialog) 方法,该方法允许对话框在被显示之前做一些修改。
常用的对话框有 AlertDialog 和 ProgressDialog,下面将通过实例讲解这两种对话框的使用方法。
AlertDialog
AlertDialog 对话框是十分常用的用于显示信息的方式,最多可提供三个按钮。AlertDialog 不能直接通过构造方法构建,而要由 AlertDialog.Builder 类来创建。
AlertDialog 对话框的标题、按钮以及按钮要响应的事件也由 AlertDialog.Builder 设置。
在使用 AlertDialog. Builder 创建对话框时常用的几个方法如下:
下面通过实例来学习创建 AlertDialog 的方法。
创建 Android 工程 DialogDemo,并在 main.xml 中添加两个按钮,分别为 AlertDialog 和 ProcessDialog。
其 main.xml 代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Dialog演示" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="AlertDialog" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="ProgressDialog" />
</LinearLayout>
其运行效果如图 1 所示。
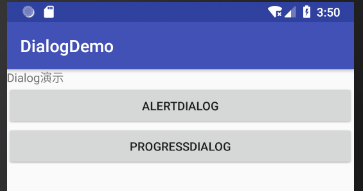
图 1 AlertDialog的运行效果
处理 AlertDialog 按钮单击事件的代码为:
btn = (Button) findViewById(R.id.button1);
btn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
showDialog(Alert_DLG);
}
});
单击 AlertDialog 按钮,调用 showDialog(ALERT_DLG),系统回调 onCreateDialog(int id) 方法,创建并弹出 AlertDialog 对话框,如图 2 所示。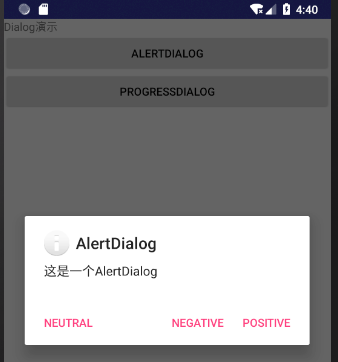
图 2 单击AlertDialog按钮的效果
相关代码为:
protected Dialog onCreateDialog(int id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Dialog dialog = null;
switch (id) {
case ALERT_DLG:
AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(DialogDemoActivity.this);
builder.setIcon(android.R.drawable.ic_dialog_info);
builder.setTitle("AlertDialog");
builder.setMessage("这是一个AlertDialog");
builder.setPositiveButton("Positive", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i("DialogDemo", "OK ! ");
}
});
builder.setNegativeButton("Negative", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i("DialogDemo", "Cancel按钮被单击! ");
}
});
builder.setNeutralButton("Neutral", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog, int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Log.i("DialogDemo", "Neutral按钮被单击!");
}
});
dialog = builder.create();
break;
default:
break;
}
return dialog;
}
onCreateDialog() 方法中创建了带有三个按钮的 AlertDialog,并且为每个按钮添加了事件处理方法,以便获知用户单击了哪个按钮。
ProgressDialog
ProgressDialog 是一个带有进度条的对话框,当应用程序在完成比较耗时的工作时,使用该对话框可以为用户提供一个总进度上的提示。为 main.xml 布局中的 ProgressDialog 按钮添加事件处理代码:
Button progressbtn = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button2);
progressbtn.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
showDialog(PROGRESS_DLG);
}
});
单击 ProgressDialog 按钮,调用 showDialog(PROGRESS_DLG) ,系统回调 onCreateDialog(int id) 方法,创建并弹出 ProgressDialog 对话框,如图 3 所示。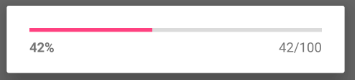
图 3 单击ProgressDialog按钮的效果
onCreateDialog() 方法中的相关代码如下:
case PROGRESS_DLG:
final ProgressDialog progressDialog;
progressDialog = new ProgressDialog(this);
//设置水平进度条
progressDialog.setProgressStyle(progressDialog.STYLE_HORIZONTAL);
//设置进度条最大值为100
progressDialog.setMax(100);
//设置进度条当前值为0
progressDialog.setProgress(0);
dialog = progressDialog;
new Thread(new Runnable() {
int count = 0;
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
while (progressDialog.getProgress() < 100) {
count += 3;
progressDialog.setProgress(count);
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
break;
