目录 声明合并 合并Interface 合并Namespace namespace和class、enum、function合并 Module扩展 全局扩展 声明合并 类型合并 表明 编译器 将 合并 两个 分开 的并且 名称 相同的声明, 合并 之后的
目录
- 声明合并
- 合并Interface
- 合并Namespace
- namespace和class、enum、function合并
- Module扩展
- 全局扩展
声明合并
类型合并表明编译器将合并两个分开的并且名称相同的声明,合并之后的声明拥有两个声明的特点,任意数量的声明可以被合并,不仅限两个。
合并Interface
1.interface的非函数成员应该是唯一的,如果两个interface都声明一个名称相同但类型不同的非函数成员,编译器将提示错误:
interface Box {
height: number;
}
interface Box {
height: string;
}

2.对于函数成员,每个相同名称的成员被看作是相同名称函数的重载,但是当出现两个interface时,第二个有更高的优先级,会覆盖前一个:
interface Cloner {
clone(animal: Animal): Animal;
}
interface Cloner {
clone(animal: Sheep): Sheep;
}
interface Cloner {
clone(animal: Dog): Dog;
clone(animal: Cat): Cat;
}
// 最终的排序是
interface Cloner {
clone(animal: Dog): Dog;
clone(animal: Cat): Cat;
clone(animal: Sheep): Sheep;
clone(animal: Animal): Animal;
}
当然这个规则有一个例外,当函数的参数类型是一个单字面量类型(single string literal type),它将会根据优先级排序,并放在声明顶部:
interface Document {
createElement(tagName: any): Element;
}
interface Document {
createElement(tagName: 'div'): HTMLDivElement;
createElement(tagName: 'span'): HTMLSpanElement;
}
interface Document {
createElement(tagName: string): HTMLElement;
createElement(tagName: 'canvas'): HTMLCanvasElement;
}
// 字面量根据冒泡排序并放在了声明顶部
interface Document {
createElement(tagName: 'canvas'): HTMLCanvasElement;
createElement(tagName: 'div'): HTMLDivElement;
createElement(tagName: 'span'): HTMLSpanElement;
createElement(tagName: string): HTMLElement;
createElement(tagName: any): Element;
}
合并Namespace
- 合并两个相同名称的
namespace时,将进一步添加第二个namespace中导出的成员到第一个namespace。
namespace Animals {
export class Zebra {}
}
namespace Animals {
export interface Legged {
numberOfLegs: number;
}
export class Dog {}
}
// 合并到了第一个
namespace Animals {
export interface Legged {
numberOfLegs: number;
}
export class Zebra {}
export class Dog {}
}
- 当一个
namespace发生合并时,和它合并的namesapce不能访问它的未导出的成员:
namespace Animal {
const haveMuscles = true;
export function animalsHaveMuscles() {
return haveMuscles;
}
}
namespace Animal {
export function doAnimalsHaveMuscles() {
return haveMuscles; // Error, because haveMuscles is not accessible here
}
}
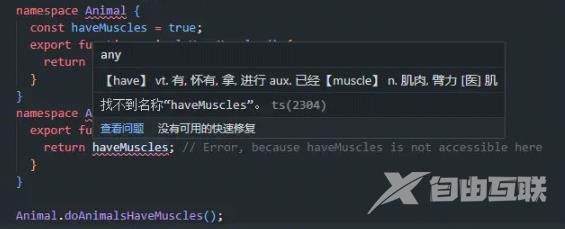
可以看到无法访问haveMuscles,同时运行也会报错,可以结合编译后的例子看:
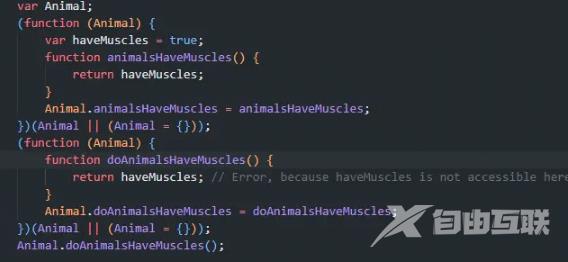
namespace和class、enum、function合并
- 和合并
namespace一样,class可以访问namespace中导出的类型和值:
class Album {
label: Album.AlbumLabel;
}
namespace Album {
export class AlbumLabel {}
}
namespace和function合并可以像javascript那样在方法上添加属性:
function buildLabel(name: string): string {
return buildLabel.prefix + name + buildLabel.suffix;
}
namespace buildLabel {
export const suffix = '';
export const prefix = 'Hello, ';
}
console.log(buildLabel('Sam Smith'));
可以看编译之后的代码,可以看到直接在buildLabel上添加了属性:
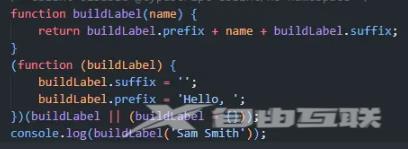
namespace和enum发生合并时,namespace可以扩展enum
enum Color {
red = 1,
green = 2,
blue = 4,
}
namespace Color {
export function mixColor(colorName: string) {
if (colorName == 'yellow') {
return Color.red + Color.green;
} else if (colorName == 'white') {
return Color.red + Color.green + Color.blue;
} else if (colorName == 'magenta') {
return Color.red + Color.blue;
} else if (colorName == 'cyan') {
return Color.green + Color.blue;
}
}
}
可以看编译之后的:
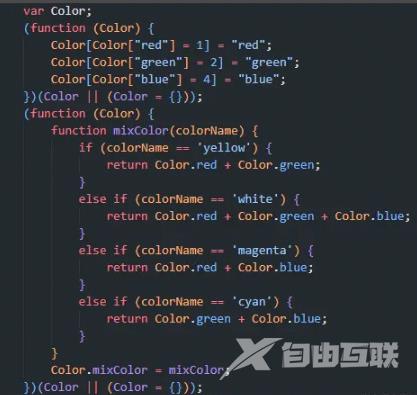
class之间不允许合并,但是如果需要模仿类似功能,可以参照 Mixins in Typscripts
Module扩展
尽管Module之间是不支持合并的,但是你可以通过导入需要扩展的方法,然后再更改它,这种方式去实现:
// observable.ts
export class Observable<T> {
// ... implementation left as an exercise for the reader ...
}
// map.ts
import { Observable } from "./observable";
Observable.prototype.map = function (f) {
// ... another exercise for the reader
};
但是这样编译器并不能提供良好的提示,所以需要扩展module的声明:
// observable.ts
export class Observable<T> {
// ... implementation left as an exercise for the reader ...
}
// map.ts
import { Observable } from "./observable";
declare module "./observable" {
interface Observable<T> {
map<U>(f: (x: T) => U): Observable<U>;
}
}
// 扩展声明
Observable.prototype.map = function (f) {
// ... another exercise for the reader
};
// consumer.ts
import { Observable } from "./observable";
import "./map";
let o: Observable<number>;
o.map((x) => x.toFixed());
全局扩展
如果在模块中,也可以在全局声明中来扩展:
// observable.ts
export class Observable<T> {
// ... still no implementation ...
}
// 在这里扩展
declare global {
interface Array<T> {
toObservable(): Observable<T>;
}
}
Array.prototype.toObservable = function () {
// ...
};
到此这篇关于typescript中声明合并介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关typescript声明合并内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
