目录
- 什么是RabbitMQ
- 消息队列:接受并转发消息,类似于快递公司
- 消息队列的优点
- 消息队列的特性
- RabbitMQ特点
- RabbitMQ核心概念
- Producer :消息生产者
- Message :消息
- Exchange :交换机
- Binding :绑定交换机和队列
- Routing key :路由键,决定路由规则
- Queue :队列,存储消息
- Connection :连接服务端
- Channel :信道,读写数据.
- Consumer :消费者
- Broker :服务实例
- Virtual host :虚拟主机,用于区分不同服务,类似于不同域名,不会相互影响
- 安装RabbitMQ
- LINUX环境下安装3.8.2 使用Xshell
- 常用命令
- Windows
- RabbitMQ实操分布了解
- 1 生产者
- 2 消费者
- Springboot 整合RabbitMQ代码实操
- 生产者
- 消费者
- 运行结果
什么是RabbitMQ
一款基于AMQP用于软件之间通信的中间件 。消费并不需要确保提供方存在,实现了服务之间的高度解耦
AMQP,即Advanced Message Queuing Protocol,高级消息队列协议,是应用层协议的一个开放标准,为面向消息的中间件设计。消息中间件主要用于组件之间的解耦,消息的发送者无需知道消息使用者的存在,反之亦然。AMQP的主要特征是面向消息、队列、路由(包括点对点和发布/订阅)、可靠性、安全。
RabbitMQ是一个开源的AMQP实现,服务器端用Erlang语言编写,支持多种客户端,如:Python、Ruby、.NET、Java、JMS、C、PHP、ActionScript、XMPP、STOMP等,支持AJAX。用于在分布式系统中存储转发消息,在易用性、扩展性、高可用性等方面表现不俗。
基本组成:Queue:消息队列,存储消息的队列,消息到达队列并转发给指定的消费方;
Exchange消息队列交换机,按一定的规则将消息路由转发到某个队列,对消息进行过虑;
消费者:消费信息;
提供者:发送消息;
官网 Messaging that just works — RabbitMQ


消息队列:接受并转发消息,类似于快递公司
product : 消息的发送者,生产者
consumer:消息的消费者,从队列获取消息,并且使用
queue :先进先出,一个queue可以对应多个consumer
消息队列的优点
代码解耦,提高系统稳定性
应对流量高峰,降低流量冲击,面对秒杀这种情况时,请求进来先去排队,可以保证系统的稳定
异步执行,提高系统响应速度
消息队列的特性
性能好
它是一种基础组件
支持消息确认,为了防止数据丢失以及应对特殊情况,在数据没有处理完,没有确认之前消息不会丢掉。
RabbitMQ特点
路由能力灵活强大
开源免费
支持编程语言多
应用广泛,社区活跃
有开箱即用的监控和管理后台
RabbitMQ核心概念
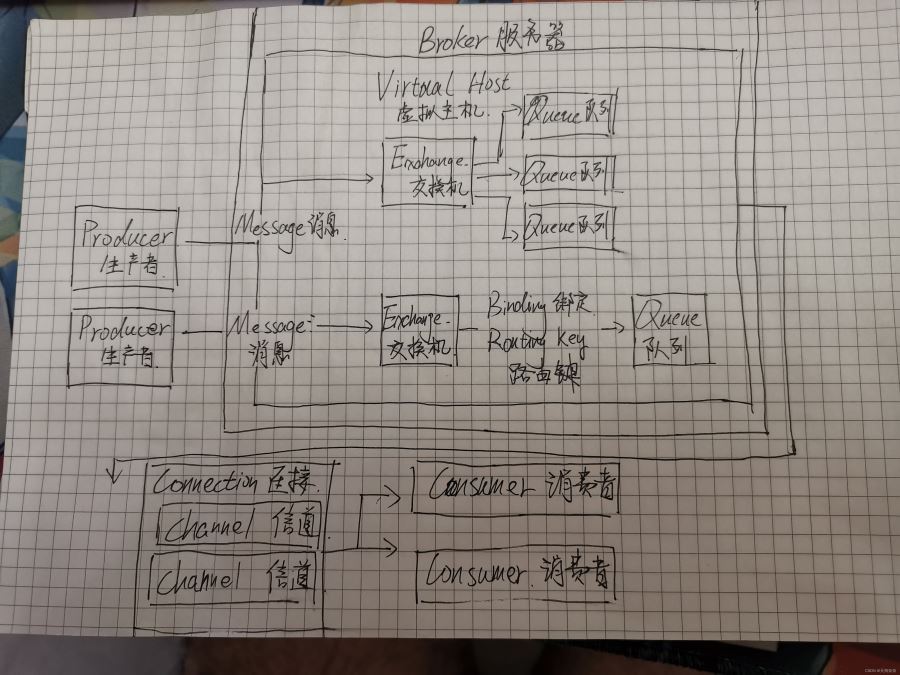
生产者数量是不限制的,生产者生产的消息Message进入交换机,交换一可以连接多个队列也可以仅连接一个对联,交换机与队列的关系是不固定的,交换机会绑定到队列上(Binding)根据的规则就是Routing Key路由键用来确定交换机与队列如何进行绑定 ,消息经过交换机经过连接发送个消费者,在连接中多多个信道,数据都是在信道中进行读写的,消费者从中提取想要的消息进行处理。Broker(服务实例)也就是服务端,Virtual Host (虚拟主机)同一个RabbitMQ可能给多个服务进行使用,服务与服务之间想要隔离开就可以使用虚拟主机进行隔离。
Producer :消息生产者
Message :消息
Exchange :交换机
Binding :绑定交换机和队列
Routing key :路由键,决定路由规则
Queue :队列,存储消息
Connection :连接服务端
Channel :信道,读写数据.
Consumer :消费者
Broker :服务实例
Virtual host :虚拟主机,用于区分不同服务,类似于不同域名,不会相互影响
安装RabbitMQ
LINUX环境下安装3.8.2 使用Xshell
先进行环境配置
连接成功以后输入
echo "export LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-8" >> /etc/profile 把编码设置成utf-8
source /etc/profile 使设置生效
输入curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash 配置RabbitMQ源

看到这个命令就可以进行下一步了
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/rabbitmq/erlang/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
配置erlang环境
看到这个命令进行下一步
sudo yum install rabbitmq-server-3.8.2-1.el7.noarch
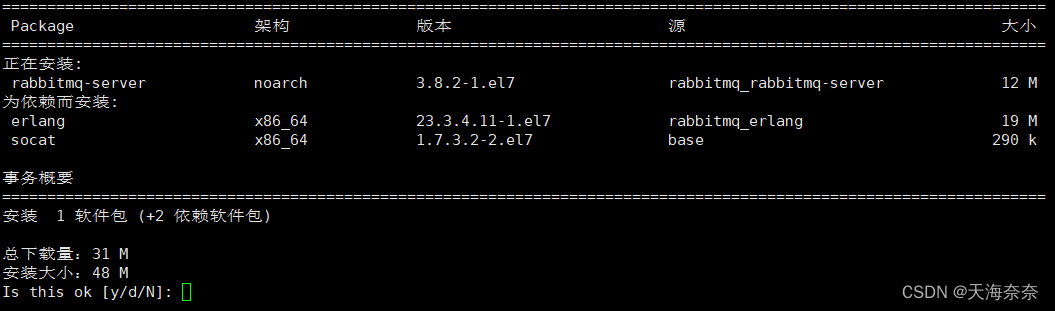
输入y
常用命令
开启web管理界面
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
停止RabbitMQ
rabbitmqctl stop
设置开机启动
systemctl enable rabbitmq-server
启动RabbitMQ
systemctl start rabbitmq-server
看看端口有没有起来,查看状态
rabbitmqctl status
要检查RabbitMQ服务器的状态,请运行:
systemctl status rabbitmq-server
Windows
先安装erlang并配置环境,安装RabbitMQ
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1S4D2zh-NSoXh-QPQVNBi-w
提取码:1111
这里直接放上链接,erlang安装好后要去配置环境

解压缩后sbin目录下,rabbitmq-server.bat 这个文件就是启动
用终端cmd输入:
cd d:\你的RabbitMQ按照地址\sbin
rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
rabbitmq-server
然后就可以用guest访问http://127.0.0.1:15672/#/
账号密码都是guest
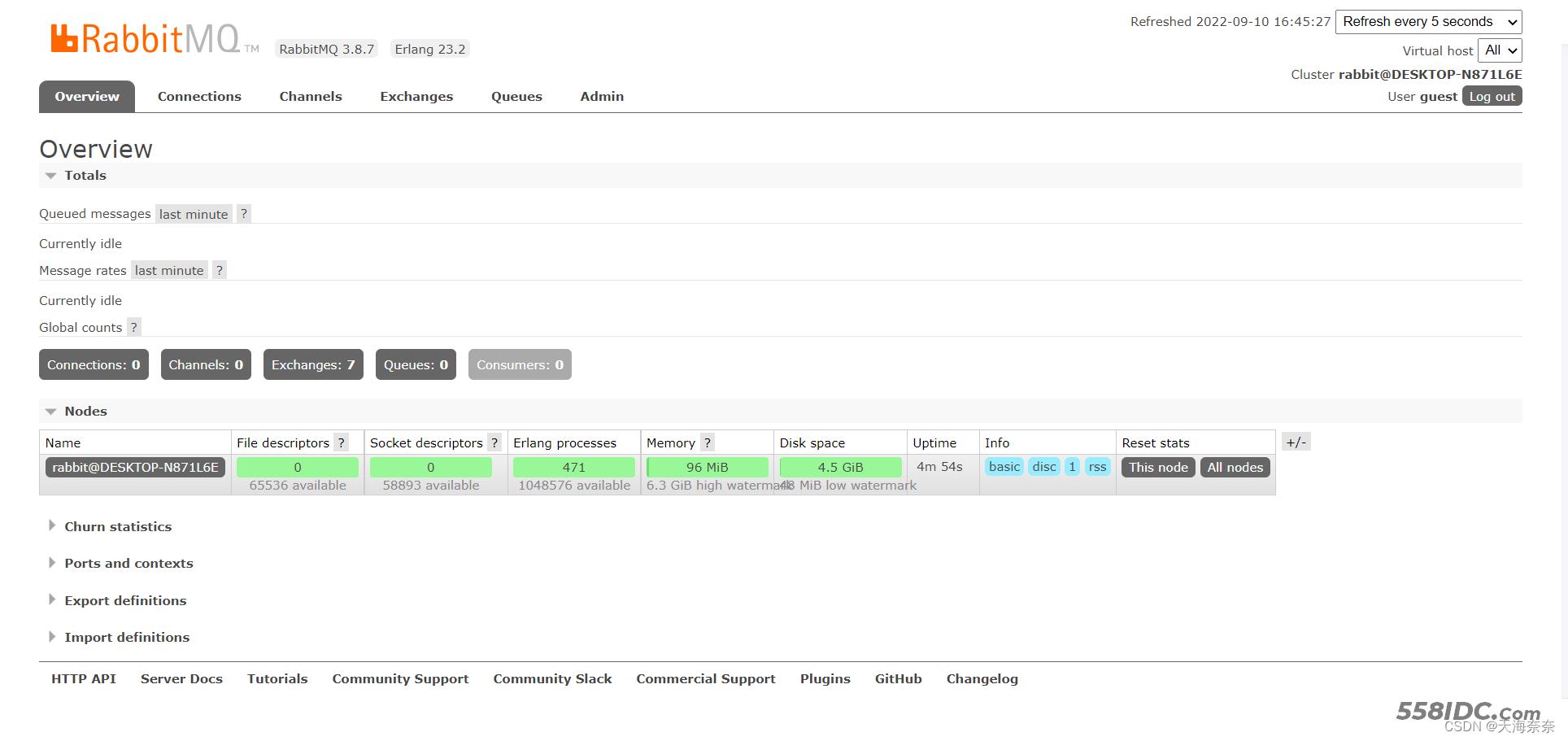
RabbitMQ实操分布了解
1 生产者
这里的前提是你有个云服务器,并且已经完成了配置,为了操作简便这里就用本机了哈
我们要有一个管理者啊在sbin目录输入
rabbitmqctl add_user newadmin newpassword
rabbitmqctl set_user_tags newadmin administrator
rabbitmqctl set_permissions -p / newadmin ".*" ".*" ".*"//这一步已经把在虚拟主机上把权限配置了
账号test 密码123456
新建一个mavene项目,

2 引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.rabbitmq</groupId>
<artifactId>amqp-client</artifactId>
<version>5.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 记录日志-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-nop</artifactId>
<version>1.7.29</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
/**
* 描述 发送类 连接到服务端 发送 退出
*/
public class Send {
//设置队列的名字
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "hello";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
//设置RabbitMQ地址
factory.setHost("127.0.0.1");
factory.setUsername("test");
factory.setPassword("123456");
//建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//获得信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列
// queueName 持久存在? 独有? 自动删除?
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
//发布消息
String message = "Hello World! ";
channel.basicPublish("", QUEUE_NAME, null, message.getBytes("UTF-8"));
System.out.println("发送了消息:" + message);
//关闭连接
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
}
运行一下

发送成功了 如果我么连接不到RabbitMQ是无法正常发送的
2 消费者
我么要做的就是把刚刚发送的存储在队列里的消息拿到并打印出来
**
* 描述: 接收消息,并打印,持续运行
*/
public class Recvice {
private final static String QUEUE_NAME = "hello";
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
//创建连接工厂
ConnectionFactory factory = new ConnectionFactory();
//设置RabbitMQ地址
factory.setHost("127.0.0.1");
factory.setUsername("test");
factory.setPassword("123456");
//建立连接
Connection connection = factory.newConnection();
//获得信道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
//声明队列
channel.queueDeclare(QUEUE_NAME, false, false, false, null);
//接收消息并消费 queueName 自动签收 处理消息
channel.basicConsume(QUEUE_NAME, true, new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope,
BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
String message = new String(body, "UTF-8");
System.out.println("收到消息:" + message);
}
});
}
}

可以看到Receive是(打错了,尬)一直运行的,我么把发送的消息改一下再发送试试


我们之前设置的是自动接收消息们可以看到运行时成功的

去web控制台也能看到是有hello这个队列的 还有更多的功能就靠你们自己去探索了
Springboot 整合RabbitMQ代码实操
1 新建两个Spring项目 一个生产者,一个消费者不需要引入依赖一会儿手动加


主要关键是定义队列 queue 定义routingKey
生产者
配置文件
guest是默认的用户只能本机时使用
server.port=8080 spring.application.name=producer spring.rabbitmq.addresses=127.0.0.1:5672 spring.rabbitmq.username=guest spring.rabbitmq.password=guest spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/ spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout=15000
依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-rabbirmq-producer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-boot-rabbirmq-producer</name>
<description>spring-boot-rabbirmq-producer</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
我们只在原基础上加了一个依赖
spring-boot-starter-amqp
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootRabbirmqProducerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRabbirmqProducerApplication.class, args);
}
}
发送消息类
/**
* 描述: 发送消息
*/
@Component
public class MessageSender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitmqTemplate;
public void send1() {
String message = "This is message 1, routing key is hello.sayHello";
System.out.println("发送了:"+message);
// 交换机 key 内容
this.rabbitmqTemplate.convertAndSend("bootExchange", "hello.sayHello", message);
}
public void send2() {
String message = "This is message 2, routing key is hello.sayNothing";
System.out.println("发送了:"+message);
this.rabbitmqTemplate.convertAndSend("bootExchange", "hello.sayNothing", message);
}
}
配置类
/**
* 描述: rabbitmq配置类
*/
@Configuration
public class TopicRabbitConfig {
//定义队列 注意类型:import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
@Bean
public Queue queue1() {
return new Queue("queue1");
}
@Bean
public Queue queue2() {
return new Queue("queue2");
}
//交换机
@Bean
TopicExchange exchange() {
return new TopicExchange("bootExchange");
}
//将队列绑定到交换机
@Bean
Binding bingdingExchangeMessage1(Queue queue1, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue1).to(exchange).with("hello.sayHello");
}
@Bean
Binding bingdingExchangeMessage2(Queue queue2, TopicExchange exchange) {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue2).to(exchange).with("hello.#");
}
}
这里注意第一个消息的routingkey是跟配置类一样的hello.sayHello 就代表 我们这个交换机是仅能识别hello.sayHello的
第二个交换机的routingkey是hello.# 那就意味着只要key是hello.()类型我们都能识别到也就是第一个和第二个消息都能识别到
编写测试类用来发送消息
@SpringBootTest
class SpringBootRabbirmqProducerApplicationTests {
@Autowired
MessageSender messageSender;
@Test
public void send1(){
messageSender.send1();
}
@Test
public void send2(){
messageSender.send2();
}
}
生产者就编写完成
消费者
配置文件,大体一样,用户我用的管理者权限的用户test 端口号不能一样
server.port=8081 spring.application.name=consumer spring.rabbitmq.addresses=127.0.0.1:5672 spring.rabbitmq.username=test spring.rabbitmq.password=123456 spring.rabbitmq.virtual-host=/ spring.rabbitmq.connection-timeout=15000
依赖 与生产者一样只用加一个
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-rabbitmq-consumer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-boot-rabbitmq-consumer</name>
<description>spring-boot-rabbitmq-consumer</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootRabbitmqConsumerApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootRabbitmqConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
}
消费者1 消费者一绑的队列是queue1 接收消息是要通过交换机-> 队列-> 信道 那就意味着队列1中将有hello.sayHello
/**
* 描述: 消费者1
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue1")
public class Receiver1 {
//处理方法
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("Receiver1: " + message);
}
}
消费者2
/**
* 描述: 消费者2
*/
@Component
@RabbitListener(queues = "queue2")
public class Receiver2 {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String message) {
System.out.println("Receiver2: " + message);
}
}
运行结果
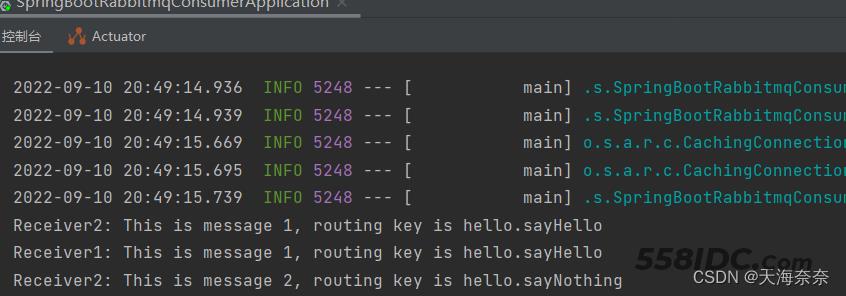
这本身是两个独立的项目,但是通过RabbitMQ使两个项目产生了连接,Springboot完成了对RabbitMQ的整合。
到此这篇关于Springboot整合RabbitMQ实现通过RabbitMQ进行项目的连接的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Springboot整合RabbitMQ内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
