目录
- 基本要点
- 1、定义
- 2、传统方式与Restful风格的区别
- 3、如何使用Restful风格
- 4、为什么要用restful
- 5、乱码问题
基本要点
1、定义
根据百度百科的定义,RESTFUL是一种网络应用程序的设计风格和开发方式
2、传统方式与Restful风格的区别
在我们学习restful风格之前,我们请求接口,都是使用http://localhost:8080/controller?method=add这种方式携带接口所需要的参数
而调用restful风格的接口时,我们可以改成http://localhost:8080/controller/add这种类型
3、如何使用Restful风格
我们通过一个代码demo来了解一下它的使用方法
首先,我们设置当前module为web项目,在web.xml中配置一下DispatcherServlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
然后我们配置一下springmvc的配置文件springmvc-servlet.xml
这里使用<mvc:annotation-driven/>,会在Spring MVC上下文中定义一个org.springframework.web.servlet.resource.DefaultServletHttpRequestHandler,它会像一个检查员,对DispatcherServlet的请求进行处理,如果该请求已经作了映射,那么会接着交给后台对应的处理程序,如果没有作映射,就交给 WEB 应用服务器默认的 Servlet 处理,从而找到对应的静态资源,只有再找不到资源时才会报错
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
https://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!-- 开启自动扫描,让指定包下的注解生效,由IOC容器统一管理 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.decade3.controller"/>
<!-- 支持mvc注解驱动 -->
<mvc:annotation-driven/>
<!-- 让Spring MVC不处理静态资源 -->
<mvc:default-servlet-handler/>
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="internalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
</beans>
接着我们在WEB-INF下新建一个jsp文件夹,在下面新建一个rest.jsp页面,写一个form表单,点击按钮触发post方法
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${msg}
<form action="/restful/add/spring-/mvc" method="post">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
和一个rest2.jsp页面
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${msg}
</body>
</html>
最后我们写一个控制器类HelloController.java,使用相同的路径但是使用不同的请求方法
package com.decade3.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/restful")
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String test1(@PathVariable(value = "a") int a, @PathVariable(value = "b")int b, Model model) {
int result = a + b;
model.addAttribute("msg", result);
return "rest";
}
@PostMapping(value = "/add/{a}/{b}")
public String test2(@PathVariable(value = "a") String a, @PathVariable(value = "b")String b, Model model) {
String result = a + b;
model.addAttribute("msg", result);
return "rest2";
}
}
最后我们启动tomcat验证一下,如果出现报错请参考我之前的博客SpringMVC执行过程详细讲解
在地址栏直接输入url是get请求,所以我们走的是test1方法,页面会跳转到rest.jsp
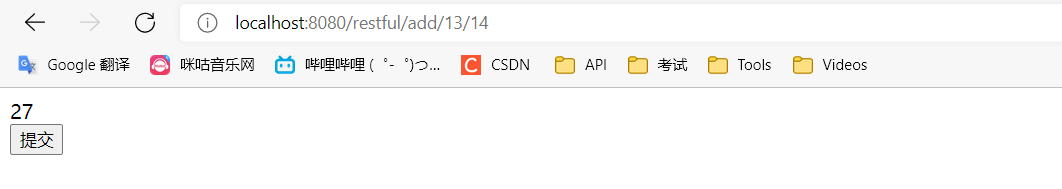
我们点击提交按钮,会触发调用post方法,走test2,跳转到rest2.jsp
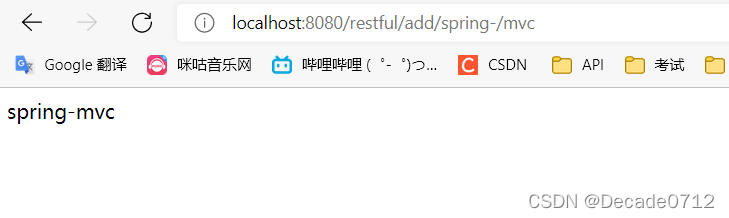
如图所示,结果符合我们的预期
- 关于@PathVariable注解
我们可以通过@PathVariable将url中的参数与方法上的参数绑定起来
- 关于请求方法类型
我们可以使用POST、DELETE、PUT、GET,使用不同方法对资源进行操作。
分别对应 添加、 删除、修改、查询
我们可以通过限制method类型,来实现url请求地址的复用
如上图中,我们可以都使用http://localhost:8080/restful/add/a/b的形式,通过限制方法去调用不同的接口
- 控制器类中的@PostMapping(value = “/add/{a}/{b}”)和@RequestMapping(value = “/add/{a}/{b}”, method = RequestMethod.POST)是一样
除了@PostMapping之外,常用的还有
@GetMapping
@PutMapping
@DeleteMapping
@PatchMapping
4、为什么要用restful
我个人认为,使用restful风格的接口,使得我们的请求路径更加简洁,而且相同的接口可以通过限制请求方式实现不同的功能,增加了代码的复用性,最后,restful风格的参数是直接拼接在url上的,我们不需要对参数做出解释,提升了安全性
5、乱码问题
有时候我们使用post请求时,如果参数中携带中文汉字,可能会出现解析乱码的情况
这个时候,我们就可以使用spring提供的过滤器来解决,我们需要在web.xml中增加如下配置
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>utf-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
到此这篇关于SpringMVC Restful风格与中文乱码问题解决方案介绍的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关SpringMVC Restful内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
