目录
- 正文
- 1.初始化张量
- 1.1 直接从列表数据初始化
- 1.2 用 NumPy 数组初始化
- 1.3 从另一个张量初始化
- 1.4 使用随机值或常量值初始化
- 2.张量的属性
- 3.张量运算
- 3.1 标准的类似 numpy 的索引和切片:
- 3.2 连接张量
- 3.3 算术运算
- 3.4单元素张量 Single-element tensors
- 3.5 In-place 操作
- 4. 张量和NumPy 桥接
- 4.1 张量到 NumPy 数组
- 4.2 NumPy 数组到张量
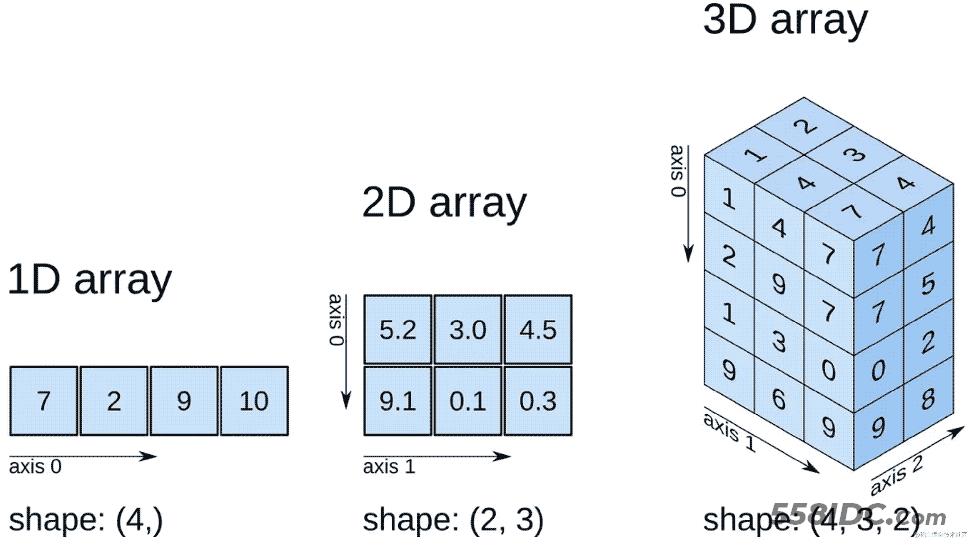
正文
张量是一种特殊的数据结构,与数组和矩阵非常相似。在 PyTorch 中,我们使用张量对模型的输入和输出以及模型的参数进行编码。
张量类似于NumPy 的ndarray,除了张量可以在 GPU 或其他硬件加速器上运行。事实上,张量和 NumPy 数组通常可以共享相同的底层内存,从而无需复制数据(请参阅Bridge with NumPy)。张量也针对自动微分进行了优化(我们将在稍后的Autograd 部分中看到更多相关内容)。如果您熟悉 ndarrays,那么您对 Tensor API 会很快熟悉。
# 导入需要的包 import torch import numpy as np
1.初始化张量
张量可以以各种方式初始化。请看以下示例:
1.1 直接从列表数据初始化
张量可以直接从列表数据中创建。数据类型是自动推断的。
# 创建python list 数据 data = [[1, 2],[3, 4]] # 初始化张量 x_data = torch.tensor(data)
1.2 用 NumPy 数组初始化
张量可以从 NumPy 数组创建(反之亦然 - 请参阅Bridge with NumPy)。
# 创建numpy 数组 np_array = np.array(data) # from_numpy初始化张量 x_np = torch.from_numpy(np_array)
1.3 从另一个张量初始化
新张量保留原张量的属性(形状shape、数据类型datatype),除非显式覆盖。
# 创建和x_data (形状shape、数据类型datatype)一样的张量并全部初始化为1
x_ones = torch.ones_like(x_data) # retains the properties of x_data
print(f"Ones Tensor: \n {x_ones} \n")
# 创建和x_data (形状shape)一样的张量并随机初始化,覆盖其数据类型datatype 为torch.float
x_rand = torch.rand_like(x_data, dtype=torch.float) # overrides the datatype of x_data
print(f"Random Tensor: \n {x_rand} \n")
Ones Tensor:
tensor([[1, 1],
[1, 1]])
Random Tensor:
tensor([[0.5001, 0.2973],
[0.8085, 0.9395]])
1.4 使用随机值或常量值初始化
shape是张量维度的元组。在下面的函数中,它决定了输出张量的维度。
# 定义形状元组
shape = (2,3,)
# 随机初始化
rand_tensor = torch.rand(shape)
# 全部初始化为1
ones_tensor = torch.ones(shape)
# 全部初始化为0
zeros_tensor = torch.zeros(shape)
print(f"Random Tensor: \n {rand_tensor} \n")
print(f"Ones Tensor: \n {ones_tensor} \n")
print(f"Zeros Tensor: \n {zeros_tensor}")
Random Tensor:
tensor([[0.0032, 0.5302, 0.2832],
[0.0826, 0.3679, 0.8727]])
Ones Tensor:
tensor([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
Zeros Tensor:
tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
2.张量的属性
张量属性描述了它们的形状Shape、数据类型Datatype和存储它们的设备Device。
tensor = torch.rand(3,4)
print(f"Shape of tensor: {tensor.shape}")
print(f"Datatype of tensor: {tensor.dtype}")
print(f"Device tensor is stored on: {tensor.device}")
Shape of tensor: torch.Size([3, 4]) Datatype of tensor: torch.float32 Device tensor is stored on: cpu
3.张量运算
这里全面介绍了超过 100 种张量运算,包括算术、线性代数、矩阵操作(转置、索引、切片)、采样等。
这些操作中的每一个都可以在 GPU 上运行(通常以比 CPU 更高的速度)。
默认情况下,张量是在 CPU 上创建的。我们需要使用 .to方法明确地将张量移动到 GPU(在检查 GPU 可用性之后)。请记住,跨设备复制大张量在时间和内存方面可能会很昂贵!
# We move our tensor to the GPU if available
if torch.cuda.is_available():
tensor = tensor.to("cuda")
尝试列表中的一些操作。如果您熟悉 NumPy API,您会发现 Tensor API 使用起来轻而易举。
3.1 标准的类似 numpy 的索引和切片:
tensor = torch.ones(4, 4)
print(f"First row: {tensor[0]}")
print(f"First column: {tensor[:, 0]}")
print(f"Last column: {tensor[..., -1]}")
tensor[:,1] = 0
print(tensor)
First row: tensor([1., 1., 1., 1.])
First column: tensor([1., 1., 1., 1.])
Last column: tensor([1., 1., 1., 1.])
tensor([[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.]])
3.2 连接张量
您可以用来torch.cat沿给定维度连接一系列张量。另请参阅torch.stack,另一个与torch.cat.
t1 = torch.cat([tensor, tensor, tensor], dim=1) print(t1)
tensor([[1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1., 1., 0., 1., 1.]])
3.3 算术运算
# This computes the matrix multiplication between two tensors. y1, y2, y3 will have the same value y1 = tensor @ tensor.T y2 = tensor.matmul(tensor.T) y3 = torch.rand_like(y1) torch.matmul(tensor, tensor.T, out=y3) # This computes the element-wise product. z1, z2, z3 will have the same value z1 = tensor * tensor z2 = tensor.mul(tensor) z3 = torch.rand_like(tensor) torch.mul(tensor, tensor, out=z3)
tensor([[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.]])
3.4单元素张量 Single-element tensors
如果您有一个单元素张量,例如通过将张量的所有值聚合为一个值,您可以使用以下方法将其转换为 Python 数值item():
agg = tensor.sum() agg_item = agg.item() print(agg_item, type(agg_item))
12.0 <class 'float'>
3.5 In-place 操作
将结果存储到操作数中的操作称为In-place操作。它们由_后缀表示。例如:x.copy_(y), x.t_(), 会变x。
print(f"{tensor} \n")
tensor.add_(5)
print(tensor)
tensor([[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.],
[1., 0., 1., 1.]])
tensor([[6., 5., 6., 6.],
[6., 5., 6., 6.],
[6., 5., 6., 6.],
[6., 5., 6., 6.]])
注意:
In-place 操作可以节省一些内存,但在计算导数时可能会出现问题,因为会立即丢失历史记录。因此,不鼓励使用它们。
4. 张量和NumPy 桥接
CPU 和 NumPy 数组上的张量可以共享它们的底层内存位置,改变一个会改变另一个。
4.1 张量到 NumPy 数组
t = torch.ones(5)
print(f"t: {t}")
n = t.numpy()
print(f"n: {n}")
t: tensor([1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]) n: [1. 1. 1. 1. 1.]
张量的变化反映在 NumPy 数组中。
t.add_(1)
print(f"t: {t}")
print(f"n: {n}")
t: tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2.]) n: [2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
4.2 NumPy 数组到张量
n = np.ones(5) t = torch.from_numpy(n)
NumPy 数组的变化反映在张量中。
np.add(n, 1, out=n)
print(f"t: {t}")
print(f"n: {n}")
t: tensor([2., 2., 2., 2., 2.], dtype=torch.float64) n: [2. 2. 2. 2. 2.]
以上就是python机器学习pytorch 张量基础教程的详细内容,更多关于python机器学习pytorch张量的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
