目录 一、文件 1、基本解释 2、常用的文件操作 3、获取文件相关信息 4、目录操作和文件删除 二、IO流原理及分类 1、IO流原理 2、流的分类 3、IO流体系图 一、文件 1、基本解释 (1)什
目录
- 一、文件
- 1、基本解释
- 2、常用的文件操作
- 3、获取文件相关信息
- 4、目录操作和文件删除
- 二、IO流原理及分类
- 1、IO流原理
- 2、流的分类
- 3、IO流体系图
一、文件
1、基本解释
(1)什么是文件?
文件是保存数据的地方,比如大家经常使用的word文档、txt文件、excel文件等都是文件。它还可以保存一张图片,也可以保存视频声音
(2)文件流

流 :数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径
输入流 : 数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
输出流 :数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
2、常用的文件操作
(1)相关方法
- new File(String pathname) --> 根据路径构建一个File对象
- new File(File parent,String child) --> 根据父目录文件+子路径构建
- new File(String parent,String child) --> 根据父目录+子路径构建
- createNewFile 创建新文件
(2)代码示例
(①)方式一:new File(String pathname)
//方式1 new File(String pathname)
public void create01(){
//定好路径
String filePath = "D:\\news1.txt";
//创建路径对象
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
//根据路径创建文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建文件成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
(②)方式二:new File(File parent,String child)
//第二种方式 new File(File parent,String child) ,根据父目录文件 + 子路径构建
//D:\\news2.txt
public void create02(){
File parentFile = new File("D:\\");
String fileName = "news2.txt";
//创建路径对象
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
try {
//根据路径创建文件
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
(③)方式三:new File(String parent,String child)
//第三种方式 new File(String parent,String child) ,根据父目录文件 + 子路径构建
//D:\\news3.txt
public void create03(){
String parentFile = "D:\\";
String fileName = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3、获取文件相关信息
(1)常用方法:代码示例
//获取文件的信息
public void info(){
//先创建文件对象
File file = new File("D:\\news1.txt");
//调用相应的方法,得到对应的信息
System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("是否有文件存在=" + file.exists());
System.out.println("是不是有一个文件=" + file.isFile());
System.out.println("是不是有一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());
}
4、目录操作和文件删除
- mkdir 创建一级目录
- mkdirs 创建多级目录
- delete 删除空目录或文件
==》代码示例1:
//判断 d:\\news1.txt 是否存在,如果存在就删除
public void m1(){
//文件路径
String filePath = "d:\\news1.txt";
//创建文件路径对象
File file = new File(filePath);
//首先判断文件是否存在
if (file.exists()){
//如果存在,就删除
if (file.delete()){
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("该文件不存在.....");
}
}
==》代码示例2:
//判断 d:\\demo02 是否存在,如果存在就删除
//这里我们需要体会到,在Java编程中,目录也被当做文件
public void m2(){
//文件路径
String filePath = "d:\\demo02";
//创建文件路径对象
File file = new File(filePath);
//首先判断文件是否存在
if (file.exists()){
//如果存在,就删除
if (file.delete()){
System.out.println(filePath + "删除成功");
}else {
System.out.println("删除失败");
}
}else {
System.out.println("该目录不存在.....");
}
}
==》代码示例3:
//判断:D:\\demo\\a\\b\\c 目录是否存在,如果存在就提示已经存在,否则就创建
public void m3(){
//文件路径
String directoryPath = "D:\\demo\\a\\b\\c";
//路径对象
File file = new File(directoryPath);
//首先判断文件是否存在
if (file.exists()){
System.out.println(directoryPath + "存在");
}else {
if (file.mkdirs()){
System.out.println(directoryPath + "创建成功");
}else {
System.out.println("创建失败");
}
}
}
二、IO流原理及分类
1、IO流原理
- I / O是 Input / Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输,如读文件、写文件,网结通讯等
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入/输出操作以”流(stream)" 的方式进行。
- java.io 包下提供了各种“流”的类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或输出数据
- 输入(input) : 读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
- 输出(output): 将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、 光盘等存储设备中
- 原理示意图:
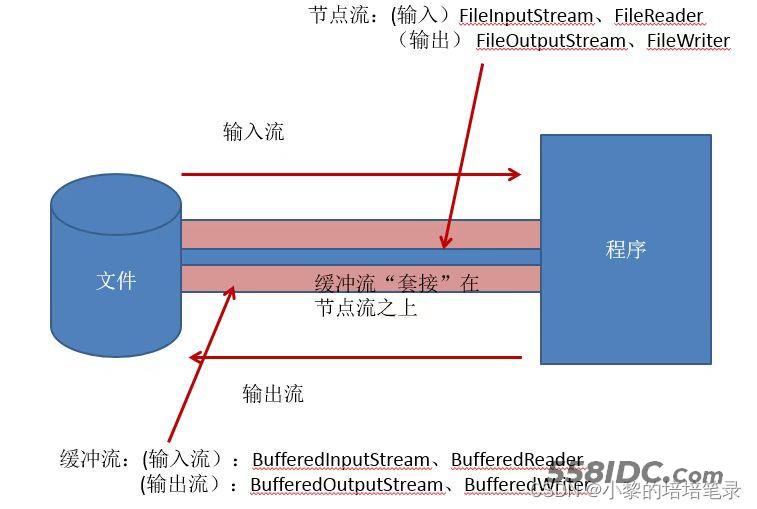
2、流的分类
- 按操作数据单位不同分为 : 字节流(8 bit)二进制文件,字符流(按字符)文本文件
- 按数据流的流向不同分为 : 输入流,输出流
- 按流的角色的不同分为 : 节点流,处理流/包装流

注意:
1、Java的I0流共涉及40多个类 实际上非常规则 都是从如上4个抽象基类派生的
2、由这四个类派生出来的子类名称都是以其父类名作为子类名后缀
3、IO流体系图
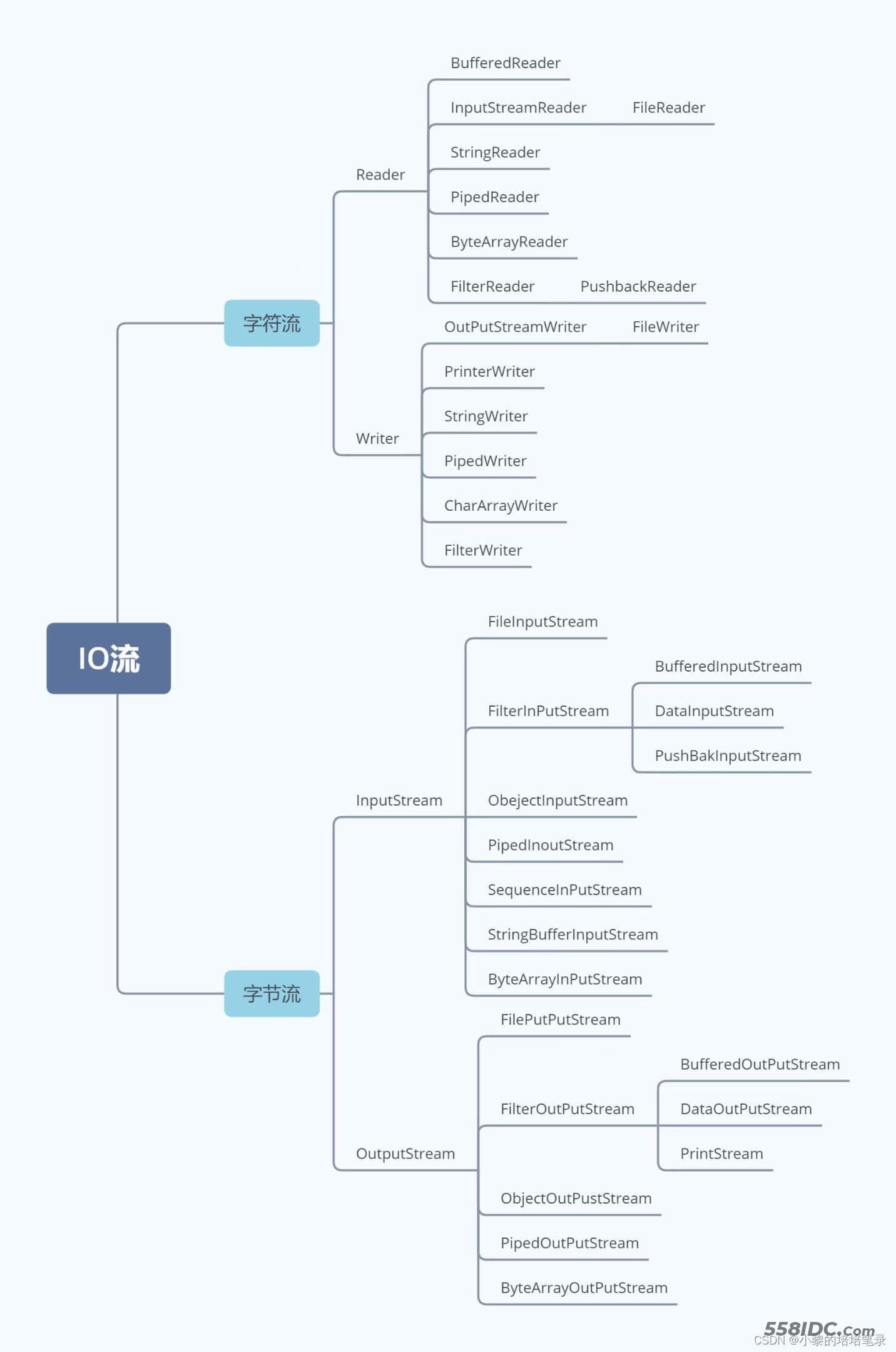
到此这篇关于Java文件与IO流操作原理详细分析的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Java文件与IO流内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
