在编写 CSS 时,有时可能会使用很长的选择器列表来定位具有相同样式规则的多个元素。例如,如果您想对标题中的 b 标签进行颜色调整,我们应该都写过这样的代码: h1 b, h2 b, h3 b,
在编写 CSS 时,有时可能会使用很长的选择器列表来定位具有相同样式规则的多个元素。例如,如果您想对标题中的 b 标签进行颜色调整,我们应该都写过这样的代码:
h1 > b, h2 > b, h3 > b, h4 > b, h5 > b, h6 > b {
color: hotpink;
}
现在,我们可以使用 :is() 缩减代码并提高其可读性:
:is(h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6) > b {
color: hotpink;
}
可以放在选择器之后
article :is(.header,.footer) > b {
color: gray;
}
相当于:
article .header b, article .footer b {
color: gray;
}
可以组合使用:
:is(h1,h6):is(.header,.footer) > b {
color: blue;
}
相当于
h1.header > b, h1.footer > b, h6.header > b, h6.footer > b {
color: blue;
}
:where() 函数 和 :is()函数功能一样,不过:is()权重比:where()权重高
:is(h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6) > b { /* :is 生效 */
color: hotpink;
}
:where(h1,h2,h3,h4,h5,h6) > b {
color: red;
}
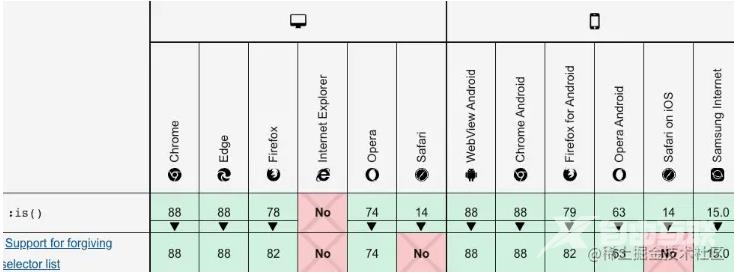
浏览器兼容性:
到此这篇关于新的CSS 伪类函数 :is() 和 :where()示例详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关CSS 伪类函数内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章,希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
