代码案例 简单Demo 代码: public static void Main() { //创建一个任务 Taskint task = new Taskint(() = { int sum = 0; Console.WriteLine("使用Task異步執行操作."); for (int i = 0; i = 100; i++) { sum += i; } return sum; })
代码案例
简单Demo
代码:
public static void Main()
{
//创建一个任务
Task<int> task = new Task<int>(() =>
{
int sum = 0;
Console.WriteLine("使用Task異步執行操作.");
for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++)
{
sum += i;
}
return sum;
});
//启动任务,并安排到当前任务队列线程中执行任务(System.Threading.Tasks.TaskScheduler)
task.Start();
Console.WriteLine("主線程執行其他程序.");
//任务完成时执行处理。
Task cwt = task.ContinueWith(t =>
{
Console.WriteLine("任務完成後的結果是:{0}", t.Result.ToString());
});
task.Wait();
cwt.Wait();
Console.ReadLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
结果:

任务的串行
代码:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
ConcurrentStack<int> stack = new ConcurrentStack<int>();
//t1先串行
var t1 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
//入棧
stack.Push(1);
stack.Push(2);
});
//t2,t3并行执行
var t2 = t1.ContinueWith(t =>
{
int result;
//出棧
stack.TryPop(out result);
Console.WriteLine("Task t2 result={0},Thread id {1}", result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
});
//t2,t3并行执行
var t3 = t1.ContinueWith(t =>
{
int result;
//出棧
stack.TryPop(out result);
Console.WriteLine("Task t3 result={0},Thread id {1}", result, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
});
//等待t2和t3执行完
Task.WaitAll(t2, t3);
//t7串行执行
var t4 = Task.Factory.StartNew(() =>
{
Console.WriteLine("當前的集合數目:{0},Thread id {1}", stack.Count, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
});
t4.Wait();
Console.ReadKey();
}
结果:

子任务
代码:
public static void Main()
{
Task<string[]> parent = new Task<string[]>(state =>
{
Console.WriteLine(state);
string[] result = new string[2];
//创建并启动子任务
new Task(() => { result[0] = "我是子任務1。"; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start();
new Task(() => { result[1] = "我是子任務2。"; }, TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent).Start();
return result;
}, "我是父任務,並在處理過程中創建多個子任務,所有的子任務完成以後我才會開始執行。");
//任务处理完成后执行的操作
parent.ContinueWith(t =>
{
Array.ForEach(t.Result, r => Console.WriteLine(r));
});
//启动父任务
parent.Start();
//等待任务结束 Wait只能等待父线程结束,没办法等到父线程的ContinueWith结束
//parent.Wait();
Console.ReadLine();
}
结果:

动态并行
代码:
class Node
{
public Node Left { get; set; }
public Node Right { get; set; }
public string Text { get; set; }
}
class Program
{
static Node GetNode()
{
Node root = new Node
{
Left = new Node
{
Left = new Node
{
Text = "L-L"
},
Right = new Node
{
Text = "L-R"
},
Text = "L"
},
Right = new Node
{
Left = new Node
{
Text = "R-L"
},
Right = new Node
{
Text = "R-R"
},
Text = "R"
},
Text = "Root"
};
return root;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Node root = GetNode();
DisplayTree(root);
}
static void DisplayTree(Node root)
{
var task = Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DisplayNode(root),
CancellationToken.None,
TaskCreationOptions.None,
TaskScheduler.Default);
task.Wait();
}
static void DisplayNode(Node current)
{
if (current.Left != null)
Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DisplayNode(current.Left),
CancellationToken.None,
TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent,
TaskScheduler.Default);
if (current.Right != null)
Task.Factory.StartNew(() => DisplayNode(current.Right),
CancellationToken.None,
TaskCreationOptions.AttachedToParent,
TaskScheduler.Default);
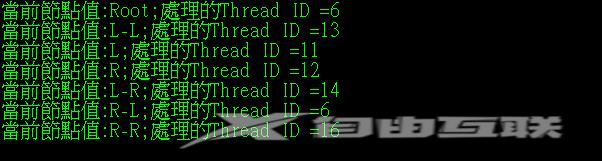
Console.WriteLine("當前節點值:{0};處理的Thread ID ={1}", current.Text, Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);
}
}
结果:
到此这篇关于C#使用Task.ContinueWith组合任务的文章就介绍到这了。希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
