目录
- jsx
- v16.x及以前版本
- v17及之后版本
- ReactElement
- React.createElement
- ReactElement
- React.Component
- 总结
经过多年的发展,React已经更新了大版本16、17、18,本系列主要讲的是 version:17.0.2,在讲这个版本之前,我们先看一看在babel的编译下,每个大版本之下会有什么样的变化。
jsx
<div className='box'>
<h1 className='title' style={{'color':'red'}}>React源码解析</h1>
<ul>
<li>第一章</li>
<li>第二章</li>
<li>第三章</li>
<li>第四章</li>
</ul>
</div>
v16.x及以前版本
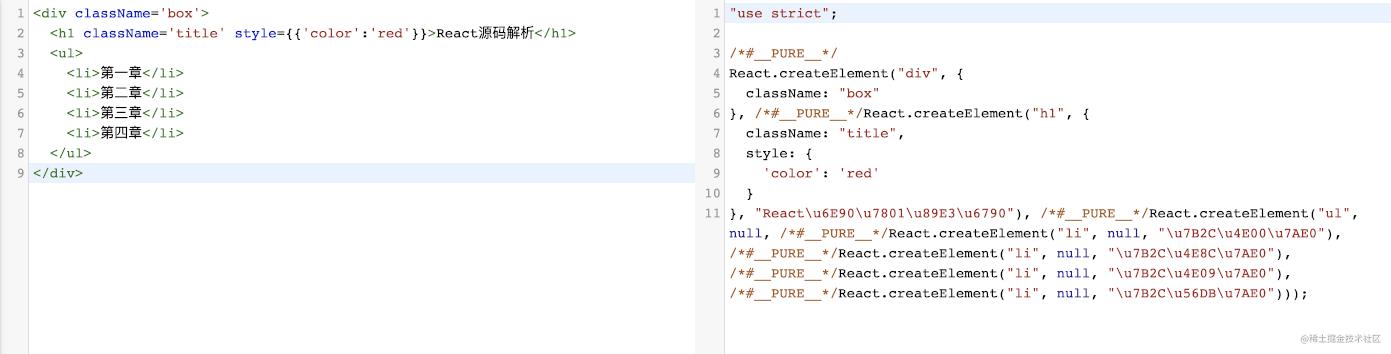
v17及之后版本

所以各位看到了,在v16及以前我们babel进行jsx解析编译的是根据@babel/babel-preset-react-app解析成React.createElement进行包裹的,而v17以及之后的版本,官网早就说明,对jsx的转换用react/jsx-runtime,而不再依赖React.createElement了,看到这里我想各位对不同版本的babel解析jsx已经有了眉目了,早已经迫不及待想去看看jsx-runtime和createElement到底是如何玩的,那么进入源码
在babel解析后的v17产物中我们可以看得到 var _jsxRuntime = require("react/jsx-runtime");那么我们追本溯源可以找到在packages/react/src/jsx/ReactJSX.js里面的jsxs是怎么来的
// packages/react/src/jsx/ReactJSX.js
import {REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE} from 'shared/ReactSymbols';
import {
jsxWithValidationStatic,
jsxWithValidationDynamic,
jsxWithValidation,
} from './ReactJSXElementValidator';
import {jsx as jsxProd} from './ReactJSXElement';
const jsx = __DEV__ ? jsxWithValidationDynamic : jsxProd;
const jsxs = __DEV__ ? jsxWithValidationStatic : jsxProd;
const jsxDEV = __DEV__ ? jsxWithValidation : undefined;
export {REACT_FRAGMENT_TYPE as Fragment, jsx, jsxs, jsxDEV};
在非dev环境下我们继续去找jsProd
export function jsx(type, config, maybeKey) {
let propName;
//标签上的属性集合
const props = {};
//单独处理key ref
let key = null;
let ref = null;
if (maybeKey !== undefined) {
key = '' + maybeKey;
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
// 处理合法的key
key = '' + config.key;
}
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
// 处理合法的ref
ref = config.ref;
}
// 把属性加到props中
for (propName in config) {
if (
hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)
) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
// 处理默认props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
undefined,
undefined,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props
)
}
ReactElement
const ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
const element = {
// 表示是否为ReactElement
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// 元素自身属性
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
if (__DEV__) {
element._store = {};
// 开发环境下将_store、_self、_source属性变为不可枚举
Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
value: false,
});
Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: self,
});
Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: source,
});
// 冻结props、element防止被手动修改
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(element.props);
Object.freeze(element);
}
}
return element;
};
这上面便是v17及之后版本的jsx-runtime所做的事情。那么这里再去看一下v16中的createElement所做的事情吧。
相关参考视频讲解:进入学习
React.createElement
// packages/react/src/ReactElement.js
export function createElement(type, config, children) {
let propName;
// 记录标签上的属性集合
const props = {};
//单独处理key ref
let key = null;
let ref = null;
let self = null;
let source = null;
// 当config部位null的时候,表示标签上有属性,加到props里面去
if (config != null) {
// 合法的ref才做处理
if (hasValidRef(config)) {
ref = config.ref;
if (__DEV__) {
warnIfStringRefCannotBeAutoConverted(config);
}
}
if (hasValidKey(config)) {
// 有合法的key才做处理
key = '' + config.key;
}
// 记录信息用于debug
self = config.__self === undefined ? null : config.__self;
source = config.__source === undefined ? null : config.__source;
// 处理self,source,key,ref以外的属性,加入props中
for (propName in config) {
if (
hasOwnProperty.call(config, propName) &&
!RESERVED_PROPS.hasOwnProperty(propName)
) {
props[propName] = config[propName];
}
}
}
// 处理子节点
const childrenLength = arguments.length - 2;
// 单标签子节点
if (childrenLength === 1) {
props.children = children;
//嵌套子节点
} else if (childrenLength > 1) {
const childArray = Array(childrenLength);
for (let i = 0; i < childrenLength; i++) {
childArray[i] = arguments[i + 2];
}
//开发环境冻结,childArray防止被修改
if (__DEV__) {
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(childArray);
}
}
props.children = childArray;
}
// 处理默认props
if (type && type.defaultProps) {
const defaultProps = type.defaultProps;
for (propName in defaultProps) {
if (props[propName] === undefined) {
props[propName] = defaultProps[propName];
}
}
}
if (__DEV__) {
// dev环境下,key 与 ref不挂到props中去
if (key || ref) {
const displayName =
typeof type === 'function'
? type.displayName || type.name || 'Unknown'
: type;
if (key) {
defineKeyPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
if (ref) {
defineRefPropWarningGetter(props, displayName);
}
}
}
// 调用返回
return ReactElement(
type,
key,
ref,
self,
source,
ReactCurrentOwner.current,
props,
);
}
由React.createElement源码得知,他做了如下事情
- 解析
config参数中是否有合法的key、ref属性,并处理,并将其他的属性挂到props上。 - 解析函数的第三参数,并分情况将第三参数挂到
props.children上。 - 对默认props进行处理,如果存在该属性则直接挂载到props上,不存在则要添加上。
- 开发环境下将
_store、_self、_source设置为不可枚举状态,为后期的diff比较作优化,提高比较性能。 - 将
type、key、ref、props等属性通过调用ReactElement函数创建虚拟dom。
ReactElement
const ReactElement = function(type, key, ref, self, source, owner, props) {
const element = {
// This tag allows us to uniquely identify this as a React Element
$$typeof: REACT_ELEMENT_TYPE,
// Built-in properties that belong on the element
type: type,
key: key,
ref: ref,
props: props,
// Record the component responsible for creating this element.
_owner: owner,
};
if (__DEV__) {
// The validation flag is currently mutative. We put it on
// an external backing store so that we can freeze the whole object.
// This can be replaced with a WeakMap once they are implemented in
// commonly used development environments.
element._store = {};
// To make comparing ReactElements easier for testing purposes, we make
// the validation flag non-enumerable (where possible, which should
// include every environment we run tests in), so the test framework
// ignores it.
Object.defineProperty(element._store, 'validated', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: true,
value: false,
});
// self and source are DEV only properties.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_self', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: self,
});
// Two elements created in two different places should be considered
// equal for testing purposes and therefore we hide it from enumeration.
Object.defineProperty(element, '_source', {
configurable: false,
enumerable: false,
writable: false,
value: source,
});
if (Object.freeze) {
Object.freeze(element.props);
Object.freeze(element);
}
}
return element;
};
仔细瞧一瞧,这个其实跟jsxs调用的ReactElement实现的差不多的功能,但是为什么要写两遍?仔细看来,在两个版本的ReactElement中,传入的参数不一致,在开发环境下,分别对其做劫持不可枚举状态,仅此而已
React.Component
写惯了hooks组件,但是Class组件也别忘了哟,因为在React17里面Class组件也是没有被抹去的,所以既然是源码解析,那么我们也要来看一看这个Component到底干了啥。
// packages/react/src/ReactBaseClasses.js
function Component(props, context, updater) {
// 接受各种参数,挂到this上
this.props = props;
this.context = context;
this.refs = emptyObject;
// updater ??
this.updater = updater || ReactNoopUpdateQueue;
}
// 原型上挂载了isReactComponent用来区分函数组件与类组件
Component.prototype.isReactComponent = {};
//原型上挂载了setState方法用来触发更新
Component.prototype.setState = function(partialState, callback) {
invariant(
typeof partialState === 'object' ||
typeof partialState === 'function' ||
partialState == null,
'setState(...): takes an object of state variables to update or a ' +
'function which returns an object of state variables.',
);
// 调用updater上的enqueueSetState方法???
this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, 'setState');
};
// 原型上挂载了强制更新的方法
Component.prototype.forceUpdate = function(callback) {
this.updater.enqueueForceUpdate(this, callback, 'forceUpdate');
};
从源码上可以得知,React.Component 主要做了以下几件事情:
- 将
props, context, updater挂载到this上,props,context一目了然,后面的updater位触发器,上面挂了很多方法,我们后面再谈。 - 在
Component原型链上添加isReactComponent对象,用于区分函数组件还是类组件。 - 在
Component原型链上添加setState方法,触发更新。 - 在
Component原型链上添加forceUpdate方法,强制更新。
总结
不管是类组件还是函数组件,最终我们写的jsx都被babel转化成了可识别的元素,其中我们也看了ReactElement,createElement,Component等内部实现,了解到了作为ReactElement他是怎么被创建的,但是远远没有完,因为我们知道我们在写React的时候,会在后面带上一个ReactDOM.render(<Element/>, 'root'),没错我们下一章节就要去探索一下ReactDOM.render方法了。
到此这篇关于react源码层深入刨析babel解析jsx实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关react babel解析jsx内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
