目录 题目要求 思路一:DFS+序列化 Java C++ Rust 思路二:DFS+三元组 Java C++ Rust 总结 题目要求 思路一:DFS+序列化 设计一种规则将所有子树序列化,保证不同子树的序列化字符串不同,相
目录
- 题目要求
- 思路一:DFS+序列化
- Java
- C++
- Rust
- 思路二:DFS+三元组
- Java
- C++
- Rust
- 总结
题目要求
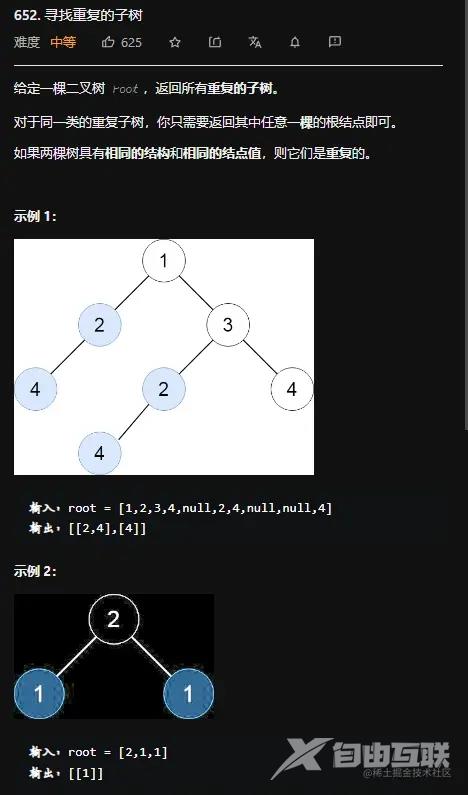
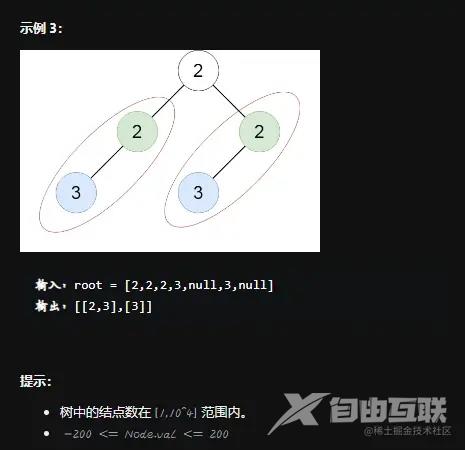
思路一:DFS+序列化
- 设计一种规则将所有子树序列化,保证不同子树的序列化字符串不同,相同子树的序列化串相同。
- 用哈希表存所有的字符串,统计出现次数即可。
- 定义map中的关键字(
key)为子树的序列化结果,值(value)为出现次数。
- 定义map中的关键字(
- 此处采用的方式是在DFS遍历顺序下的每个节点后添加"-",遇到空节点置当前位为空格。
Java
class Solution {
Map<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>();
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
DFS(root);
return res;
}
String DFS(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return " ";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(root.val).append("-");
sb.append(DFS(root.left)).append(DFS(root.right));
String sub = sb.toString(); // 当前子树
map.put(sub, map.getOrDefault(sub, 0) + 1);
if (map.get(sub) == 2) // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.add(root);
return sub;
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
C++
- 要把节点值转换为字符串格式……呜呜呜卡了半天才意识到
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<string, int> map;
vector<TreeNode*> res;
vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) {
DFS(root);
return res;
}
string DFS(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return " ";
string sub = "";
sub += to_string(root->val); // 转换为字符串!!!
sub += "-";
sub += DFS(root->left);
sub += DFS(root->right);
if (map.count(sub))
map[sub]++;
else
map[sub] = 1;
if (map[sub] == 2) // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.emplace_back(root);
return sub;
}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
Rust
- 在判定等于222的地方卡了好久,报错
borrow of moved value sub,没认真学rust导致闭包没搞好,然后根据报错内容猜了下,把上面的加了个clone()果然好了。
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
pub fn find_duplicate_subtrees(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>> {
let mut res = Vec::new();
fn DFS(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, map: &mut HashMap<String, i32>, res: &mut Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>) -> String {
if root.is_none() {
return " ".to_string();
}
let sub = format!("{}-{}{}", root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val, DFS(&root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left, map, res), DFS(&root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right, map, res));
*map.entry(sub.clone()).or_insert(0) += 1;
if map[&sub] == 2 { // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.push(root.clone());
}
sub
}
DFS(&root, &mut HashMap::new(), &mut res);
res
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n^2)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
思路二:DFS+三元组
- 和上面其实差不多,三元组本质上也是一种序列化形式,可以指代唯一的子树结构:
- 三元组中的内容为(根节点值,左子树标识,右子树标识)(根节点值, 左子树标识,右子树标识)(根节点值,左子树标识,右子树标识);
- 这个标识是给每个不同结构的子树所赋予的唯一值,可用于标识其结构。
- 所以三元组相同则判定子树结构相同;
- 该方法使用序号标识子树结构,规避了思路一中越来越长的字符串,也减小了时间复杂度。
- 三元组中的内容为(根节点值,左子树标识,右子树标识)(根节点值, 左子树标识,右子树标识)(根节点值,左子树标识,右子树标识);
- 定义哈希表mapmapmap存储每种结构:
- 关键字为三元组的字符串形式,值为当前子树的标识和出现次数所构成的数对。
- 其中标识用从000开始的整数flagflagflag表示。
Java
class Solution {
Map<String, Pair<Integer, Integer>> map = new HashMap<String, Pair<Integer, Integer>>();
List<TreeNode> res = new ArrayList<>();
int flag = 0;
public List<TreeNode> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode root) {
DFS(root);
return res;
}
public int DFS(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null)
return 0;
int[] tri = {root.val, DFS(root.left), DFS(root.right)};
String sub = Arrays.toString(tri); // 当前子树
if (map.containsKey(sub)) { // 已统计过
int key = map.get(sub).getKey();
int cnt = map.get(sub).getValue();
map.put(sub, new Pair<Integer, Integer>(key, ++cnt));
if (cnt == 2) // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.add(root);
return key;
}
else { // 首次出现
map.put(sub, new Pair<Integer, Integer>(++flag, 1));
return flag;
}
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
C++
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<string, pair<int, int>> map;
vector<TreeNode*> res;
int flag = 0;
vector<TreeNode*> findDuplicateSubtrees(TreeNode* root) {
DFS(root);
return res;
}
int DFS(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == nullptr)
return 0;
string sub = to_string(root->val) + to_string(DFS(root->left)) + to_string(DFS(root->right)); // 当前子树
if (auto cur = map.find(sub); cur != map.end()) { // 已统计过
int key = cur->second.first;
int cnt = cur->second.second;
map[sub] = {key, ++cnt};
if (cnt == 2) // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.emplace_back(root);
return key;
}
else { // 首次出现
map[sub] = {++flag, 1};
return flag;
}
}
};
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
Rust
- 三元组不好搞,所以用了两个二元哈希表替代一个存放三元组和标识,另一个存放标识与出现次数。
use std::rc::Rc;
use std::cell::RefCell;
use std::collections::HashMap;
impl Solution {
pub fn find_duplicate_subtrees(root: Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>) -> Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>> {
let mut res = Vec::new();
fn DFS(root: &Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>, sub_flag: &mut HashMap<String, i32>, flag_cnt: &mut HashMap<i32, i32>, res: &mut Vec<Option<Rc<RefCell<TreeNode>>>>, flag: &mut i32) -> i32 {
if root.is_none() {
return 0;
}
let (lflag, rflag) = (DFS(&root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().left, sub_flag, flag_cnt, res, flag), DFS(&root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().right, sub_flag, flag_cnt, res, flag));
let sub = format!("{}{}{}", root.as_ref().unwrap().borrow().val, lflag, rflag);
if sub_flag.contains_key(&sub) { // 已统计过
let key = sub_flag[&sub];
let cnt = flag_cnt[&key] + 1;
flag_cnt.insert(key, cnt);
if cnt == 2 { // ==保证统计所有且只记录一次
res.push(root.clone());
}
key
}
else { // 首次出现
*flag += 1;
sub_flag.insert(sub, *flag);
flag_cnt.insert(*flag, 1);
*flag
}
}
DFS(&root, &mut HashMap::new(), &mut HashMap::new(), &mut res, &mut 0);
res
}
}
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
总结
两种方法本质上都是基于哈希表,记录重复的子树结构并统计个数,在超过111时进行记录,不过思路二更巧妙地将冗长的字符串变为常数级的标识符。
以上就是Java C++ 算法题解leetcode652寻找重复子树的详细内容,更多关于Java C++ 寻找重复子树的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
