目录
- 1.运行时类型转换
- 2.typeid操作符
- 2.1类型转换到中间层次类型
- 2.2void型指针
- 2.3运用带模板的RTTI
- 3.多重继承
- 4.合理使用RTTI
- 5.RTTI的机制和开销
- 6.小结
当仅有一个指针或引用指向基类型时,利用运行时类型识别(RTTI)可以找到一个对象的动态类型。
运行时类型识别可能被认为是C++中一个”次要“的特征,当程序员在编程过程中陷入非常困难的境地时,实用主义将会帮助他走出困境。正常情况下,程序员需要有意忽略对象的准确类型,而利用虚函数机制实现那个类型正确操作过程。然而,有时知道一个仅含一个基类指针的对象的准确的运行时类型(即多半是派生的类型)是非常有用的。有了此信息,就可以更有效地进行某些特殊情况的操作,或者预防基类接口因无此信息而变得笨拙。
1.运行时类型转换
通过指针或者引用决定对象运行时类型的一种方法是使用运行时类型转换(runtime cast),用这种方法可以查证所尝试进行的转换正确与否。当要把基类指针类型转换为派生类时,这个方法非常有用。由于继承的层次结构的典型描述说基类在派生类之上,所以这种类型转换也成为向下类型转换(downcast)。
请看下面的类层次结构:
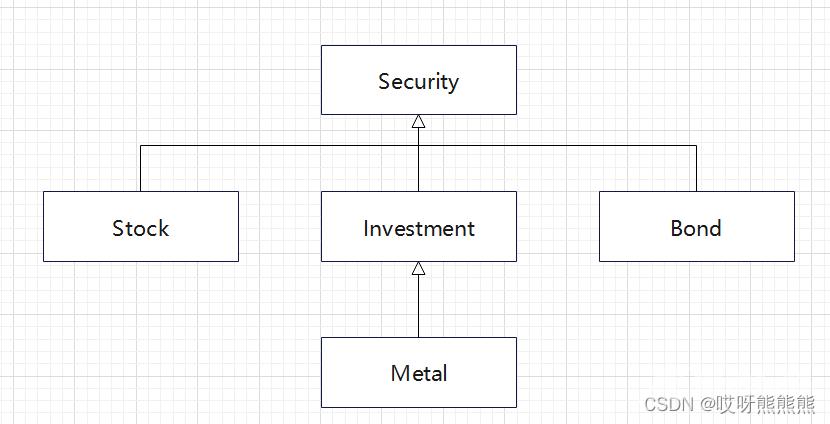
在下面的程序代码中,Investment类中有一个其他类没有的额外操作,所以能够运行时知道Security指针是否引用了Investment对象是很重要的。为了实现检查运行时的类型转换,每个类都持有一个整数标识符,以便可以与层次结构中其他的类区别开来。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include "../purge.h"
using namespace std;
class Security {
protected:
enum { BASEID = 0 };
public:
virtual ~Security() {}
virtual bool isA(int id) { return (id == BASEID); }
};
class Stock : public Security {
typedef Security Super;
protected:
enum { OFFSET = 1, TYPEID = BASEID + OFFSET };
public:
bool isA(int id) {
return id == TYPEID || Super::isA(id);
}
static Stock* dynacast(Security* s) {
return (s->isA(TYPEID)) ? static_cast<Stock*>(s) : 0;
}
};
class Bond : public Security {
typedef Security Super;
protected:
enum { OFFSET = 2, TYPEID = BASEID + OFFSET };
public:
bool isA(int id) {
return id == TYPEID || Super::isA(id);
}
static Bond* dynacast(Security* s) {
return (s->isA(TYPEID)) ? static_cast<Bond*>(s) : 0;
}
};
class Investment : public Security {
typedef Security Super;
protected:
enum { OFFSET = 3, TYPEID = BASEID + OFFSET };
public:
bool isA(int id) {
return id == TYPEID || Super::isA(id);
}
static Investment* dynacast(Security* s) {
return (s->isA(TYPEID)) ?
static_cast<Investment*>(s) : 0;
}
void special() {
cout << "special Investment function" << endl;
}
};
class Metal : public Investment {
typedef Investment Super;
protected:
enum { OFFSET = 4, TYPEID = BASEID + OFFSET };
public:
bool isA(int id) {
return id == TYPEID || Super::isA(id);
}
static Metal* dynacast(Security* s) {
return (s->isA(TYPEID)) ? static_cast<Metal*>(s) : 0;
}
};
int main() {
vector<Security*> portfolio;
portfolio.push_back(new Metal);
portfolio.push_back(new Investment);
portfolio.push_back(new Bond);
portfolio.push_back(new Stock);
for(vector<Security*>::iterator it = portfolio.begin();
it != portfolio.end(); ++it) {
Investment* cm = Investment::dynacast(*it);
if(cm)
cm->special();
else
cout << "not an Investment" << endl;
}
cout << "cast from intermediate pointer:" << endl;
Security* sp = new Metal;
Investment* cp = Investment::dynacast(sp);
if(cp) cout << " it's an Investment" << endl;
Metal* mp = Metal::dynacast(sp);
if(mp) cout << " it's a Metal too!" << endl;
purge(portfolio);
} ///:~
多态的isA()函数检查其参数是否与它的类型参数(id)相容,就意味着或者id与对象的typeID准确地匹配,或者与对象的祖先之一的类型匹配(因为在这种情况下调用Super::isA())。函数dynacast()在每个类中都是静态的,dynacast()为其指针参数调用isA()来检查类型转换是否有效。
借助dynamic_cast操作符,C++提供这样一个可检查的类型转换。使用dynamic_cast对前面的程序例子进行重写,就得到下面的程序:
//: C08:Security.h
#ifndef SECURITY_H
#define SECURITY_H
#include <iostream>
class Security {
public:
virtual ~Security() {}
};
class Stock : public Security {};
class Bond : public Security {};
class Investment : public Security {
public:
void special() {
std::cout << "special Investment function" <<std::endl;
}
};
class Metal : public Investment {};
#endif // SECURITY_H ///:~
// Uses RTTI's dynamic_cast.
#include <vector>
#include "../purge.h"
#include "Security.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<Security*> portfolio;
portfolio.push_back(new Metal);
portfolio.push_back(new Investment);
portfolio.push_back(new Bond);
portfolio.push_back(new Stock);
for(vector<Security*>::iterator it =
portfolio.begin();
it != portfolio.end(); ++it) {
Investment* cm = dynamic_cast<Investment*>(*it);
if(cm)
cm->special();
else
cout << "not a Investment" << endl;
}
cout << "cast from intermediate pointer:" << endl;
Security* sp = new Metal;
Investment* cp = dynamic_cast<Investment*>(sp);
if(cp) cout << " it's an Investment" << endl;
Metal* mp = dynamic_cast<Metal*>(sp);
if(mp) cout << " it's a Metal too!" << endl;
purge(portfolio);
} ///:~
由于原来例子中大部分的代码开销用在了类型转换检查上,所以这个例子就变得如此之短。如果想要安全地进行向下类型转换,dynamic_cast要求使用的目标类型是多态的(polymorphic)。这就要求该类必须至少有一个虚函数。幸运的是,Security基类有一个虚析构函数,所以这里不需要再创建一个额外的函数去做这项工作。因为dynamic_cast在程序运行时使用了虚函数表,所以比其他新式风格的类型转换操作来说它的代价更高。
用引用而非指针同样也可以使用dynamic_cast,但是由于没有诸如空引用这样的情况,这就需要采用其他方法来了解类型转换是否失败。这个”其他方法“就是捕获bad_cast异常,如下所示:
#include <typeinfo>
#include "Security.h"
using namespace std;
int main() {
Metal m;
Security& s = m;
try {
Investment& c = dynamic_cast<Investment&>(s);
cout << "It's an Investment" << endl;
} catch(bad_cast&) {
cout << "s is not an Investment type" << endl;
}
try {
Bond& b = dynamic_cast<Bond&>(s);
cout << "It's a Bond" << endl;
} catch(bad_cast&) {
cout << "It's not a Bond type" << endl;
}
} ///:~
2.typeid操作符
获得有关一个对象运行时信息的另一个方法,就是typeid操作符来完成。这种操作符返回一个type_info类的对象,该对象给出与其应用有关的对象类型的信息。如果该对象的类型是多态的,它将给出那个应用(动态类型(dynamic type))的大部分派生类信息;否则,它将给出静态类型信息。typeid操作符的一个用途是获得一个对象的动态类型的名称,例如const char * ,就像在下面例子中可以看到的:
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
struct PolyBase { virtual ~PolyBase() {} };
struct PolyDer : PolyBase { PolyDer() {} };
struct NonPolyBase {};
struct NonPolyDer : NonPolyBase { NonPolyDer(int) {} };
int main() {
// Test polymorphic Types
const PolyDer pd;
const PolyBase* ppb = &pd;
cout << typeid(ppb).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(*ppb).name() << endl;
cout << boolalpha << (typeid(*ppb) == typeid(pd))
<< endl;
cout << (typeid(PolyDer) == typeid(const PolyDer))
<< endl;
// Test non-polymorphic Types
const NonPolyDer npd(1);
const NonPolyBase* nppb = &npd;
cout << typeid(nppb).name() << endl;
cout << typeid(*nppb).name() << endl;
cout << (typeid(*nppb) == typeid(npd)) << endl;
// Test a built-in type
int i;
cout << typeid(i).name() << endl;
} ///:~
这是使用一个特定编译器的程序的输出是:
struct PolyBase const *
struct Polyder
true
true
struct NonPolyBase const *
struct NonPolyBase
false
int
因为ppb是一个指针,所以输出的第1行是他的静态类型。为了在程序中得到RTTI的结果,需要检查指针或引用目标对象,这在第2行说明。需要注意的是,RTTI忽略了顶层的const和volatile限定符。借助非多态类型,正好可以获得静态类型(该指针本身的类型)。正如读者所见,这里也支持内置类型。
2.1类型转换到中间层次类型
#include <cassert>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
class B1 {
public:
virtual ~B1() {}
};
class B2 {
public:
virtual ~B2() {}
};
class MI : public B1, public B2 {};
class Mi2 : public MI {};
int main() {
B2* b2 = new Mi2;
Mi2* mi2 = dynamic_cast<Mi2*>(b2);
MI* mi = dynamic_cast<MI*>(b2);
B1* b1 = dynamic_cast<B1*>(b2);
assert(typeid(b2) != typeid(Mi2*));
assert(typeid(b2) == typeid(B2*));
delete b2;
} ///:~
如果创建一个Mi2对象并将它向上类型转换到该继承层次结构的根(在这种情况下,选择两个可能的根中的一个),可以成功地使dynamic_cast回退至两个派生层MI或Mi2中的任何一个。
甚至可以从一个根到另一个根进行类型转换:
B1* b1 = dynamic_cast<B1*>(b2);
这也是成功的,因为B2实际上指向一个Mi2对象,该Mi2对象含有一个B1类型的子对象。
2.2void型指针
RTTI仅仅为完整的类型工作,这就意味着当使用typeid时,所有的类型信息必须是可利用的。特别是,它不能与void型指针一起工作:
//!#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
class Stimpy {
public:
virtual void happy() {}
virtual void joy() {}
virtual ~Stimpy() {}
};
int main() {
void* v = new Stimpy;
// Error:
//! Stimpy* s = dynamic_cast<Stimpy*>(v);
// Error:
//! cout << typeid(*v).name() << endl;
} ///:~
一个void* 真是的意思是”无类型信息“。
2.3运用带模板的RTTI
因为所有的类模板所做的工作就是产生类,所以类模板可以很好地与RTTI一起工作。RTTI提供了一条方便的途径来获得对象所在类的名称。下面的示例打印出构造函数和析构函数的调用顺序:
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
template<int id> class Announce {
public:
Announce() {
cout << typeid(*this).name() << " constructor" << endl;
}
~Announce() {
cout << typeid(*this).name() << " destructor" << endl;
}
};
class X : public Announce<0> {
Announce<1> m1;
Announce<2> m2;
public:
X() { cout << "X::X()" << endl; }
~X() { cout << "X::~X()" << endl; }
};
int main() { X x; } ///:~
在构造函数内和析构函数内部,RTTI信息产生打印的类名。类X利用继承和组合两个方式创建一个类。输出如下:
Announce<0> constructor
Announce<1> constructor
Announce<2> constructor
X::X()
X::~X()
Announce<2> destructor
Announce<1> destructor
Announce<0> destructor
当然,可能会得到不同的结果,这取决于编译器如何表示它的name()信息。
3.多重继承
RTTI机制必须正确地处理多重继承的所有复杂性,包括虚基类virtual:
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
using namespace std;
class BB {
public:
virtual void f() {}
virtual ~BB() {}
};
class B1 : virtual public BB {};
class B2 : virtual public BB {};
class MI : public B1, public B2 {};
int main() {
BB* bbp = new MI; // Upcast
// Proper name detection:
cout << typeid(*bbp).name() << endl;
// Dynamic_cast works properly:
MI* mip = dynamic_cast<MI*>(bbp);
// Can't force old-style cast:
//! MI* mip2 = (MI*)bbp; // Compile error
} ///:~
typeid()操作符正确地检测出实际对象的名字,即便它采用virtual基类指针完成这个任务的,dynamic_cast也正确地进行工作。但实际上,编译器不允许程序员用以前的方法尝试强制进行类型转换:
MI* mip2 = (MI*)bbp; // Compile error
编译器知道这样做绝不是正确的方法,因此需要程序员使用dynamic_cast。
4.合理使用RTTI
垃圾再生器
为了进一步地举例说明RTTI的实际用途,下面的程序模拟了一个垃圾再生器。不同种类的”垃圾“被插入一个容器中,然后根据它们的动态类型进行分类。
// Describing trash.
#ifndef TRASH_H
#define TRASH_H
#include <iostream>
class Trash {
float _weight;
public:
Trash(float wt) : _weight(wt) {}
virtual float value() const = 0;
float weight() const { return _weight; }
virtual ~Trash() {
std::cout << "~Trash()" << std::endl;
}
};
class Aluminum : public Trash {
static float val;
public:
Aluminum(float wt) : Trash(wt) {}
float value() const { return val; }
static void value(float newval) {
val = newval;
}
};
class Paper : public Trash {
static float val;
public:
Paper(float wt) : Trash(wt) {}
float value() const { return val; }
static void value(float newval) {
val = newval;
}
};
class Glass : public Trash {
static float val;
public:
Glass(float wt) : Trash(wt) {}
float value() const { return val; }
static void value(float newval) {
val = newval;
}
};
#endif // TRASH_H ///:~
用来表示垃圾类型单价的static值定义在实现文件中:
// A Trash Recycler. #include "Trash.h" float Aluminum::val = 1.67; float Paper::val = 0.10; float Glass::val = 0.23; ///:~
sunValue()模板从头到尾对一个容器进行迭代,显示并计算结果:
//{L} Trash
// A Trash Recycler.
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <vector>
#include "Trash.h"
#include "../purge.h"
using namespace std;
// Sums up the value of the Trash in a bin:
template<class Container>
void sumValue(Container& bin, ostream& os) {
typename Container::iterator tally = bin.begin();
float val = 0;
while(tally != bin.end()) {
val += (*tally)->weight() * (*tally)->value();
os << "weight of " << typeid(**tally).name()
<< " = " << (*tally)->weight() << endl;
++tally;
}
os << "Total value = " << val << endl;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0)); // Seed the random number generator
vector<Trash*> bin;
// Fill up the Trash bin:
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++)
switch(rand() % 3) {
case 0 :
bin.push_back(new Aluminum((rand() % 1000)/10.0));
break;
case 1 :
bin.push_back(new Paper((rand() % 1000)/10.0));
break;
case 2 :
bin.push_back(new Glass((rand() % 1000)/10.0));
break;
}
// Note: bins hold exact type of object, not base type:
vector<Glass*> glassBin;
vector<Paper*> paperBin;
vector<Aluminum*> alumBin;
vector<Trash*>::iterator sorter = bin.begin();
// Sort the Trash:
while(sorter != bin.end()) {
Aluminum* ap = dynamic_cast<Aluminum*>(*sorter);
Paper* pp = dynamic_cast<Paper*>(*sorter);
Glass* gp = dynamic_cast<Glass*>(*sorter);
if(ap) alumBin.push_back(ap);
else if(pp) paperBin.push_back(pp);
else if(gp) glassBin.push_back(gp);
++sorter;
}
sumValue(alumBin, cout);
sumValue(paperBin, cout);
sumValue(glassBin, cout);
sumValue(bin, cout);
purge(bin);
} ///:~
因为垃圾被不加分类地投入到一个容器,这样一来,垃圾的所有信息就”丢失“了。但是,为了稍后适当地对废料进行分类,具体类型信息必须恢复,这将用到RTTI。
可以通过使用map来改进这种解决方案,该map将指向type_info对象的指针与一个包含Trash指针的vector关联起来。因为映像需要一个能识别排序的判定函数,这里提供了一个名为TInfoLess的结构,它调用type_info::before()。注意,这里必须对sumValue()进行不同的定义。
//{L} Trash
// Recyling with a map.
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <utility>
#include <vector>
#include "Trash.h"
#include "../purge.h"
using namespace std;
// Comparator for type_info pointers
struct TInfoLess {
bool operator()(const type_info* t1, const type_info* t2)
const { return t1->before(*t2); }
};
typedef map<const type_info*, vector<Trash*>, TInfoLess>
TrashMap;
// Sums up the value of the Trash in a bin:
void sumValue(const TrashMap::value_type& p, ostream& os) {
vector<Trash*>::const_iterator tally = p.second.begin();
float val = 0;
while(tally != p.second.end()) {
val += (*tally)->weight() * (*tally)->value();
os << "weight of "
<< p.first->name() // type_info::name()
<< " = " << (*tally)->weight() << endl;
++tally;
}
os << "Total value = " << val << endl;
}
int main() {
srand(time(0)); // Seed the random number generator
TrashMap bin;
// Fill up the Trash bin:
for(int i = 0; i < 30; i++) {
Trash* tp;
switch(rand() % 3) {
case 0 :
tp = new Aluminum((rand() % 1000)/10.0);
break;
case 1 :
tp = new Paper((rand() % 1000)/10.0);
break;
case 2 :
tp = new Glass((rand() % 1000)/10.0);
break;
}
bin[&typeid(*tp)].push_back(tp);
}
// Print sorted results
for(TrashMap::iterator p = bin.begin();
p != bin.end(); ++p) {
sumValue(*p, cout);
purge(p->second);
}
} ///:~
为了直接调用type_info::name(),我们在这里修改了sunValue(),因为作为TrashMap::value_type对的第1个成员,type_info对象现在是可获得的。这样就避免了为了获得正在处理的Trash的类型名而额外调用typeid,而这在该程序的以前版本中却是必须做的。
5.RTTI的机制和开销
实现RTTI典型的方法是,通过在类的虚函数表中放置一个附加的指针。这个指针指向那个特别类型的type_info结构。typeid()表达式的结果非常简单:虚函数表指针取得type_info指针,并且产生一个对type_info结构的引用。因为这正好是一个双指针的解析操作,这是一个代价为常量时间的操作。
6.小结
尽管通常情况下会为一个指向其基类的指针进行向上类型转换,然后再使用那个基类的通用接口(通过虚函数),但是如果知道一个由基类指针指向的对象的动态类型,有时候根据获得的这些信息进行相关处理可能会使事情变得更加有效,而这些正是RTTI所提供的。大部分通常的误用来自一些程序员,这些误用是由于他们不理解虚函数而实采用RTTI来做类型检查的编码所造成的。C++的基本原理似乎提供了对违反类型的定义规则和完整性的情况进行监督和纠正的强有力的工具和保护,但是如果有谁想故意误用或回避某一语言的特征,那么将没有人可以组织他这样做。
到此这篇关于C++运行时类型识别与转换实现方法的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关C++类型识别内容请搜索自由互联以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持自由互联!
