什么是原子类
- 原子是不可分割的最小单位,故原子类可以认为其操作都是不可分割
- 一个操作时不可中断的,即便是在多线程的情况下也可以保证
- 原子类的作用和锁类似,是为了保证并发情况下线程安全,不过原子类相比于锁,有一定的优势
- 粒度更细:原子变量可以把竞争范围缩小到变量级别,这是我们可以获得的最细粒度的情况了,通常锁的粒度都要大于原子变量的粒度
- 效率更高:通常,使用原子类的效率会比使用锁的效率更高,除了高度竞争的情况
6类原子类纵览
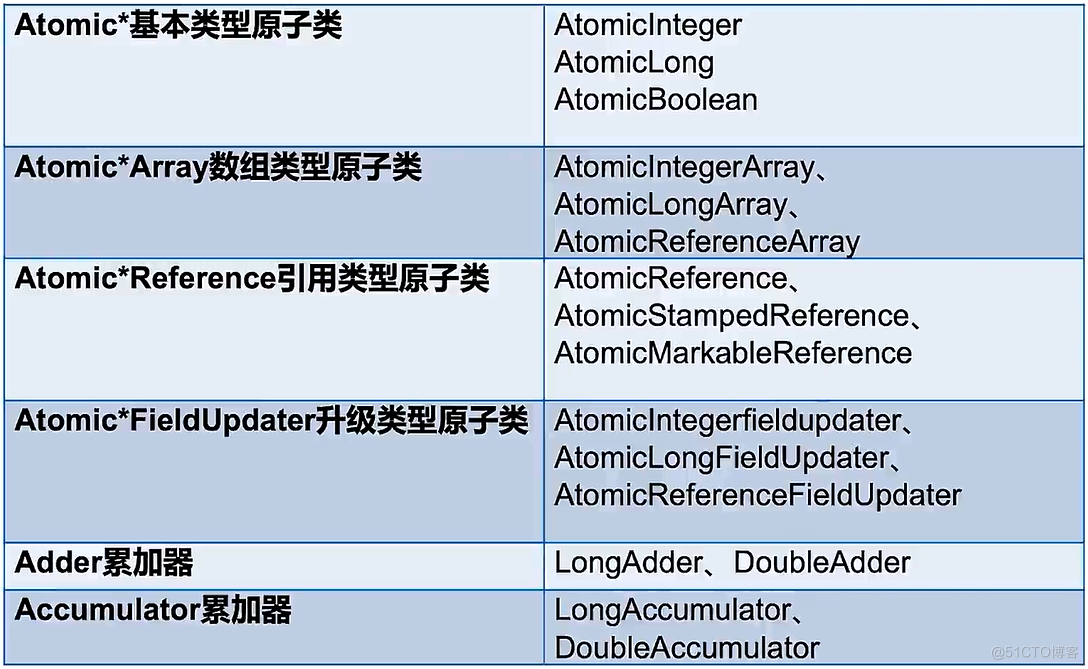
Atomic基本原子类型
AtomicBoolean布尔型原子类、AtomicInteger整型原子类、AutomicLong长整型原子类,元老级的原子更新,方法几乎一模一样
以AtomicInteger为例
AtomicInteger常用方法
- public final int get():获取当前的值
- public final int getAndSet(int newValue):获取当前的值,并设置新值
- public final int getAndIncrement():获取当前的值,并自增
- public final int getAndDecrement():获取当前的值,并自减
- public final int getAndAdd(int delta):获取当前的值,并加上预期的值
- public final boolean compareAndSet(int expect, int update):如果输入的值等于预期的值,则以原子方式将该值设置为输入的值(update)
原子更新数组
通过原子的方式更新数组里的某个元素,Atomic包提供了以下三个类:
- AtomicIntegerArray:原子更新整型数组里的元素。
- AtomicLongArray:原子更新长整型数组里的元素。
- AtomicReferenceArray:原子更新引用类型数组里的元素。
AtomicIntegerArray类主要是提供原子的方式更新数组里的整型,其常用方法如下
- int addAndGet(int i, int delta):以原子方式将输入值与数组中索引i的元素相加。
- boolean compareAndSet(int i, int expect, int update):如果当前值等于预期值,则以原子方式将数组位置i的元素设置成update值。
AtomicIntegerArray的使用
/** * @Description: 演示原子数组的使用方法 */ public class AtomicArrayDemo1 { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AtomicIntegerArray atomicIntegerArray = new AtomicIntegerArray(1000); Thread[] threads1 = new Thread[100]; Thread[] threads2 = new Thread[100]; Decrement decrement = new Decrement(atomicIntegerArray); Increment increment = new Increment(atomicIntegerArray); for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { threads1[i] = new Thread(decrement); threads2[i] = new Thread(increment); threads1[i].start(); threads2[i].start(); } for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { threads1[i].join(); threads2[i].join(); } for (int i = 0; i < atomicIntegerArray.length(); i++) { if(atomicIntegerArray.get(i) != 0){ System.out.println("发现了错误:错误的索引:"+i); } } System.out.println("运行结束"); } } class Decrement implements Runnable{ private AtomicIntegerArray array; public Decrement(AtomicIntegerArray array) { this.array = array; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) { array.getAndDecrement(i); } } } class Increment implements Runnable{ private AtomicIntegerArray array; public Increment(AtomicIntegerArray array) { this.array = array; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) { array.getAndIncrement(i); } } }AtomicIntegerArray类需要注意的是,数组value通过构造方法传递进去,然后AtomicIntegerArray会将当前数组复制一份,所以当AtomicIntegerArray对内部的数组元素进行修改时,不会影响到传入的数组。
原子更新引用类型
原子更新基本类型的AtomicInteger,只能更新一个变量,如果要原子的更新多个变量,就需要使用这个原子更新引用类型提供的类。Atomic包提供了以下三个类:
- AtomicReference:原子更新引用类型。
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater:原子更新引用类型里的字段。
- AtomicMarkableReference:原子更新带有标记位的引用类型。可以原子的更新一个布尔类型的标记位和引用类型。构造方法是AtomicMarkableReference(V initialRef, boolean initialMark)
AtomicReference引用类型原子类
- AtomicReference:AtomicReference类的作用,和AtomicInteger并没有本质区别,AtomicInteger可以让一个整数保证原子性,AtomicReference可以让一个对象保证原子性,当然,AtomicReference的功能明显比AtomicInteger强,因为一个对象里可以包含很多属性,其用法和AtomicInteger类似
AtomicReference的使用
public class SpinLock { private AtomicReference<Thread> sign = new AtomicReference<>(); public void lock(){ Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); while(!sign.compareAndSet(null,current)){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "自旋锁获取失败,再次尝试"); } } public void unlock(){ Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); sign.compareAndSet(current,null); } public static void main(String[] args) { SpinLock spinLock = new SpinLock(); Runnable runnable = new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "尝试获取自旋锁"); spinLock.lock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到了自旋锁"); try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { spinLock.unlock(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放了自旋锁"); } } }; Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable); Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }原子更新字段类
如果我们只需要更新某个类里的某个字段,那么就需要使用原子更新字段类,Atomic包提供了以下三个类:
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:原子更新整型的字段的更新器。
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater:原子更新长整型字段的更新器。
- AtomicStampedReference:原子更新带有版本号的引用类型。该类将整数值与引用关联起来,可用于原子的更数据和数据的版本号,可以解决使用CAS进行原子更新时,可能出现的ABA问题。
- 原子更新字段类都是抽象类,每次使用都时候必须使用静态方法newUpdater创建一个更新器。原子更新类的字段的必须使用public volatile修饰符。
使用上述类是必须遵循以下原则:
- 字段必须是voliatile类型的,在线程之间共享变量时能保持可见性。
- 字段的描述类型是与调用者的操作对象字段保持一致。
- 也就是说调用者可以直接操作对象字段,那么就可以反射进行原子操作。
- 对父类的字段,子类不能直接操作的,尽管子类可以访问父类的字段
- 只能是实例变量,不能是类变量,也就是说不能加static关键字
- 只能是可修改变量,不能使用final修饰变量,final的语义,不可更改。
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater:对普通变量进行升级,让其拥有原子操作能力
- 使用场景:偶尔需要一个原子get-set操作
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater注意点
- 可以修改的变量具有可见性,即volatile修饰的变量
- 该变量不可以被static修饰
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater使用
/** * @Description: 演示AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater用法 */ public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo implements Runnable { static Candidate tom; static Candidate peter; public static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Candidate> scoreUpdater = AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Candidate.class,"score"); @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { peter.score++; scoreUpdater.getAndIncrement(tom); } } public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { tom = new Candidate(); peter = new Candidate(); AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo updaterDemo = new AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(updaterDemo); Thread thread2 = new Thread(updaterDemo); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); thread1.join(); thread2.join(); System.out.println("普通变量自增:"+peter.score); System.out.println("AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater操作的变量:"+tom.score); } public static class Candidate{ volatile int score; } }高性能原子类
高性能原子类,是java8中增加的原子类,它们使用分段的思想,把不同的线程hash到不同的段上去更新,最后再把这些段的值相加得到最终的值,这些类主要有:
- 1、Striped64:下面四个类的父类。
- 2、LongAccumulator:long类型的聚合器,需要传入一个long类型的二元操作,可以用来计算各种聚合操作,包括加乘等。
- 3、LongAdder:long类型的累加器,LongAccumulator的特例,只能用来计算加法,且从0开始计算。
- 4、DoubleAccumulator:double类型的聚合器,需要传入一个double类型的二元操作,可以用来计算各种聚合操作,包括加乘等。
- 5、DoubleAdder:double类型的累加器,DoubleAccumulator的特例,只能用来计算加法,且从0开始计算。
- 这几个类的操作基本类似,其中DoubleAccumulator和DoubleAdder底层其实也是用long来实现的
Adder累加器
- 高并发下LongAdder比AtomicLong效率高,不过本质是空间换时间
- 在竞争激烈的时候,LongAdder把不同线程对应到不同的Cell上进行修改,降低了冲突的概率,是多段锁的理念,提高了并发性
- AtomicLong中有个内部变量value保存着实际的long值,所有的操作都是针对该变量进行。也就是说,高并发环境下,value变量其实是一个热点,也就是N个线程竞争一个热点。由于竞争很激烈,每一次操作,都要flush和refresh,导致很多资源浪费
- LongAdder的基本思路就是分散热点,将value值分散到一个数组中,不同线程会命中到数组的不同槽中,各个线程只对自己槽中的那个值进行CAS操作,这样热点就被分散了,冲突的概率就小很多。如果要获取真正的long值,只要将各个槽中的变量值累加返回。
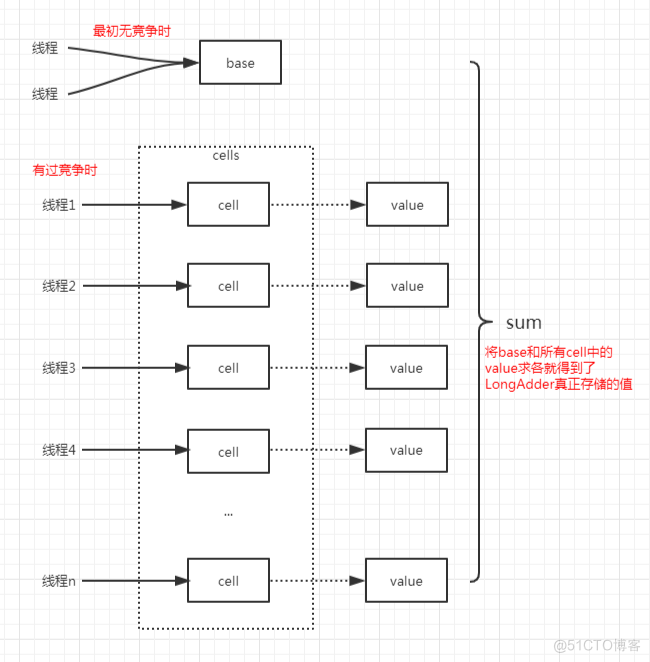
演示高并发场景下LongAdder比AtomicLong性能好
/** * @Description: 演示高并发场景下LongAdder比AtomicLong性能好 */ public class AtomicLongDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { AtomicLong counter = new AtomicLong(0); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { executorService.submit(new Task(counter)); } executorService.shutdown(); while(!executorService.isTerminated()){ } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(counter.get()); System.out.println("AtomicLong耗时:"+(end - start)); } static class Task implements Runnable{ private AtomicLong counter; public Task(AtomicLong counter) { this.counter = counter; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { counter.incrementAndGet(); } } } } /** * @Description: 演示高并发场景下LongAdder比AtomicLong性能好 */ public class LongAdderDemo { public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { LongAdder counter = new LongAdder(); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(20); long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { executorService.submit(new Task(counter)); } executorService.shutdown(); while(!executorService.isTerminated()){ } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(counter.sum()); System.out.println("LongAdder耗时:"+(end - start)); } static class Task implements Runnable{ private LongAdder counter; public Task(LongAdder counter) { this.counter = counter; } @Override public void run() { for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { counter.increment(); } } } }LongAdder比AtomicLong对比
- 在低征用下,AtomicLong和LongAdder这两个类具有相似的特征,但在竞争激烈的情况下,LongAdder的预期吞吐量要高得多,但要消耗更多的空间
- LongAdder适合的场景是统计求和计数的场景,而且LongAdder基本只提供了add等方法,而AtomicLong还具有CAS方法
Accumulator累加器
- Accumulator和Adder非常相似,Accumulator就是一个更通用版本的Adder
LongAccumulator的用法
/** * @Description: 演示LongAccumulator的用法 * */ public class LongAccumulatorDemo { public static void main(String[] args) { LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x+y,0); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(8); IntStream.range(1,10).forEach(i -> executorService.submit(() -> longAccumulator.accumulate(i))); executorService.shutdown(); while(!executorService.isTerminated()){ } System.out.println(longAccumulator.getThenReset()); demo2(); } public static void demo1(){ LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> x+y,0); longAccumulator.accumulate(1); longAccumulator.accumulate(2); System.out.println(longAccumulator.getThenReset()); } public static void demo2(){ LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x,y) -> Math.max(x,y),0); ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(8); IntStream.range(1,10).forEach(i -> executorService.submit(() -> longAccumulator.accumulate(i))); executorService.shutdown(); while(!executorService.isTerminated()){ } System.out.println(longAccumulator.getThenReset()); } }LongAccumulator类原理探究
LongAdder类是LongAccumulator的一个特例,LongAccumulator提供了比LongAdder更强大的功能,如下构造函数其中accumulatorFunction一个双目运算器接口,根据输入的两个参数返回一个计算值,identity则是LongAccumulator累加器的初始值。
public LongAccumulator(LongBinaryOperator accumulatorFunction, long identity) { this.function = accumulatorFunction; base = this.identity = identity; } @FunctionalInterface public interface LongBinaryOperator { /** * Applies this operator to the given operands. * * @param left the first operand * @param right the second operand * @return the operator result */ //根据两个参数计算返回一个值 long applyAsLong(long left, long right); }LongAccumulator相比于LongAdder,可以为累加器提供非0的初始值,而LongAdder只能提供默认的0值。 另外,LongAccumulator还可以指定累加规则,比如累加或者相乘,只需要在构造LongAccumulator时,传入自定义的双目运算器即可,后者则内置累加规则。
LongAddr与LongAccumulator类相同点?
- LongAddr与LongAccumulator类都是使用非阻塞算法CAS实现的,这相比于使用锁实现原子性操作在性能上有很大的提高。
- LongAddr类是LongAccumulator类的一个特例,只是LongAccumulator提供了更强大的功能,可以让用户自定义计算规则。
参考: https://ifeve.com/java-atomic/
https://www.cnblogs.com/tong-yuan/p/Atomic.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/tong-yuan/p/LongAdder.html
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1466107
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000015865714
