目录 代理服务器的原理 案例 搭建代理服务器解决跨域问题 原理解释 代理服务器的原理 案例 安装 express、http-proxy-middleware app.js 文件 node app.js var express = require('express');var app = express(
目录
- 代理服务器的原理
- 案例
- 搭建代理服务器解决跨域问题
- 原理解释
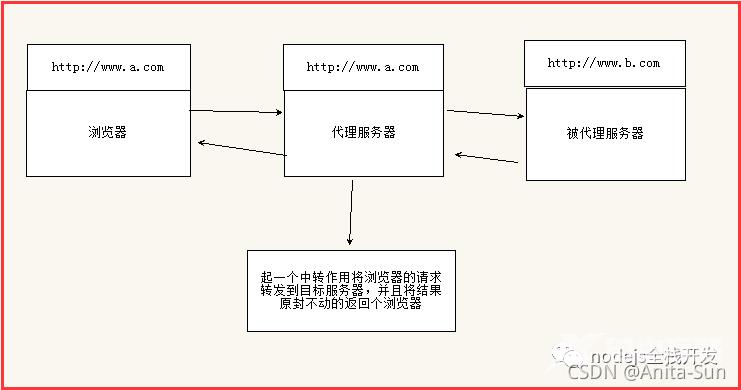
代理服务器的原理
案例
安装 express、http-proxy-middleware
app.js 文件 node app.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.use(express.static('./public'));
app.listen(3000);
在 public 文件夹下建立 a.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="Click()">点击发送请求</button>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
function Click() {
axios('http://localhost:5000/b')
.then(function(res) {
console.log(res);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
</body>
</html>
搭建接口服务器,接口服务器端口号 5000
node interface.js
var express = require('express');
var app = express();
app.get("/", (req, res) => {
res.send("123");
});
app.get("/api/a", (req, res) => {
res.send("a");
});
app.get("/b", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.headers);
res.send("b");
});
app.listen(5000);
访问http://localhost:3000/a.html

搭建代理服务器解决跨域问题
更改 app.js
var express = require('express');
var proxy = require('http-proxy-middleware');
var app = express();
app.use(express.static('./public'));
app.use('/api', proxy.createProxyMiddleware({
target: 'http://localhost:5000',
changeOrigin: false,
pathRewrite: {
"^/api": ""
}
}));
app.listen(3000);
更改 a.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<button onclick="Click()">点击发送请求</button>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/axios/dist/axios.min.js"></script>
<script>
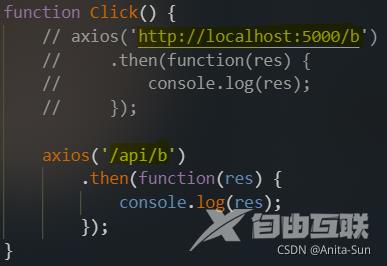
function Click() {
// axios('http://localhost:5000/b')
// .then(function(res) {
// console.log(res);
// });
axios('/api/b')
.then(function(res) {
console.log(res);
});
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
</body>
</html>
访问 http://localhost:3000/a.html
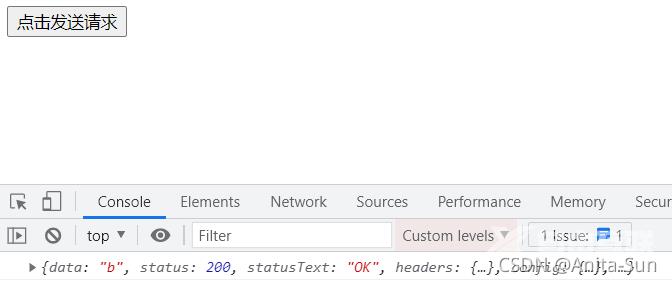
原理解释
将 a.html 请求地址改为 /api/b,那么发送请求的时候会自动补上主机和端口号http://localhost:3000
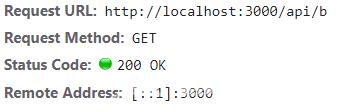
所以请求发送到了3000端口
参数含义
target: 转发到的目标地址changeOrigin: 是否更改host。默认为false,不重写
true
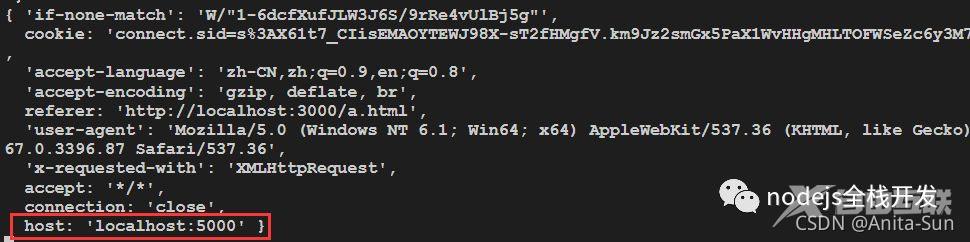
false
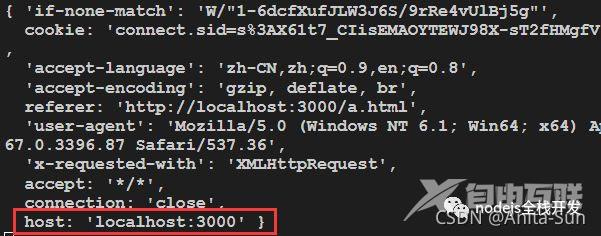
pathRewrite:路径重写(在这里是去掉’api’)

最终请求被转发到了 http://localhost:5000/b
app.get("/b", (req, res) => {
console.log(req.headers);
res.send("b");
});
整个过程就像这样
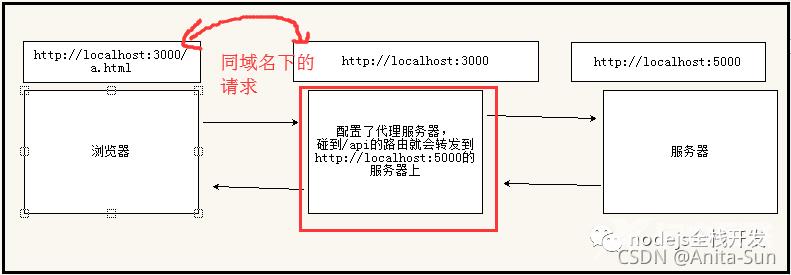
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。
