目录
- 一、安装boostrap、axios
- 二、在src目录下新建一个List.js,在List.js中
- 三、在app.js中引入List.js并渲染
- 四、在create-react-app脚手架跑起来项目
开始这个实例之前需要对es6、react、axios有一定的了解
安装一个react项目的脚手架 create react-app
在开始之前,你可能需要安装 yarn。
$ yarn create react-app antd-demo
工具会自动初始化一个脚手架并安装 React 项目的各种必要依赖,如果在过程中出现网络问题,请尝试配置代理或使用其他 npm registry。
然后我们进入项目并启动。
$ cd antd-demo $ yarn start
此时浏览器会访问 http://localhost:3000/ ,看到 Welcome to React 的界面就算成功了。
想了解create react-app脚手架结合antd使用的可以访问这个地址:
https://ant.design/docs/react/use-with-create-react-app-cn
在前端开发的时候,需要获取后台的数据,并把数据渲染到组件展示给用户看,那么这个过程如何实现呢
一般的思路是请求后端提供的接口数据,再把数据渲染出来。
下面一个实例展示:
我打算分为两个部分来写,第一个部分就是红色的表格头,固定的内容,一个是绿色的数据表格行,把他抽成一个组件的形式来渲染数据,而这些数据呢,我打算用https://www.mockapi.io来模拟真实数据了,也就是说模拟后端提供的接口数据,如果没用过mockapi的话也可以上网查一下。
大家也可以用这个数据接口:https://5b5e71c98e9f160014b88cc9.mockapi.io/api/v1/lists
接口的数据大概这样子,json的数据格式
[
{
"id": "1",
"name": "小红",
"age": 20,
"sex": "女"
},
{
"id": "2",
"name": "小明",
"age": 21,
"sex": "男"
},
{
"id": "3",
"name": "翠花",
"age": 24,
"sex": "女"
},
{
"id": "4",
"name": "秋香",
"age": 25,
"sex": "女"
},
{
"id": "5",
"name": "张三",
"age": 30,
"sex": "男"
}
]
开始写代码:
为了方便不用写css,直接安装个boostrap,然后引入boostrap的样式好了
一、安装boostrap、axios
npm install bootstrap@3.3.7 --save
请求数据就用axios吧,也可以用JQuery的ajax(),我这里用axios
npm isntall axios --save
如果安装完成,可以看到
二、在src目录下新建一个List.js,在List.js中
在create-react-app可以尽情使用es6、es7的语法了,我们会对项目打包。
import React from 'react'; import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css'; import axios from 'axios';
首先先把组件写好,在List.js中,我先第一个表格数据的组件TrData
//List.js
class TrData extends React.Component{
constructor(props){
super(props);
}
render(){
return (
this.props.users.map((user,i)=>{
return (
<tr key={user.id} className="text-center">
<td>{user.id}</td>
<td>{user.title}</td>
<td>{user.name}</td>
<td>{user.sex}</td>
</tr>
)
})
)
}
}
首先用React.Component创建一个TrData组件,然后渲染传进来的数据users,循环遍历出来.遍历users的方法是es6的map()方法,大家也可用其他方法遍历了,只要数据能出来。
通过props给这个组件导入数据。接下来,我再创建一个List的组件,来显示UI视图
//List.js
class List extends React.Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th className="text-center">ID</th>
<th className="text-center">姓名</th>
<th className="text-center">年龄</th>
<th className="text-center">性别</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<TrData users={this.state.users}/>
</tbody>
</table>
)
}
}
并且导出这个组件
//List.js export default List;
接下来,我们来请求数据,我们知道在vue中有生命周期,可以选择在特定的生命周期上进行数据挂载。同样React也有生命周期。
当组件输出到 DOM 后会执行 componentDidMount()钩子,也就是说我们可以在componentDidMount()内请求数据,并更新数据。
还有一点就是我们请求的数据要放在那儿,没错,这就是state。可能有些读者不懂这个state,这里简单讲一下,state就是可以存储组件的一系列状态。只能定义在组件内部。接下来,我两个state的两个状态,一个是users,一个是是否已经加载数据完成的isLoaded。
在组件List内部加入
constructor(props){
super(props);
this.state={
users:[],
isLoaded:false
}
}
state需要在constructor上定义。这涉及ES6的语法特性,这里就不过多讲其他的了。
我们再在List内部添加
//当组件输出到 DOM 后会执行 componentDidMount()
componentDidMount(){
const _this=this; //先存一下this,以防使用箭头函数this会指向我们不希望它所指向的对象。
axios.get('https://5b5e71c98e9f160014b88cc9.mockapi.io/api/v1/lists')
.then(function (response) {
_this.setState({
users:response.data,
isLoaded:true
});
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.log(error);
_this.setState({
isLoaded:false,
error:error
})
})
}
通过axios请求数据,(在我之前的文章有)当请求成功后就更新state的users和isLoaded状态。更新state需要用this.setState()来更新状态,这个很类似微信小程序的setData(),state一发生改变,绑定那些状态的试图也会相应刷新改变。
我再写得合理一些,修改一下List 得render()
//List.js
render() {
if(!this.state.isLoaded){
return <div>Loading</div>
}else{
return (
<table className="table table-bordered">
<thead>
<tr>
<th className="text-center">ID</th>
<th className="text-center">姓名</th>
<th className="text-center">年龄</th>
<th className="text-center">性别</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<TrData users={this.state.users}/>
</tbody>
</table>
)
}
}
当再请求数据得时候显示Loading,请求完成直接显示数据。
三、在app.js中引入List.js并渲染
//app.js
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import './App.css';
import List from './List';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props){
super(props);
}
render() {
return (
<div className="container">
<List />
</div>
);
}
}
export default App;
四、在create-react-app脚手架跑起来项目
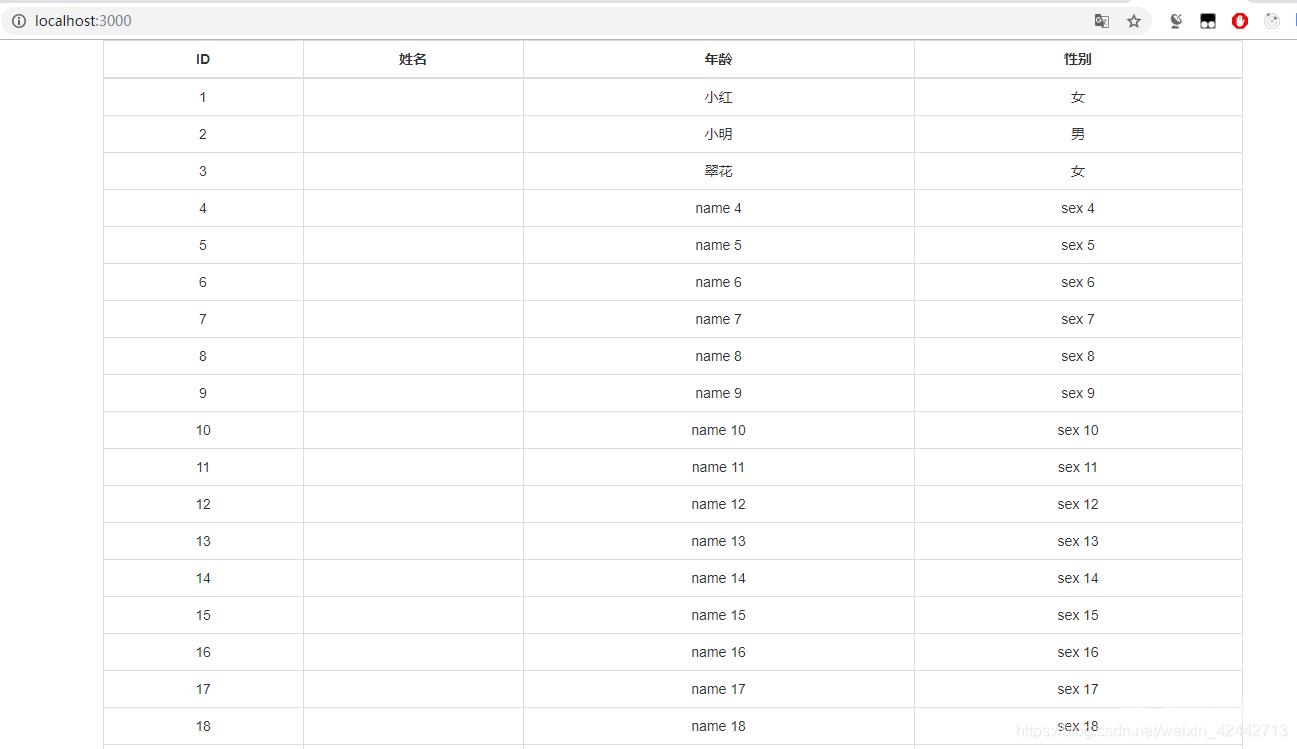
npm start
访问http://localhost:3000/即可看到如下界面:
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持易盾网络。
