目录
- 概述
- 坑是啥?
- 怎么坑的?
- 总结
概述
最近在做一些优化的时候用到了ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor。
虽然知道这个玩意,但是也很久没用,本着再了解了解的心态,到网上搜索了一下,结果就发现网上有些博客在说ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor有巨坑!!!
瞬间,我的兴趣就被激起来了,马上进去学习了一波~
不看不知道,看完后马上把我的代码坑给填上了~
下面就当记录一下吧,顺便也带大家了解了解,大家看完后也赶紧看看自己公司的项目代码有没有这种漏洞,有的话赶紧给填上,升级加薪指日可待!!!
坑是啥?
先看下面案例代码
public class ScheduledThreadPoolExecutorTest {
public static ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor scheduledThreadPoolExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(2);
public static AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
public static void main(String[] args) {
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
// 模拟业务逻辑
int num = atomicInteger.getAndIncrement();
// 模拟出现异常
if (num > 3) {
throw new RuntimeException("定时任务执行异常");
}
System.out.println("别坑我!");
}, 0, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
scheduledThreadPoolExecutor.shutdown();
}
}
案例代码逻辑很简单,主线程等待5秒后关闭线程池,定时任务执行三次后模拟抛出RuntimeException
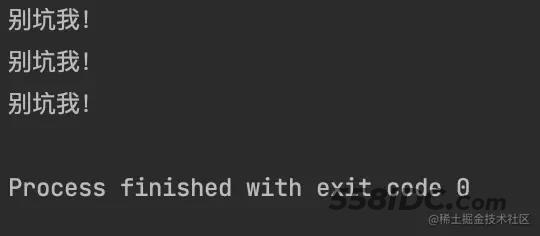
但是我们看看执行结果,只执行了三次!
因为某种情况下,定时任务在执行第四次时出现异常,从而导致任务调度被取消,不会继续执行
而且,异常信息也没有对外抛出!
那么咋解决嘞?try-catch就行了呗~
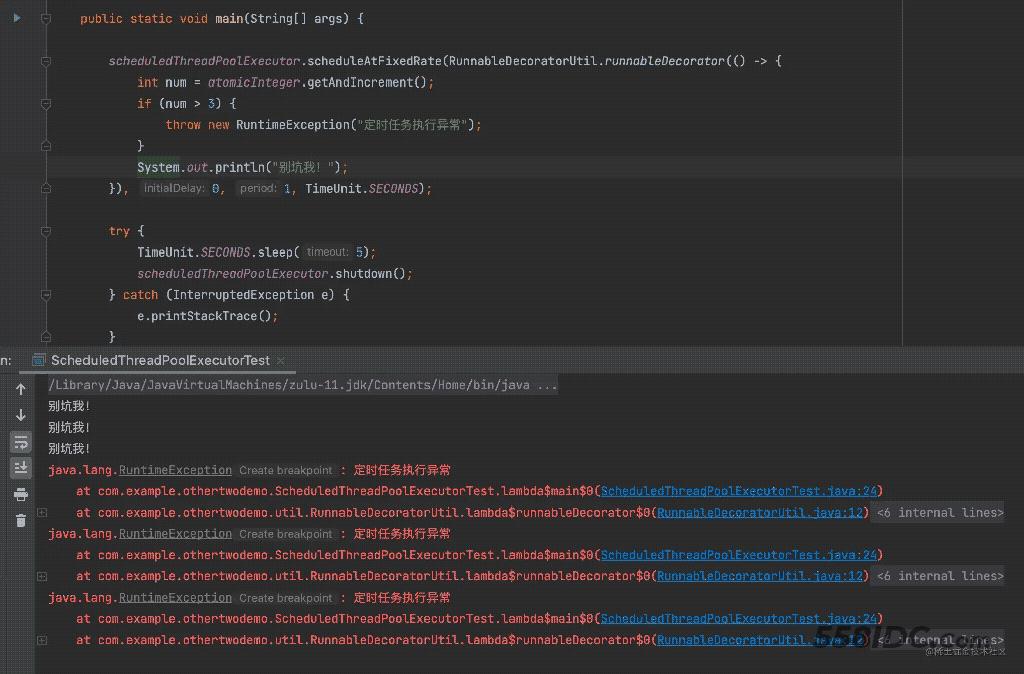
可以看到执行结果,虽然执行异常,但是任务却还是一直在调度~
代码里使用工具类对Runnable任务包了一层,就是加了try-catch
public class RunnableDecoratorUtil {
public static Runnable runnableDecorator(Runnable runnable) {
return () -> {
try {
runnable.run();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
};
}
}
okok,总结一下,坑就是: 任务如果抛出异常就不会继续调度执行了,赶紧去try-catch吧!!!
大家赶紧去看看自己代码有没有这个坑吧,本文到此结束!
开个玩笑~ 光知道有坑哪能不知道为啥坑,接下来就带大家了解一下坑到底是啥!
怎么坑的?
直接进入scheduleAtFixedRate源码查看
public ScheduledFuture<?> scheduleAtFixedRate(Runnable command,
long initialDelay,
long period,
TimeUnit unit) {
// 参数校验
if (command == null || unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (period <= 0L)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
// 将任务、执行时间、周期等封装到ScheduledFutureTask内
ScheduledFutureTask<Void> sft =
new ScheduledFutureTask<Void>(command,
null,
triggerTime(initialDelay, unit),
unit.toNanos(period),
sequencer.getAndIncrement());
RunnableScheduledFuture<Void> t = decorateTask(command, sft);
sft.outerTask = t;
// 延时执行
delayedExecute(t);
return t;
}
因为我们提交的任务被封装在ScheduledFutureTask,所以我们直接来看ScheduledFutureTask的run方法
public void run() {
// 校验当前状态是否还能执行任务,不能执行直接cancel取消
if (!canRunInCurrentRunState(this))
cancel(false);
else if (!isPeriodic())
// 如果不是周期性的,直接调用父类run方法执行一次即可
super.run();
else if (super.runAndReset()) { // 周期性任务,调用runAndReset运行并重置
// 设置下一次的执行时间
setNextRunTime();
// 将任务重新加入队列,进行调度
reExecutePeriodic(outerTask);
}
}
public boolean isPeriodic() {
return period != 0;
}
我们是周期性任务,所以直接看runAndReset源码
protected boolean runAndReset() {
// 检查任务状态,cas机制防止并发执行任务
if (state != NEW ||
!RUNNER.compareAndSet(this, null, Thread.currentThread()))
return false;
// 默认不周期执行任务
boolean ran = false;
// state为NEW状态
int s = state;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
if (c != null && s == NEW) {
try {
// 执行任务
c.call();
// 正常执行成功,设置为true代表周期执行
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 但是,如果执行异常!则不会将ran = true,所以最终返回false
setException(ex);
}
}
} finally {
runner = null;
// 设置为NEW状态
s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
// 正常执行完之后,结果为true,能够周期执行
// 但如果执行异常,ran为false,返回结果为false
return ran && s == NEW;
}
通过上面源码,我们可以很清楚的了解到,就是因为任务执行异常,且没有被try-catch,所以导致任务没有被再次加入到队列中进行调度。
并且通过文章开头,我们还能看到任务执行异常,但是却没有抛出异常信息
那是因为异常被封装了,只有调用get方法时,才会抛出异常
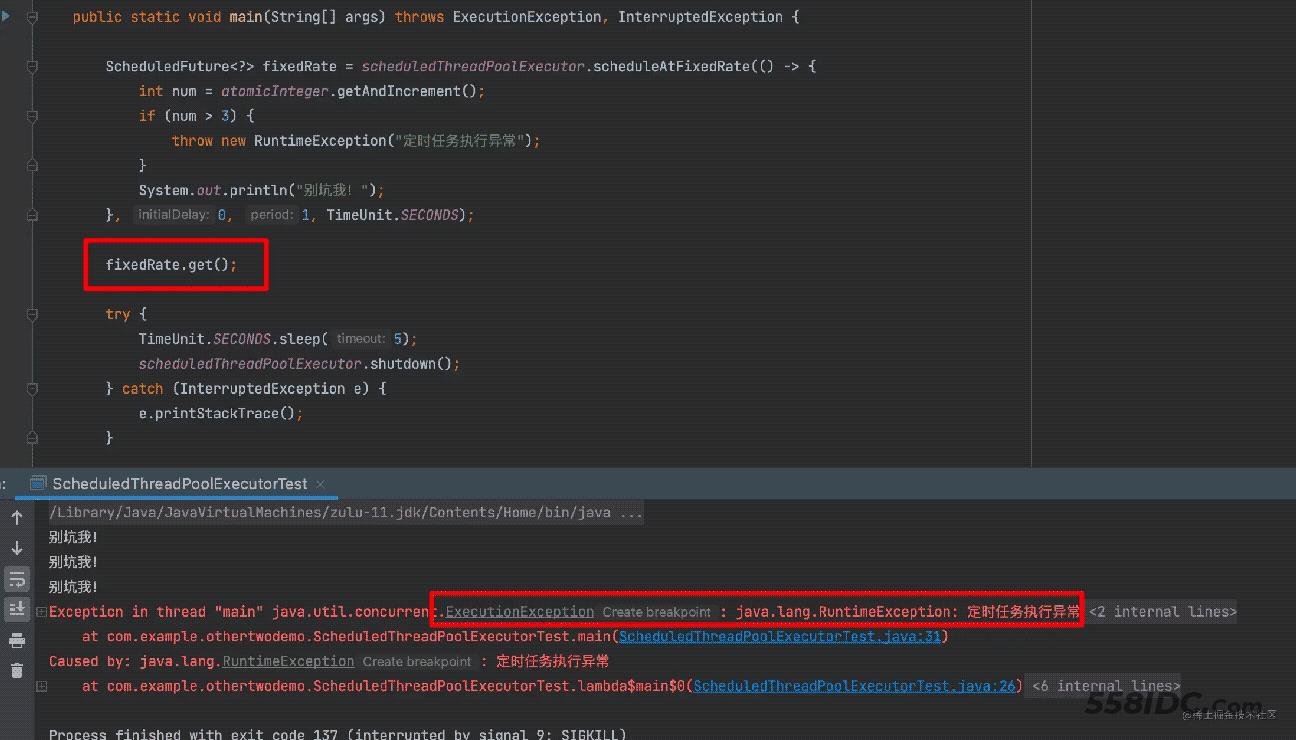
/** The result to return or exception to throw from get() */
private Object outcome;
private volatile int state;
private static final int NEW = 0;
private static final int COMPLETING = 1;
private static final int NORMAL = 2;
private static final int EXCEPTIONAL = 3;
private static final int CANCELLED = 4;
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (STATE.compareAndSet(this, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
// 将异常信息赋值给outcome
// outcome既可以为任务执行结果也可以为异常信息
outcome = t;
// 将state设置为异常状态,state=3
STATE.setRelease(this, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
// 调用get方法阻塞获取结果
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING)
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
// 此时s = EXCEPTIONAL = 3
if (s == NORMAL)
return (V)x;
if (s >= CANCELLED)
throw new CancellationException();
// 所以会走到这里,对外抛出了任务执行的异常
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable)x);
}
总结
通过上面对源码的了解,我们了解到,如果周期性任务执行出现异常,并且没有被try-catch,会导致该周期性任务不会再被放入到队列中进行调度执行。
以上就是ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor巨坑解决的详细内容,更多关于ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor坑的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
