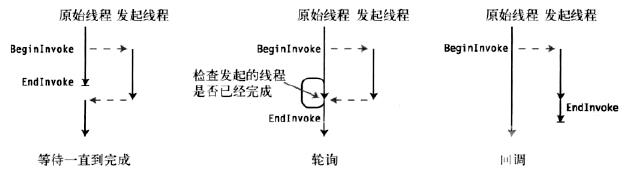
目录 1.等待模式 2.轮询模式 3.回调模式 总结 BeginInvoke实现异步编程的三种模式: 1.等待模式 在发起了异步方法以及做了一些其他处理之后,原始线程就中断并且等异步方法完成之后再
目录
- 1.等待模式
- 2.轮询模式
- 3.回调模式
- 总结
BeginInvoke实现异步编程的三种模式:
1.等待模式
在发起了异步方法以及做了一些其他处理之后,原始线程就中断并且等异步方法完成之后再继续;
eg:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace BeginInvokeDemo
{
public delegate int myDelegate(int num1,int num2); //声明委托
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
} private int Cal_Task1(int num1, int num2) //方法一
{
Thread.Sleep(3000); //进程延时3S,延长执行时间
return num1 + num2;
}
private int Cal_Task2(int num1, int num2) //方法二
{
return num1 + num2;
}
private void button_Calculate_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
myDelegate objTest = new myDelegate(Cal_Task1); //定义委托变量,引用任务1
IAsyncResult iar = objTest.BeginInvoke(3,4,null,null); //异步调用
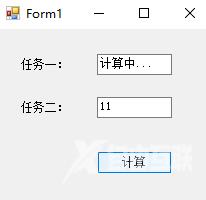
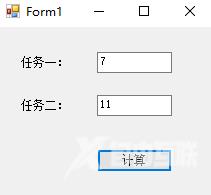
textBox_Result1.Text = "计算中..."; textBox_Result2.Text = Cal_Task2(5,6).ToString(); //同时可以并行其他任务 int result = objTest.EndInvoke(iar); //获取异步执行结果
//委托类型的EndInvoke()方法:借助IAsyncResult接口对象,不断查询异步调用是否结束。
//该方法知道被异步调用的方法所有的参数,所以,异步调用结束后,取出异步调用结果作为返回值
textBox_Result1.Text = result.ToString();
}
}
}
2.轮询模式
原始线程定期检查发起的线程是否完成,如果没有则可以继续做一些其他事情;
eg:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace ConsoleApplication2
{
delegate int MyDel(int num1,int num2);
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyDel del = new MyDel(Sum);
IAsyncResult iar = del.BeginInvoke(3,4,null,null);
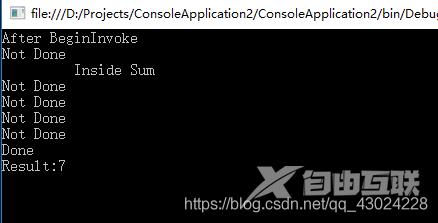
Console.WriteLine("After BeginInvoke"); while(!iar.IsCompleted)
{
Console.WriteLine("Not Done"); //继续处理
for (long i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
; //空语句
}
Console.WriteLine("Done"); int result = del.EndInvoke(iar);
Console.WriteLine("Result:{0}",result); Console.ReadLine();
} static int Sum(int x,int y)
{
Console.WriteLine(" Inside Sum");
Thread.Sleep(100); return x + y;
}
}
}
3.回调模式
原始线程一直执行,无需等待或检查发起的线程是否完成。
在发起的线程中引用方法完成之后,发起的线程就会调用回调方法,由回调方法再调用EndInvoke之前处理异步方法的结果。
eg:
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Windows.Forms;namespace _02_AsyncCallBackDemo
{
public partial class FrmCalllBack : Form
{
public FrmCalllBack()
{
InitializeComponent(); //【3】初始化委托变量
this.objMyCal = new MyCalculator(ExecuteTask); //也可以直接使用Lambda表达式
//this.objMyCal = (num, ms) =>
//{
// System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(ms);
// return num * num;
//};
} //【3】创建委托变量(因为异步函数和回调函数都要用,所以定义成成员变量)
private MyCalculator objMyCal = null; //【4】同时执行多个任务
private void btnExec_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
//发布任务
for (int i = 1; i < 11; i++)
{
//开始异步执行
objMyCal.BeginInvoke(10 * i, 1000 * i, MyCallBack, i);
//最后一个参数i给回调函数的字段AsyncState赋值,如果数据很多可以定义成类或结构
}
} //【5】回调函数
private void MyCallBack(IAsyncResult result)
{
int res = objMyCal.EndInvoke(result);
//显示异步调用结果:result.AsyncState字段用来封装回调函数自定义参数,object类型
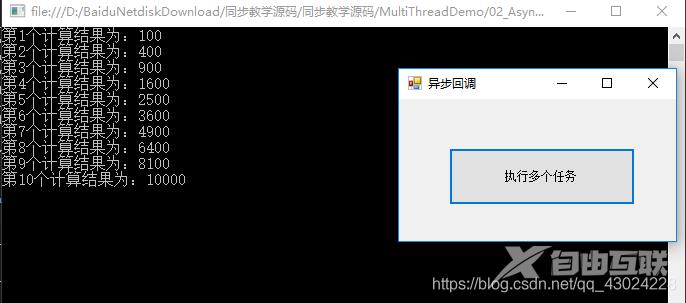
Console.WriteLine("第{0}个计算结果为:{1}", result.AsyncState.ToString(), res);
} //【2】根据委托定义一个方法:返回一个数的平方
private int ExecuteTask(int num, int ms)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(ms);
return num * num;
} //【1】声明委托
private delegate int MyCalculator(int num, int ms);
}
//异步编程的总结:
//1. 异步编程是建立在委托的基础上一种编程的方法。
//2. 异步调用的每个方法都是在独立的线程中执行的。因此,本质上就是一种多线程程序,是简化的多线程。
//3. 比较适合在后台运行较为耗时的《简单任务》,并且任务之间要求相互独立,任务中不应该有直接访问可视化控件大代码。
//4. 如果后台任务要求必须按照特定顺序执行,或者访问共享资源,则异步编程不太适合,应选择多线程开发技术。
}
总结
以上为个人经验,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
