目录
- 前言
- 消息存储格式总览
- CommitLog介绍
- MappedFile详解
- 消息存储格式介绍
- DefaultMessageStore介绍
- 消息存储源码分析
- 发送消息存储流程
- 消息预处理阶段
- 消息保存阶段
- 消息保存结果处理阶段
- 总结
前言
前面我们介绍了RocketMQ是如何接收消息的,下面我们来介绍Broker是如何保存消息的。
消息存储格式总览
Broker消息存储主要包括CommitLog,ConsumerQueue和Index三个部分。
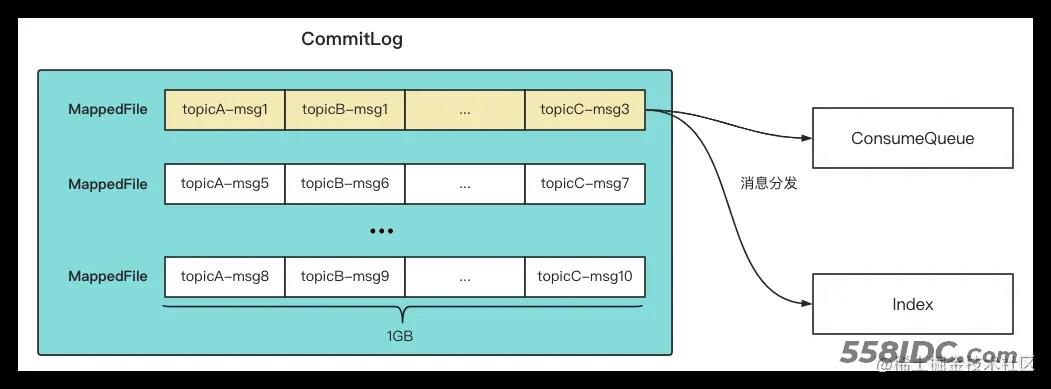
- CommitLog
CommitLog主要用于消息存储,所有topic的消息按顺序都存储在CommitLog中。
- ConsumerQueue
ConsumerQueue对应消费队列,消息存储到CommitLog后,会异步转发到ConsumerQueue文件中
- Index
消息索引,只要存储消息key与offset的关系
CommitLog介绍
CommitLog是消息和消息数据存储的主体,CommitLog存储的文件目录在${user.home}/store/commitlog中,它其实是一个目录,消息并不是直接存储在CommitLog中,而是存储在由20位数字构成的文件中。
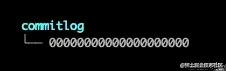
MappedFile详解
commitlog文件夹中文件单元是MappedFile,我们可以把MappedFile理解成一个文件管理的工具,如果需要将数据存储到磁盘,或者快速查找数据,都可以通过MappedFile。
每个MappedFile文件大小默认是1GB,文件名是由20位数字构成,文件名其实是MappedFile的起始偏移量,如果偏移量不足20位,则将偏移量的左边补0。上图中MappedFile的文件名是00000000000000000000,它代表的是CommitLog中的第一个文件,由于每个MappedFile文件大小是1GB,因此第二个文件的偏移量为1024*1024*1024(1GB),计算后的结果为1073741824,因此第二个文件的文件名为00000000001073741824,可依此类推其他文件的文件名。
消息存储格式介绍
消息在commitLog中存储的格式如下所示
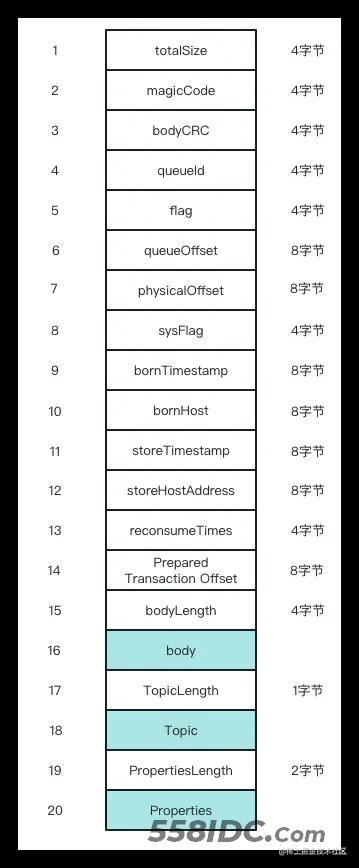
- totalSize
消息总长度,4字节
- magicCode
魔数,4字节,固定值十六进制是0xdaa320a7,10进制是-875286124
- bodyCRC
消息体crc校验码,4字节
- queueId
消息队列id,4字节
- flag
消息标记,RocketMQ不做处理,默认4字节
- queueOffset
消息在ConsumeQueue文件中的物理偏移量,默认8字节
- physicalOffset
消息在CommitLog文件中的物理偏移量,默认8字节
- sysFlag
消息系统标记,例如是否压缩、是否是事务消息等,4字节
- bornTimestamp
消息生产者调用消息API的时间戳,8字节
- bornHost
BORNHOST 消息生产者IP和端口号,8字节
- storeTimestamp
消息存储时间戳,8字节
- storeHostAddress
STOREHOSTADDRESS 消息存储Broker的IP和端口号,8字节
- reconsumeTimes
消息重试次数 4字节
- Prepared Transaction Offset
事务消息偏移量,8字节
- bodyLength
消息体长度,4字节
- body
消息体内容,它是变长的,长度为bodyLength中存储的值
- TopicLength
topicLength表示topic占用的长度,topicLength占用1字节,也就是255,也就是说topic长度最长不能超过255字节
- Topic
topic是消息主题名称,topic是变长的,实际占用topicLength字节
- PropertiesLength
propertiesLength表示properties占用的长度,propertiesLength占用2字节,也就是说properties长度最长不超过65536字节
- Properties
properties是消息属性,properties是变长的,实际占用propertiesLength字节
DefaultMessageStore介绍
Broker保存消息是通过消息存储默认实现类org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore执行的,它是Broker存储模块中最最最重要的一个类,提供了很多存储文件的API。DefaultMessageStore中和消息存储相关的属性如下所示,
// 消息存储配置
private final MessageStoreConfig messageStoreConfig;
// CommitLog文件的存储实现类
private final CommitLog commitLog;
// 消息队列存储缓存表,key是topic
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* topic */, ConcurrentMap<Integer/* queueId */, ConsumeQueue>> consumeQueueTable;
// MappedFile分配服务
private final AllocateMappedFileService allocateMappedFileService;
// 直接内存暂存池
private final TransientStorePool transientStorePool;
// broker状态管理器
private final BrokerStatsManager brokerStatsManager;
// 锁文件
// 目录: ${user.home}/store/lock
private RandomAccessFile lockFile;
消息存储源码分析
发送消息存储流程
发送消息存储的入口函数是DefaultMessageStore#asyncPutMessage,它主要分为下面三步
- 存储状态校验
- 校验消息存储服务是否关闭,当前Broker是否是从节点,queue是否可写
- 消息校验
- 校验topic名称长度是否超过了127字节和property长度是否超过了32767
- 将消息保存到commitLog
// org.apache.rocketmq.store.DefaultMessageStore#asyncPutMessage
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// 1. 存储状态校验
PutMessageStatus checkStoreStatus = this.checkStoreStatus();
if (checkStoreStatus != PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(new PutMessageResult(checkStoreStatus, null));
}
// 2. 校验topic名称和property长度
PutMessageStatus msgCheckStatus = this.checkMessage(msg);
if (msgCheckStatus == PutMessageStatus.MESSAGE_ILLEGAL) {
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(new PutMessageResult(msgCheckStatus, null));
}
// ...
long beginTime = this.getSystemClock().now();
// 3. 保存到commitLog
CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> putResultFuture = this.commitLog.asyncPutMessage(msg);
//...
return putResultFuture;
}
CommitLog#asyncPutMessage保存消息
CommitLog#asyncPutMessage保存消息可以分为三个阶段
- 消息预处理阶段
- 消息保存阶段
- 消息保存结果处理阶段
消息预处理阶段
消息预处理阶段可以分为下面三个步骤
- 设置消息存储时间戳和消息体CSC32信息
- 如果是延迟消息,则设置延迟信息
如果是非事务消息或者是提交的事务消息,并且设置了消息的延迟级别,说明当前消息是延迟消息,Broker在处理延迟消息时会将消息投递到名为SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX的Topic。在消息预处理的阶段,会先将当前消息的topic设置为SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX,queueId设置为延迟级别-1,并且将原来的Topic和queueId设置到消息的REAL_TOPIC和REAL_QID属性中。
- 设置ip及构建存储消息上下文
// org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog#asyncPutMessage
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// 1. 设置消息存储时间戳和消息体CSC32信息
msg.setStoreTimestamp(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 设置消息存储时间
msg.setBodyCRC(UtilAll.crc32(msg.getBody())); // 设置消息体CRC32校验值
// 2. 如果是非事务消息,或者是事务提交消息,判断是否是是否是延迟消息,如果是延迟消息则设置延迟相关信息
if (tranType == MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_NOT_TYPE
|| tranType == MessageSysFlag.TRANSACTION_COMMIT_TYPE) {
// Delay Delivery
// 如果延迟级别>0,说明是延迟消息
if (msg.getDelayTimeLevel() > 0) {
// 如果大于最大的延迟级别,则取最大的延迟级别
if (msg.getDelayTimeLevel() > this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel()) {
msg.setDelayTimeLevel(this.defaultMessageStore.getScheduleMessageService().getMaxDelayLevel());
}
// 消息topic改成延迟消息topic(SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX)
topic = TopicValidator.RMQ_SYS_SCHEDULE_TOPIC;
// 延迟topic的queueId:延迟级别-1
int queueId = ScheduleMessageService.delayLevel2QueueId(msg.getDelayTimeLevel());
// 消息属性中设置真实的QueueId
MessageAccessor.putProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_REAL_TOPIC, msg.getTopic());
MessageAccessor.putProperty(msg, MessageConst.PROPERTY_REAL_QUEUE_ID, String.valueOf(msg.getQueueId()));
msg.setPropertiesString(MessageDecoder.messageProperties2String(msg.getProperties()));
// 把SCHEDULE_TOPIC_XXXX设置为当前消息的topic,消息先投递到这个队列中
msg.setTopic(topic);
msg.setQueueId(queueId);
}
}
// 3. 设置ip并构建存储消息上下文信息
msg.setBornHostV6Flag(); // 如果producer的ip是IpV6,则设置生产者IpV6 flag
msg.setStoreHostAddressV6Flag(); // 如果如果broker的ip是IpV6,则设置BrokerIpV6 flag
PutMessageThreadLocal putMessageThreadLocal = this.putMessageThreadLocal.get();
// 构建存消息上下文
PutMessageContext putMessageContext = new PutMessageContext(/*key值:topic-queueId*/generateKey(putMessageThreadLocal.getKeyBuilder()/*StringBuilder*/, msg));
// ... 省略部分代码
}
消息保存阶段
消息保存阶段可以分为如下步骤
- 获取消息保存锁
- 获取最新的mappedFile
获取MappedFile调用的是MappedFileQueue中的方法,获取最新的MappedFile
- 如果最新的mappedFile为空或者已经满了,则创建新的MappedFile
- 将消息保存的mappedFile中
- 处理消息保存结果
- 释放消息保存锁
// org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog#asyncPutMessage
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// ... 省略部分代码
// 1. 消息保存锁,默认是ReentrantLock互斥锁
putMessageLock.lock();
try {
// 2. 获取最新的mappedFile
MappedFile mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile();
// 3. 如果获取到的mappedFile是null说明之前没有存储消息
// 如果mappedFile满了,说明需要创建一个新的MappedFile
if (null == mappedFile || mappedFile.isFull()) {
mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(0);
}
// 如果创建mappedFile失败,则返回异常信息
if (null == mappedFile) {
// 创建mappedFile失败
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.CREATE_MAPEDFILE_FAILED, null));
}
// 4. 将消息保存的mappedFile中
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
// 5. 处理消息保存结果
switch (result.getStatus()) {
case PUT_OK:
break;
// mappedFile满了,重新创建mappedFile后再写入消息
case END_OF_FILE:
unlockMappedFile = mappedFile;
// 创建一个新的文件,然后重新写入
mappedFile = this.mappedFileQueue.getLastMappedFile(0);
//...
// 写消息
result = mappedFile.appendMessage(msg, this.appendMessageCallback, putMessageContext);
break;
// ...
}
} finally {
// 6. 释放锁
putMessageLock.unlock();
}
// ... 省略部分代码
}
上面第4步MappedFile#appendMessage逻辑主要有三步
- 获取当前写文件位置
如果写指针小于文件大小,则对消息进行追加处理
获取写缓冲
调用AppendMessageCallback的doAppend将消息写到内存缓冲中
回调函数doAppend方法分为单条处理逻辑和批量消息处理逻辑,下面仅展示了单条消息处理逻辑
- 消息保存完成后会更新当前写文件的位置和消息保存时间戳
public AppendMessageResult appendMessagesInner(final MessageExt messageExt, final AppendMessageCallback cb,
PutMessageContext putMessageContext) {
// 获取当前写文件位置
int currentPos = this.wrotePosition.get();
// 如果写文件位置小于文件size
if (currentPos < this.fileSize) {
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = writeBuffer != null ? writeBuffer.slice() : this.mappedByteBuffer.slice();
byteBuffer.position(currentPos);
AppendMessageResult result;
// 如果是单条消息
if (messageExt instanceof MessageExtBrokerInner) {
result = cb.doAppend(this.getFileFromOffset(), byteBuffer, this.fileSize - currentPos/*文件长度-当前写位置,可以写的长度*/,(MessageExtBrokerInner) messageExt, putMessageContext);
}
//...
// 更新当前写文件位置和消息保存时间戳
this.wrotePosition.addAndGet(result.getWroteBytes());
this.storeTimestamp = result.getStoreTimestamp();
return result;
}
}
上面保存消息回调函数中的doAppend实际调用的是CommitLog中内部类DefaultAppendMessageCallback的doAppend方法,这里大致可以分为下面几个步骤
- 获取消息物理偏移量,并且创建消息id生成器,从topicQueueTable中获取Queue的最大相对便宜量。
消息id的格式如下所示,它由ip,端口和消息偏移量公共构成,长度是16字节,为了保证消息的可读性,返回给应用程序的Id转成了字符串。
消息id这么设计的原因是可以根据消息id快速找到broker的IP,端口,以及消息在的物理偏移量,通过它可以快速找到消息
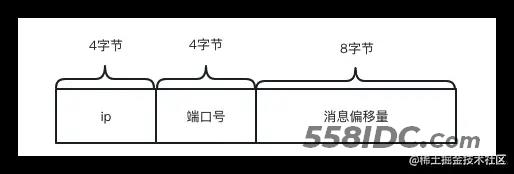
- 如果消息长度加上消息结束符(8字节)大于maxBlank,则表示该mappedFile已经没有足够的空间保存该消息了,那么就会将消息结束符写入缓冲中,并返回
END_OF_FILE,mappedFile消息结束符如下所示
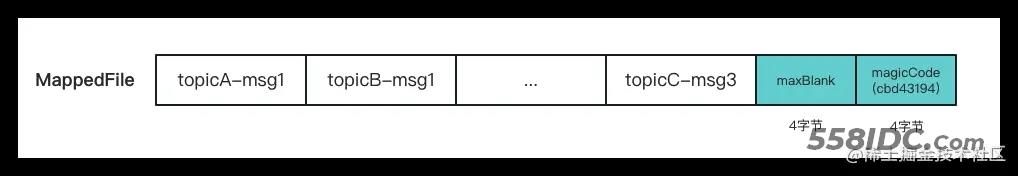
- 如果空间足够,将queue的相对偏移量,物理偏移量,sysflag,消息创建时间,消息创建ip,消息保存时间及消息体等按照上面消息格式保存到缓冲中。
- 创建AppendMessageResult对象并返回,它包括消息追加状态、消息写入物理偏移量、消息写入长度、消息ID生成器、消息开始追加的时间戳、消息队列偏移量、消息开始写入的时间戳等属性。
// org.apache.rocketmq.store.CommitLog.DefaultAppendMessageCallback#doAppend
public AppendMessageResult doAppend(final long fileFromOffset/*消息文件起始偏移量*/, final ByteBuffer byteBuffer, final int maxBlank/*文件可写长度*/,final MessageExtBrokerInner msgInner, PutMessageContext putMessageContext) {
// 1. 物理offset,文件起始offset+写offset
long wroteOffset = fileFromOffset + byteBuffer.position();
// 创建消息id supplier
Supplier<String> msgIdSupplier = () -> {
int sysflag = msgInner.getSysFlag();
int msgIdLen = (sysflag & MessageSysFlag.STOREHOSTADDRESS_V6_FLAG) == 0 ? 4 + 4 + 8 : 16 + 4 + 8;
ByteBuffer msgIdBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(msgIdLen);
MessageExt.socketAddress2ByteBuffer(msgInner.getStoreHost(), msgIdBuffer);
msgIdBuffer.clear();//because socketAddress2ByteBuffer flip the buffer
msgIdBuffer.putLong(msgIdLen - 8, wroteOffset);
return UtilAll.bytes2string(msgIdBuffer.array());
};
// topic-ququeId
String key = putMessageContext.getTopicQueueTableKey();
// 获取消息queue offset
Long queueOffset = CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.get(key);
// 如果queueOffset是null,则将其置0
if (null == queueOffset) {
queueOffset = 0L;
CommitLog.this.topicQueueTable.put(key, queueOffset);
}
// 获取写缓冲
ByteBuffer preEncodeBuffer = msgInner.getEncodedBuff();
final int msgLen = preEncodeBuffer.getInt(0);
// 2. 判断空间是否足够,如果剩余空间不足,则保存TOTAL+MAGICCODE之后,返回BLANK_MAGIC_CODE
if ((msgLen + END_FILE_MIN_BLANK_LENGTH) > maxBlank) {
this.msgStoreItemMemory.clear();
// 1 TOTALSIZE 写消息总长度
this.msgStoreItemMemory.putInt(maxBlank);
// 2 MAGICCODE 写魔数
this.msgStoreItemMemory.putInt(CommitLog.BLANK_MAGIC_CODE);
byteBuffer.put(this.msgStoreItemMemory.array(), 0, 8);
return new AppendMessageResult(/*...*/);
}
int pos = 4/*totalSize*/ + 4/*magicCode*/ + 4/*bodyCRC*/ + 4/*queueId*/ + 4/*flag*/;
// set队列的offset,
preEncodeBuffer.putLong(pos, queueOffset);
pos += 8;
// 设置物理offset: 文件起始offset+当前文件写消息的offset
preEncodeBuffer.putLong(pos, fileFromOffset + byteBuffer.position());
int ipLen = (msgInner.getSysFlag() & MessageSysFlag.BORNHOST_V6_FLAG) == 0 ? 4 + 4 : 16 + 4;
// set 8 SYSFLAG, 9 BORNTIMESTAMP, 10 BORNHOST, 11 STORETIMESTAMP
pos += 8 + 4 + 8 + ipLen;
// 设置存储消息ip地址
preEncodeBuffer.putLong(pos, msgInner.getStoreTimestamp());
// 写消息到队列缓冲
byteBuffer.put(preEncodeBuffer);
msgInner.setEncodedBuff(null);
// 4. 返回消息保存结果
AppendMessageResult result = new AppendMessageResult(AppendMessageStatus.PUT_OK, wroteOffset, msgLen, msgIdSupplier,
msgInner.getStoreTimestamp(), queueOffset, CommitLog.this.defaultMessageStore.now() - beginTimeMills);
return result;
}
消息保存结果处理阶段
消息保存结果处理阶段主要包括下面三个
- 提交刷盘请求
如果是同步刷盘,则会创建刷盘请求并返回CompleteFuture,如果是异步刷盘,则会唤醒刷盘服务,然后返回消息保存成功的CompleteFuture
- 提交消息复制请求
如果是同步复制,则创建消息同步请求然后返回CompleteFuture,如果是异步复制则直接放回消息保存成功的CompleteFuture
- 合并提交刷盘请求和提交消息复制请求
CompleteFuture#thenCombine是将两个CompleteFuture(提交刷盘请求,提交消息复制请求)组合起来,等提交刷盘请求和提交消息复制请求都执行完了之后再执行后续任务
public CompletableFuture<PutMessageResult> asyncPutMessage(final MessageExtBrokerInner msg) {
// ... 省略部分代码
PutMessageResult putMessageResult = new PutMessageResult(PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK, result);
// 1. 提交刷盘请求
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> flushResultFuture = submitFlushRequest(result, msg);
// 2. 提交复制请求
CompletableFuture<PutMessageStatus> replicaResultFuture = submitReplicaRequest(result, msg);
// 3. 合并提交刷盘请求和提交复制请求结果
return flushResultFuture.thenCombine(replicaResultFuture, (flushStatus, replicaStatus) -> {
if (flushStatus != PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK) {
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(flushStatus);
}
if (replicaStatus != PutMessageStatus.PUT_OK) {
putMessageResult.setPutMessageStatus(replicaStatus);
}
return putMessageResult;
});
}
总结
消息保存到commitLog实际上是保存到byteBuffer中,消息是在回调结果时根据配置决定同步/异步刷盘以及同步/异步同步到从节点。消息在这个阶段也并不会将消息分发到comsumeQueue以及Index中。
以上就是RocketMQ | 源码分析】Broker是如何保存消息的?的详细内容,更多关于RocketMQ Broker保存消息的资料请关注自由互联其它相关文章!
