一、运算符重载
1.1运算符重载
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
关键字: operator 后面接需要重载的运算符符号
函数的原型: 返回值类型 operator 操作符(参数列表)
注意:
- 不能通过连接其他符号来创建新的操作符:比如operator@
- 重载操作符必须有一个类类型参数
- 用于内置类型的运算符,其含义不能改变,例如:内置的整型+,不 能改变其含义
- 作为类成员函数重载时,其形参看起来比操作数数目少1,因为成员函数的第一个参数为隐藏的this
- .* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
bool operator ==(const Date& d)
{
return _day == d._day &&
_month == d._month &&
_year == d._year;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};由上面的运算符重载==可以看出来,在进行运算符重载的时候,是内置了this指针的,也就是说已经隐含了一个参数,那么传进来的参数就只需要一个,也是就const Date& d,而且这个参数类型一定要是类类型。
1.2运算符分类
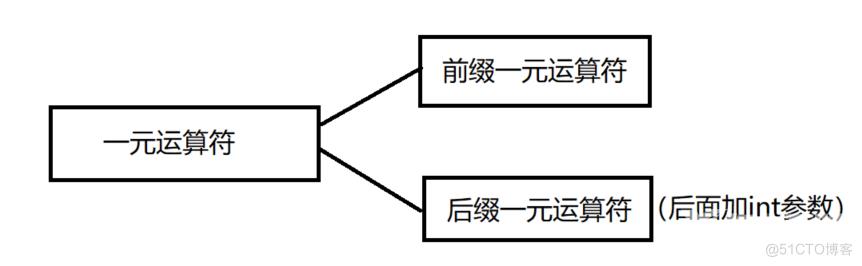
一元运算符可以分为前缀一元运算符和后缀一元运算符,最常见的是前置++ 和后置++ ,那么他们实现的区别就在于后面参数的有无,后缀一元运算符后面需要加上int参数。
1.3运算符重载实例
注意:所有的运算符重载都用到了*this这个内置参数
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d);
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d);
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d);
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d);
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d);
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d);1.3.1 >运算符重载
// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}对两个对象的_year,_month,_day不断的比较大小,返回布尔值。
1.3.2 ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._year;
}连续的&&当有一个不相等,那么就返回fasle。
1.3.3 >=运算符重载
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}本着能复用就复用的原则,复用上面的==和>运算符重载,还有注意就是要显示表达this指针那么就要用*this。
1.3.4 <运算符重载
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}复用上面的>=运算符取反面。
1.3.5 <=运算符重载
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}复用上面的>运算符取反面。
1.3.6 !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}复用上面的==运算符取反面。
二、赋值运算符重载
2.1赋值运算符重载格式
- 参数类型:const T&,传递引用可以提高传参效率
- 返回值类型:T&,返回引用可以提高返回的效率,有返回值目的是为了支持连续赋值
- 检测是否自己给自己赋值
- 返回*this :要复合连续赋值的含义
2.2获取当月天数函数
函数声明:
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month);这个函数是以日期类为例,为以后进行赋值运算符重载封装的函数,解决获取在某年某月下当月的天数情况。
函数实现:
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return arr[month];
}
}本函数的实现是枚举了正常情况下的每个月的天数,然后进行的特判,判断的是闰年还是平年来确定2月的天数,小伙伴们应该都知道&&逻辑运算符具有惰性,也就是左边为假,那么就不进行后面的判断了,所以在这里先判断month == 2那么就可以提高判断速度。
2.3 赋值运算符重载
注意:所有的运算符重载都用到了*this这个内置参数
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d);2.3.1 =赋值运算符重载
//赋值运算符重载 =
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d) //两个已经初始化过的对象之间进行赋值
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}赋值运算符是将一个已经进行初始化的对象的值赋给另一个也已经初始化的对象;而拷贝构造是把一个已经进行初始化的对象的值赋给一个刚被构造未被初始化的对象,所以可以通过这个进行区分。
2.3.2 +=赋值运算符重载
重载意义:日期+=天数(往后推算日期)
//赋值运算符重载 +=
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
//+= 是要改变自己
//考虑到day为负数的情况
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
++ _month;
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}+=赋值运算符重载要注意考虑到输入数据的合法性,增强函数的鲁棒性。这里的*this -= -day;是复用的后面实现的-=的赋值运算符重载。这里整体实现的思路是:
先把
day加到_day上,当_day超过当月天数,_month加1,当_month超过12到13的时候,_year加1,_month赋值初始化为1,直到_day回到当月合理区间范围结束。
2.3.3 +赋值运算符重载
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date d(*this); //*this本身不变 先拷贝一份来进行计算
d += day;
return d;
//d._day += day;
//while (d._day > GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month))
//{
// ++d._month;
// d._day -= GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month);
// if (d._month == 13)
// {
// ++d._year;
// d._month = 1;
// }
//}
//return d;
}
可以采用不复用来实现,需要注意+赋值运算符不影响*this本身,所以在运算前要进行一次拷贝构造Date d(*this); 。整体代码风格和格局和+=赋值运算符相似。
采用复用真的很香
Date d(*this); //*this本身不变 先拷贝一份来进行计算
d += day;
return d;2.3.4 -赋值运算符重载
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
//*this 还是不变 所以先拷贝一份
Date d(*this);
d._day -= day;
while (d._day < 0)
{
--d._month;
d._day += GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month);
if (d._month == 0)
{
--d._year;
d._month = 12;
}
}
return d;
}注意开始计算之前要进行一次拷贝构造Date d(*this);,因为-赋值运算符构造不影响*this,实现思路和+赋值运算符相反。
2.3.5 +=赋值运算符重载
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
//本身需要进行改变 所以不需要拷贝一份 直接来操作
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}2.3.6 前置++ 赋值运算符重载
//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this; //引用传值 深拷贝
}前置++是不带参数的,后置++带一个int类型参数,参数名省略。这里是直接复用了前面+赋值运算符。简化了代码。
2.3.7 后置++ 赋值运算符重载
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int) // 用int 来进行区分
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp; //虽然要++ 但是返回值是++之前的值
}后置++一定注意,返回的要和原来的一样,下一次调用这个对象才是+1,所有进行了一次拷贝构造来作为返回值。
2.3.8 前置-- 赋值运算符重载
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}2.3.9 后置-- 赋值运算符重载
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}三、实现 日期-日期
实现日期减日期获取天数,我采用的是从两个日期中较小的一个进行不断+1,计数来确定天数。
// 日期-日期 返回天数
// 运算符重载也可以进行函数重载 根据参数的类型和数量不同
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
int n = 0;
//修正
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
while (min != max)
{
++n;
++min;
}
return n * flag;
}四、整体代码
Date.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
void print()
{
cout << _year << " " << _month << " " << _day << endl;
}
// 全缺省的构造函数
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1);
// 拷贝构造函数
// d2(d1)
Date(const Date& d);
// 赋值运算符重载
// d2 = d3 -> d2.operator=(&d2, d3)
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
// 日期+=天数
Date& operator+=(int day);
// 日期+天数
Date operator+(int day);
// 日期-天数
Date operator-(int day);
// 日期-=天数
Date& operator-=(int day);
// 前置++
Date& operator++();
// 后置++
Date operator++(int);
// 后置--
Date operator--(int);
// 前置--
Date& operator--();
// >运算符重载
bool operator>(const Date& d);
// ==运算符重载
bool operator==(const Date& d);
// >=运算符重载
bool operator >= (const Date& d);
// <运算符重载
bool operator < (const Date& d);
// <=运算符重载
bool operator <= (const Date& d);
// !=运算符重载
bool operator != (const Date& d);
// 日期-日期 返回天数
int operator-(const Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
Date.cpp
#include"Date.h"
int GetMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int arr[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0))
{
return 29;
}
else
{
return arr[month];
}
}
//全缺省参数构造函数的实现
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
{
_year = year;
_month = month;
_day = day;
}
//拷贝构造
Date::Date(const Date& d) //拷贝构造是 用一个已经初始化的对象来初始化另外一个对象
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
//赋值运算符重载 =
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d) //两个已经初始化过的对象之间进行赋值
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
//赋值运算符重载 +=
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
//+= 是要改变自己
//考虑到day为负数的情况
if (day < 0)
{
return *this -= -day;
}
_day += day;
while (_day > GetMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
++ _month;
_day -= GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator+(int day)
{
Date d(*this); //*this本身不变 先拷贝一份来进行计算
d += day;
return d;
//d._day += day;
//while (d._day > GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month))
//{
// ++d._month;
// d._day -= GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month);
// if (d._month == 13)
// {
// ++d._year;
// d._month = 1;
// }
//}
//return d;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day)
{
//*this 还是不变 所以先拷贝一份
Date d(*this);
d._day -= day;
while (d._day < 0)
{
--d._month;
d._day += GetMonthDay(d._year, d._month);
if (d._month == 0)
{
--d._year;
d._month = 12;
}
}
return d;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
//本身需要进行改变 所以不需要拷贝一份 直接来操作
if (day < 0)
{
return *this += -day;
}
_day -= day;
while (_day <= 0)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += GetMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
//前置++
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this; //引用传值 深拷贝
}
// 后置++
Date Date::operator++(int) // 用int 来进行区分
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this += 1;
return tmp; //虽然要++ 但是返回值是++之前的值
}
// 后置--
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date tmp = *this;
*this -= 1;
return tmp;
}
// 前置--
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
// ==运算符重载
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d)
{
return _year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._year;
}
// >运算符重载
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d)
{
if (_year > d._year)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month > d._month)
{
return true;
}
else if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
// >=运算符重载
//能对上面进行复用尽量进行复用
bool Date::operator >= (const Date& d)
{
return (*this == d) || (*this > d);
}
// <运算符重载
//复用
bool Date::operator < (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this >= d);
}
// <=运算符重载
//复用
bool Date::operator <= (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this > d);
}
// !=运算符重载
bool Date::operator != (const Date& d)
{
return !(*this == d);
}
// 日期-日期 返回天数
// 运算符重载也可以进行函数重载 根据参数的类型和数量不同
int Date::operator-(const Date& d)
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
int n = 0;
//修正
if (*this < d)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
while (min != max)
{
++n;
++min;
}
return n * flag;
}
//这个功能的实现方法有很多,这里讲解一个思路非常简单的方法:我们前面已经实现了日期类对象的++和==两个运算符,所以我们用前面的>运算符找到比较小的日期,然后给它一直++,与此同时定义一个计数器,小日期++的同时他也跟着++,每次++之后都拿来和较大的日期进行比较,直到二者相等,返回计数器中的值即可。实现方法如下:
test.cpp
#include"Date.h"
//class Date
//{
// //构造函数
// Date()
// {
//
// }
//
//
//
// //析构函数 构造函数和析构函数其实都可以不写 因为都是内置成员变量
// ~Date()
// {
//
// }
// //构造函数和析构函数是来解决初始化和销毁的
//
//
//private:
// int year;
// int month;
// int day;
//
//
//};
void TestDate1()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 5);
d1 -= 10000;
d1.print();
}
void TestDate2()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 5);
d1 += 100;
d1.print();
d1 += -100;
d1.print();
d1 -= -100;
d1.print();
}
void TestDate3()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 5);
Date ret1 = d1++;
ret1.print();
d1.print();
Date d2(2023, 5, 6);
Date ret2 = ++d2;
ret2.print();
d2.print();
}
void TestDate4()
{
Date d1(2023, 5, 5);
Date d2(2000, 1, 1);
cout << d1 - d2 << endl;
cout << d2 - d1 << endl;
}
int main()
{
//Date d1(2003,11,4);
//Date d2(d1);
//d1.print();
//d2.print();
//d1+=1;
//d1.print();
//d2 -= 1;
//d2.print();
//d1--;
//d1.print();
//d2++;
//d2.print();
//d1 += 100;
//d1.print();
//d2 += 100;
//d2.print();
//cout << (d1 > d2) << endl;
//Date d3(2023, 5, 5);
//d3 -= 50;
//d3.print();
//TestDate1();
//TestDate2();
//TestDate3();
TestDate4();
return 0;
}