C语言函数大全 本篇介绍C语言函数大全 – f 开头的函数 1. fabs,fabsf,fabsl 1.1 函数说明 函数声明 函数功能 double fabs(double x); 返回 x 的绝对值(double) float fabsf(float x); 返回 x 的绝对值(
C语言函数大全
本篇介绍C语言函数大全 – f 开头的函数
1. fabs,fabsf,fabsl
1.1 函数说明
double fabs(double x);
返回 x 的绝对值(double)
float fabsf(float x);
返回 x 的绝对值(float)
long double fabsl(long double x);
返回 x 的绝对值(long double)
1.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
int main(void)
{
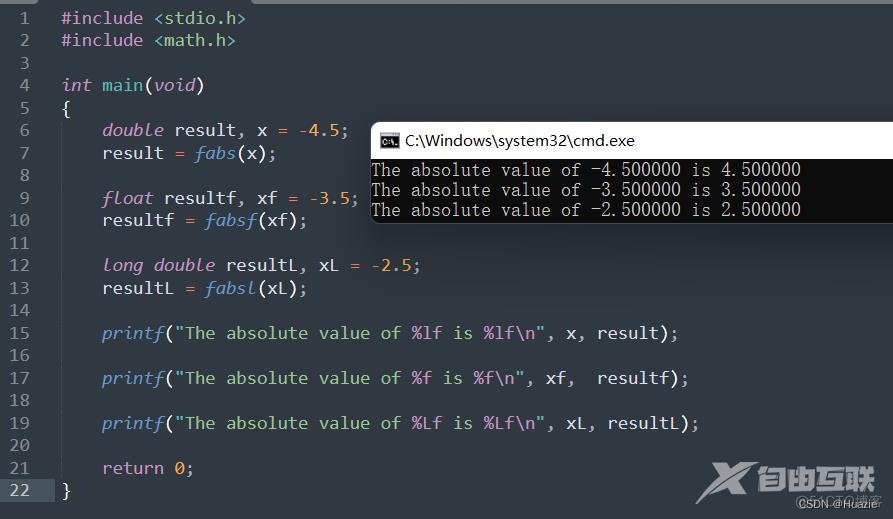
double result, x = -4.5;
result = fabs(x); // 取绝对值
float resultf, xf = -3.5;
resultf = fabsf(xf);
long double resultL, xL = -2.5;
resultL = fabsl(xL);
printf("The absolute value of %lf is %lf\n", x, result);
printf("The absolute value of %f is %f\n", xf, resultf);
printf("The absolute value of %Lf is %Lf\n", xL, resultL);
return 0;
}
1.3 运行结果
2. fclose
2.1 函数说明
int fclose(FILE *stream);
关闭一个文件流
2.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
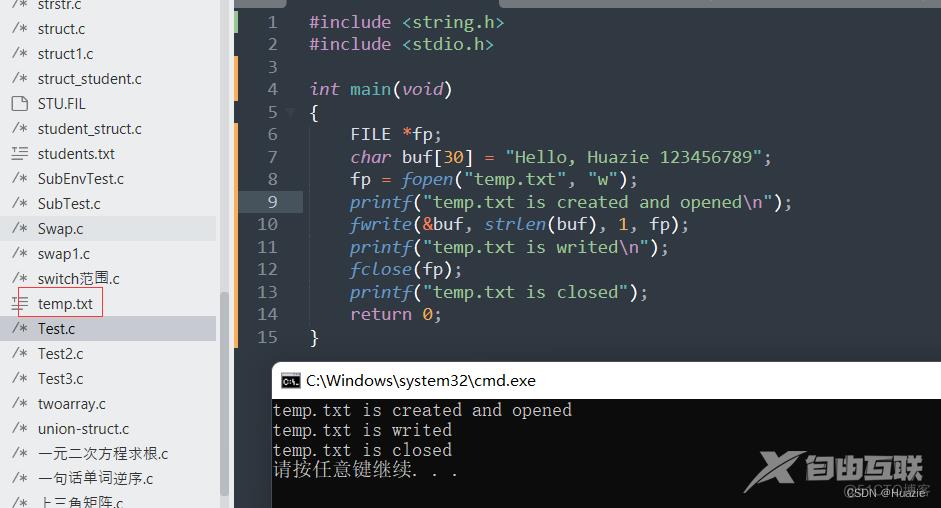
FILE *fp;
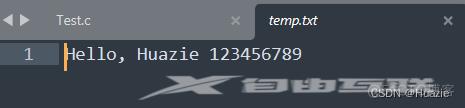
char buf[30] = "Hello, Huazie 123456789";
fp = fopen("temp.txt", "w");
printf("temp.txt is created and opened\n");
fwrite(&buf, strlen(buf), 1, fp);
printf("temp.txt is writed\n");
fclose(fp);
printf("temp.txt is closed");
return 0;
}
2.3 运行结果
3. fcloseall
3.1 函数说明
int fcloseall(void);
关闭除标准流(stdin、stdout、stderr、stdprn、stdaux)之外的所有打开的流,刷新所有的流缓冲区,并返回关闭的流数。
3.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#define fcloseall() _fcloseall();
int main()
{
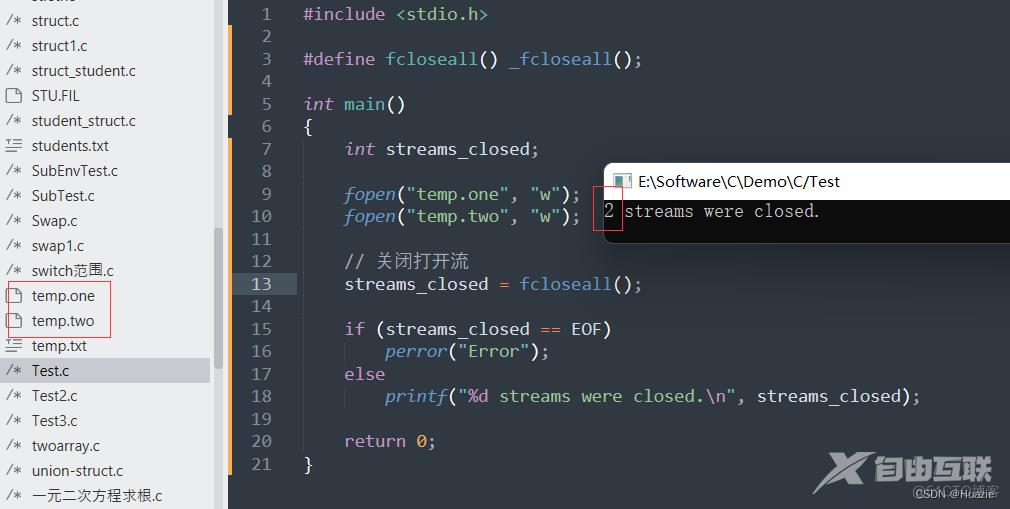
int streams_closed;
fopen("temp.one", "w");
fopen("temp.two", "w");
// 关闭打开流
streams_closed = fcloseall();
if (streams_closed == EOF)
perror("Error");
else
printf("%d streams were closed.\n", streams_closed);
return 0;
}
3.3 运行结果
4. fcvt
4.1 函数说明
char * fcvt(double value, int ndigit, int *decpt, int *sign);
把一个双精度浮点数转换为字符串
value: 要转换的双精度浮点数,输入参数 ndigit: 取小数的位数,输入参数 decpt: 表示小数点的位置,输出参数 sign: 表示value的符号,0为正数,1为负数,输出参数
4.2 演示示例
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
int main()
{
char *string;
double value;
int decpt, sign;
int ndigit = 10;
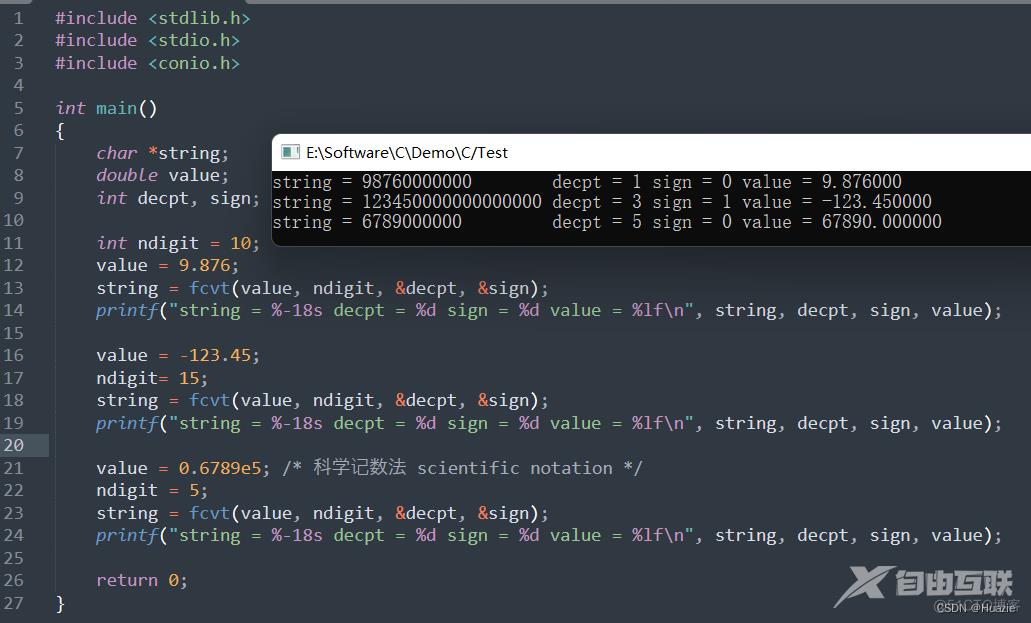
value = 9.876;
string = fcvt(value, ndigit, &decpt, &sign);
printf("string = %-18s decpt = %d sign = %d value = %lf\n", string, decpt, sign, value);
value = -123.45;
ndigit= 15;
string = fcvt(value, ndigit, &decpt, &sign);
printf("string = %-18s decpt = %d sign = %d value = %lf\n", string, decpt, sign, value);
value = 0.6789e5; /* 科学记数法 scientific notation */
ndigit = 5;
string = fcvt(value, ndigit, &decpt, &sign);
printf("string = %-18s decpt = %d sign = %d value = %lf\n", string, decpt, sign, value);
return 0;
}
4.3 运行结果
5. fdim,fdimf,fdiml
5.1 函数说明
double fdim (double x, double y);
计算 x 和 y 之间的正差值 (double)
float fdimf (float x, float y);
计算 x 和 y 之间的正差值 (float)
long double fdiml (long double x, long double y);
计算 x 和 y 之间的正差值 (long double)
5.2 演示示例
5.3 运行结果
6. fdopen
6.1 函数说明
FILE * fdopen(int handle, char *type);
将文件描述符和文件流相关联
6.2 演示示例
#include <sys\stat.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
int handle;
FILE *stream;
// 打开 temp.txt 文件
handle = open("temp.txt", O_CREAT | O_RDWR, S_IREAD | S_IWRITE);
// 将文件描述符和文件流关联
stream = fdopen(handle, "w");
if (stream == NULL)
printf("fdopen failed\n");
else
{
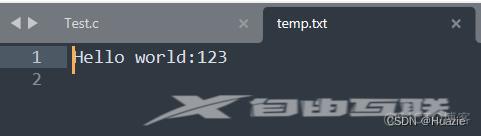
fprintf(stream, "%s:%d\n", "Hello world", 123);
fclose(stream);
}
return 0;
}
6.3 运行结果
7. feof
7.1 函数说明
int feof(FILE *stream);
检测流上的文件结束符。如果文件结束,则返回非0值,否则返回0
7.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
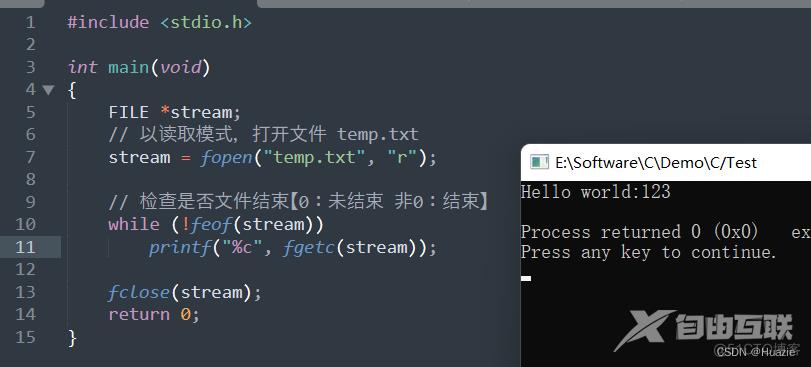
// 以读取模式,打开文件 temp.txt
stream = fopen("temp.txt", "r");
// 检查是否文件结束【0:未结束 非0:结束】
while (!feof(stream))
printf("%c", fgetc(stream));
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
7.3 运行结果
8. ferror
8.1 函数说明
int ferror(FILE *stream);
检测流上的错误【返回0,表示未出错;返回非零值,表示出错。】
8.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
// 以写模式打开文件STU.FIL
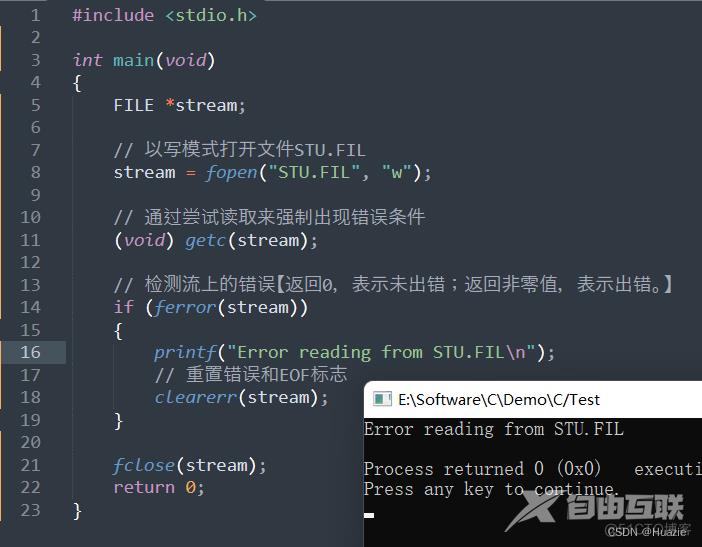
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w");
// 通过尝试读取来强制出现错误条件
(void) getc(stream);
// 检测流上的错误【返回0,表示未出错;返回非零值,表示出错。】
if (ferror(stream))
{
printf("Error reading from STU.FIL\n");
// 重置错误和EOF标志
clearerr(stream);
}
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
8.3 运行结果
9. fflush
9.1 函数说明
int fflush(FILE *stream);
清除读写缓冲区,并将缓冲区内的数据写回参数stream指向的文件中。
9.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <io.h>
void flush(FILE *stream);
int main(void)
{
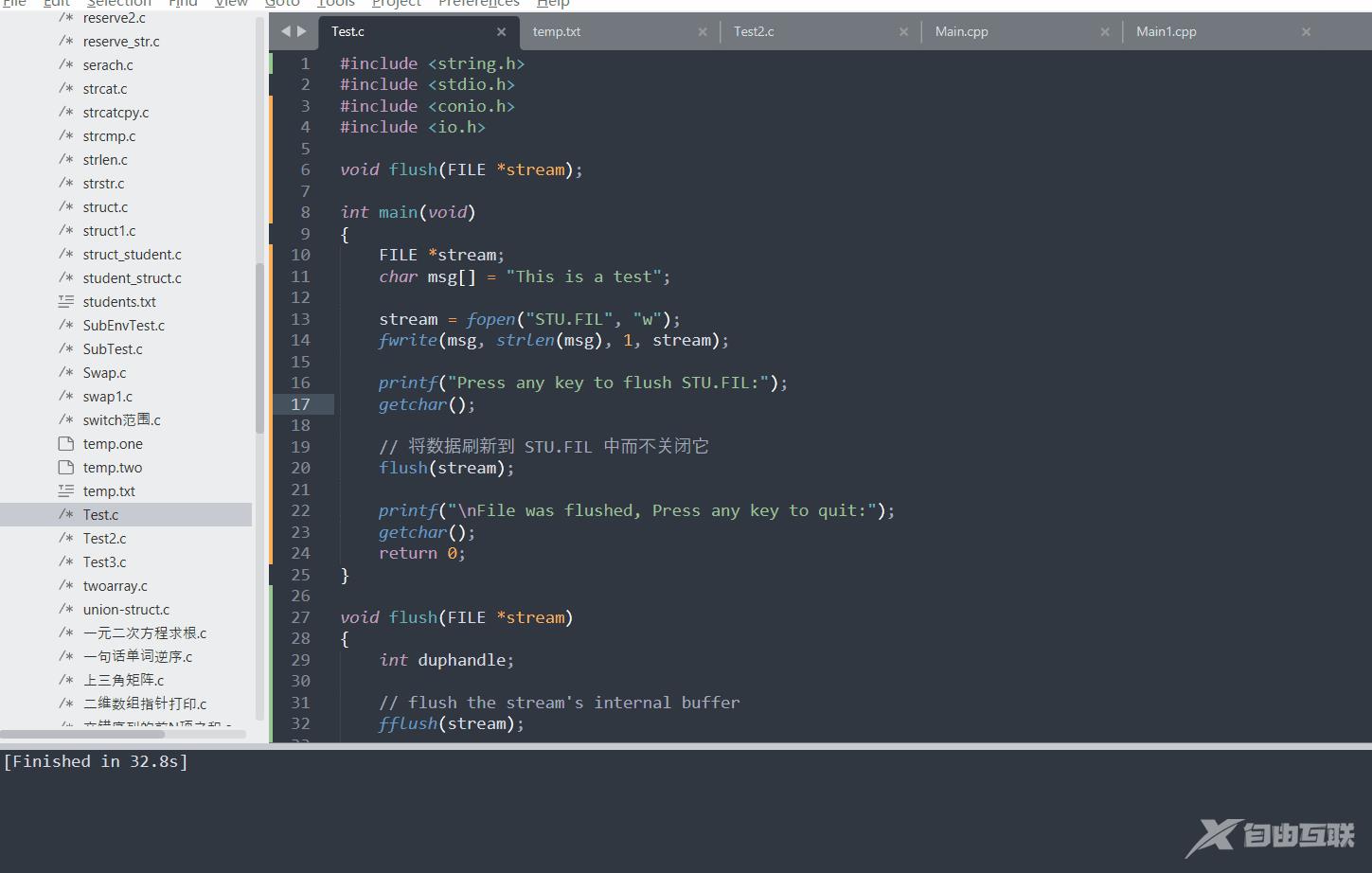
FILE *stream;
char msg[] = "This is a test";
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w");
fwrite(msg, strlen(msg), 1, stream);
printf("Press any key to flush STU.FIL:");
getchar();
// 将数据刷新到 STU.FIL 中而不关闭它
flush(stream);
printf("\nFile was flushed, Press any key to quit:");
getchar();
return 0;
}
void flush(FILE *stream)
{
int duphandle;
// flush the stream's internal buffer
fflush(stream);
// make a duplicate file handle
duphandle = dup(fileno(stream));
// close the duplicate handle to flush the DOS buffer
close(duphandle);
}
9.3 运行结果
10. fgetc
10.1 函数说明
int fgetc(FILE *stream);
从流中读取字符
10.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
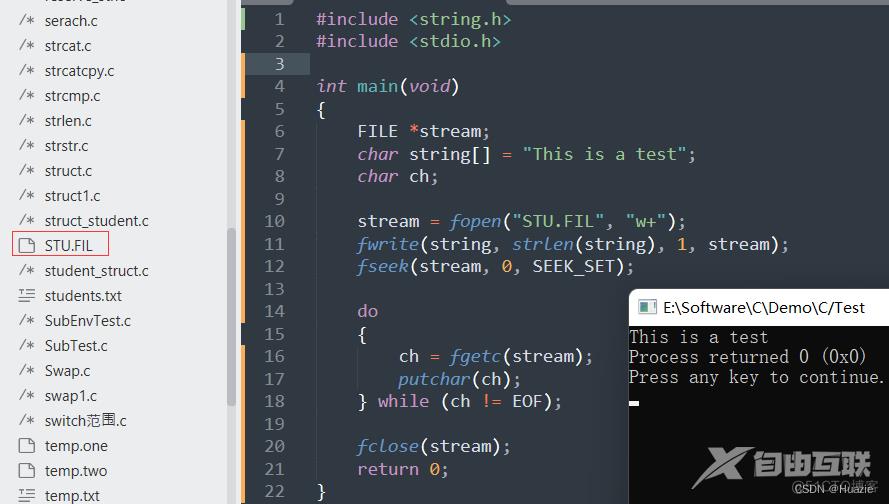
FILE *stream;
char string[] = "This is a test";
char ch;
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+");
fwrite(string, strlen(string), 1, stream);
fseek(stream, 0, SEEK_SET);
do
{
ch = fgetc(stream);
putchar(ch);
} while (ch != EOF);
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
10.3 运行结果
11. fgetchar
11.1 函数说明
int fgetchar(void);
从流中读取字符
11.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
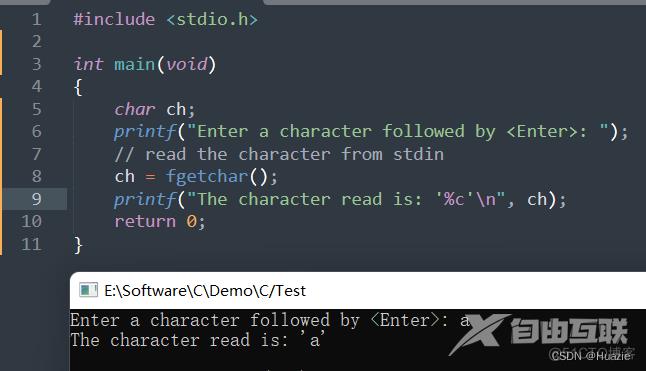
char ch;
printf("Enter a character followed by <Enter>: ");
// read the character from stdin
ch = fgetchar();
printf("The character read is: '%c'\n", ch);
return 0;
}
11.3 运行结果
12. fgetpos
12.1 函数说明
int fgetpos(FILE *stream);
依据当前文件的句柄,获取当前访问指针位置信息
12.2 演示示例
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
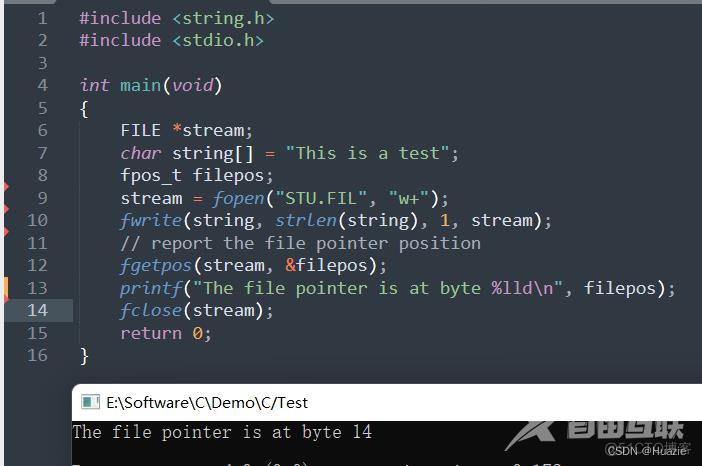
FILE *stream;
char string[] = "This is a test";
fpos_t filepos;
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+");
fwrite(string, strlen(string), 1, stream);
// report the file pointer position
fgetpos(stream, &filepos);
printf("The file pointer is at byte %lld\n", filepos);
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
12.3 运行结果
13. fgets
13.1 函数说明
char * fgets(char *str, int n, FILE *stream);
从指定的流中读取数据,每次读取一行
参数: str : 这是指向一个字符数组的指针,该数组存储了要读取的字符串。 n: 这是要读取的最大字符数(包括最后的空字符)。通常是使用以 str 传递的数组长度。 stream: 这是指向 FILE 对象的指针,该 FILE 对象标识了要从中读取字符的流。
注意: 如果文件中的一行,不足 n-1 个字符,则读完该行就直接结束。如若该行(包括最后一个换行符)的字符数超过 n-1,则 fgets 只返回一个不完整的行,但是,缓冲区总是以 NULL 字符结尾,对 fgets 的下一次调用会继续读该行。函数成功将返回 stream,失败或读到文件结尾返回 NULL。因此不能直接通过 fgets 的返回值来判断函数是否是出错而终止的,应该借助 feof 函数或者 ferror 函数来判断。
13.2 演示示例
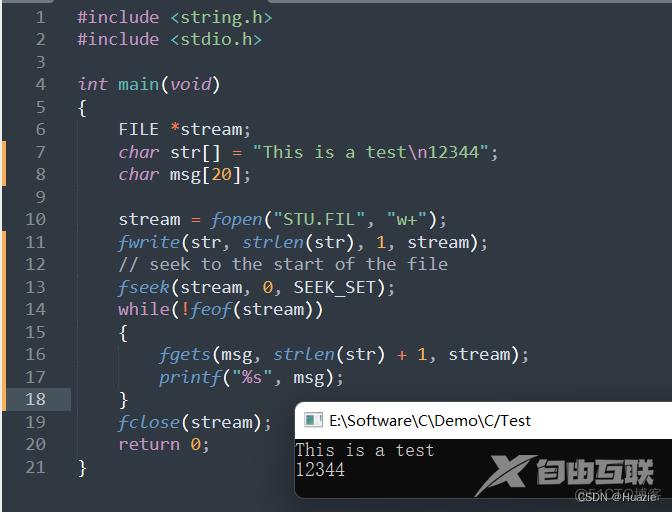
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
char str[] = "This is a test\n12344";
char msg[20];
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+");
fwrite(str, strlen(str), 1, stream);
// seek to the start of the file
fseek(stream, 0, SEEK_SET);
while(!feof(stream))
{
fgets(msg, strlen(str) + 1, stream);
printf("%s", msg);
}
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
13.3 运行结果
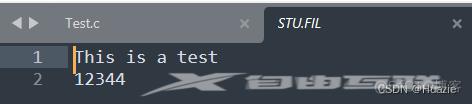
14. filelength
14.1 函数说明
long filelength(int handle);
获取文件的长度
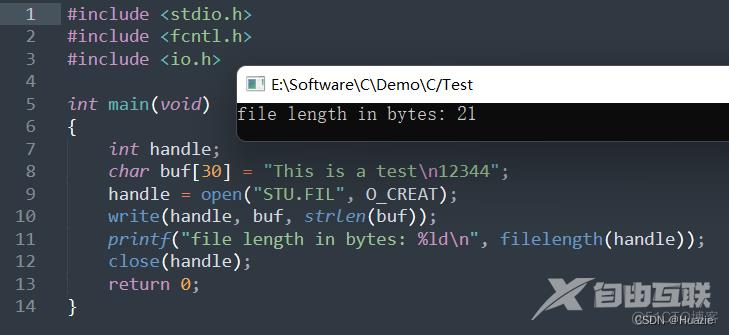
14.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
int handle;
char buf[30] = "This is a test\n12344";
handle = open("STU.FIL", O_CREAT);
write(handle, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("file length in bytes: %ld\n", filelength(handle));
close(handle);
return 0;
}
14.3 运行结果
15. fileno
15.1 函数说明
int fileno(FILE *stream);
获取参数stream指定的文件流所使用的文件描述符
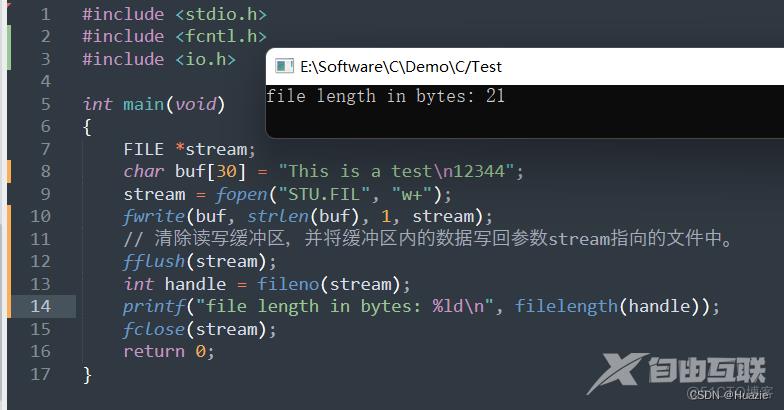
15.2 演示示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <io.h>
int main(void)
{
FILE *stream;
char buf[30] = "This is a test\n12344";
stream = fopen("STU.FIL", "w+");
fwrite(buf, strlen(buf), 1, stream);
// 清除读写缓冲区,并将缓冲区内的数据写回参数stream指向的文件中。
fflush(stream);
// 获取参数stream指定的文件流所使用的文件描述符
int handle = fileno(stream);
printf("file length in bytes: %ld\n", filelength(handle));
fclose(stream);
return 0;
}
15.3 运行结果
16. fillellipse
16.1 函数说明
void fillellipse(int x, int y, int xradius, int yradius);
画出并填充一椭圆
16.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
int main(void)
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode;
int xcenter, ycenter, i;
initgraph(&gdriver,&gmode,"");
xcenter = getmaxx() / 2;
ycenter = getmaxy() / 2;
for (i=EMPTY_FILL; i<USER_FILL; i++)
{
cleardevice();
// 设置填充图样和颜色
setfillstyle(i, WHITE);
fillellipse(xcenter, ycenter, 100, 50);
getch();
}
closegraph();
return 0;
}
16.3 运行结果
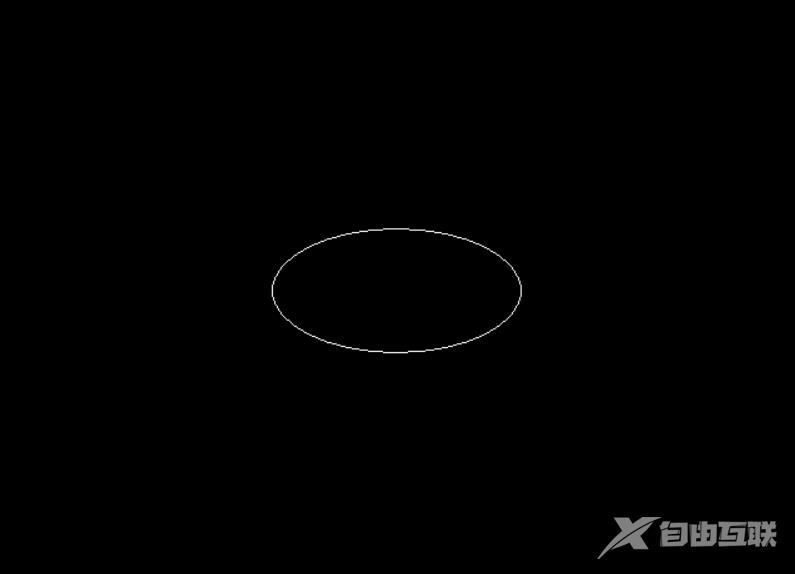
17. fillpoly
17.1 函数说明
void fillpoly(int numpoints, int *polypoints);
画并填充一个多边形
参数: numpoints: 多边形边数 polypoints: 存储各顶点坐标的数组,每两个一组表示一个顶点的X,Y坐标
17.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int i, maxx, maxy;
int poly[8];
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
maxx = getmaxx();
maxy = getmaxy();
poly[0] = 20;
poly[1] = maxy / 2;
poly[2] = maxx - 20;
poly[3] = 20;
poly[4] = maxx - 50;
poly[5] = maxy - 20;
poly[6] = maxx / 2;
poly[7] = maxy / 2;
for (i=EMPTY_FILL; i<USER_FILL; i++)
{
setfillstyle(i, getmaxcolor());
fillpoly(4, poly);
getch();
}
closegraph();
return 0;
}
17.3 运行结果
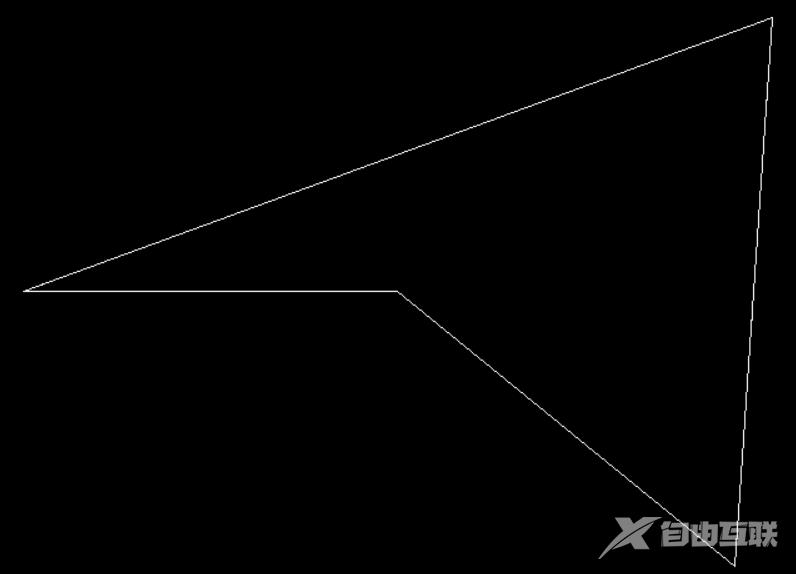
18. findfirst, findnext
18.1 函数说明
int _findfirst(char *pathname, struct _finddata_t *_FindData);
搜索与指定的文件名称匹配的第一个文件,若成功则返回第一个文件的文件描述符,否则返回-1L。
int _findnext(int handle, struct _finddata_t *_FindData);
搜索与_findfirst函数提供的文件名称匹配的下一个实例,若成功则返回0,否则返回-1
18.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<io.h>
int main()
{
int handle;
struct _finddata_t FileInfo;
// 搜索与指定的文件名称匹配的第一个文件,若成功则返回第一个文件的文件描述符,否则返回-1L。
if((handle=_findfirst("E:\\Pic\\*.png", &FileInfo))==-1L)
printf("没有找到匹配的项目\n");
else
{
printf("handle=%d\n", handle);
printf("%s\n\n", FileInfo.name);
// 搜索与_findfirst函数提供的文件名称匹配的下一个实例,若成功则返回0,否则返回-1
while(_findnext(handle, &FileInfo)==0)
printf("%s\n",FileInfo.name);
_findclose(handle);
}
return 0;
}
18.3 运行结果
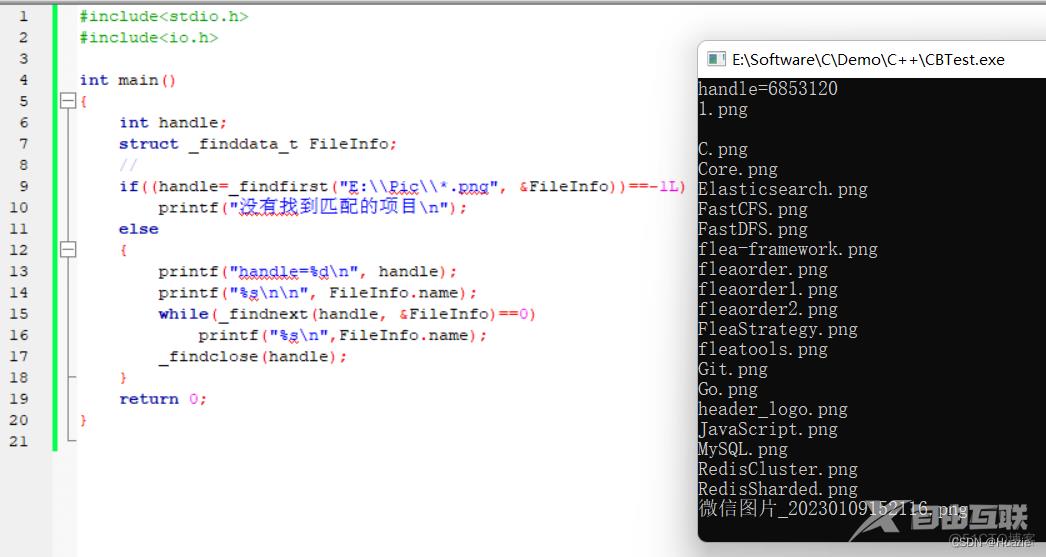
19. finite,finitef
19.1 函数说明
int finitef (double x);
检查 x 是无穷大值还是NaN 值(double)。如果是无穷大值或NaN值,返回 0;否则返回 1。
int finitef (float x);
检查 x 是无穷大值还是NaN 值(float)。如果是无穷大值或NaN值,返回 0;否则返回 1。
19.2 演示示例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main()
{
double x = NAN, y = INFINITY, z = 10.24;
printf("finite(%.2lf) = %d\n", x, finite(x));
printf("finite(%.2lf) = %d\n", y, finite(y));
printf("finite(%.2lf) = %d\n", z, finite(z));
float xf = NAN, yf = INFINITY, zf = 5.63;
printf("\nfinitef(%.2f) = %d\n", xf, finitef(xf));
printf("finitef(%.2f) = %d\n", yf, finitef(yf));
printf("finitef(%.2f) = %d\n", zf, finitef(zf));
return 0;
}
19.3 运行结果
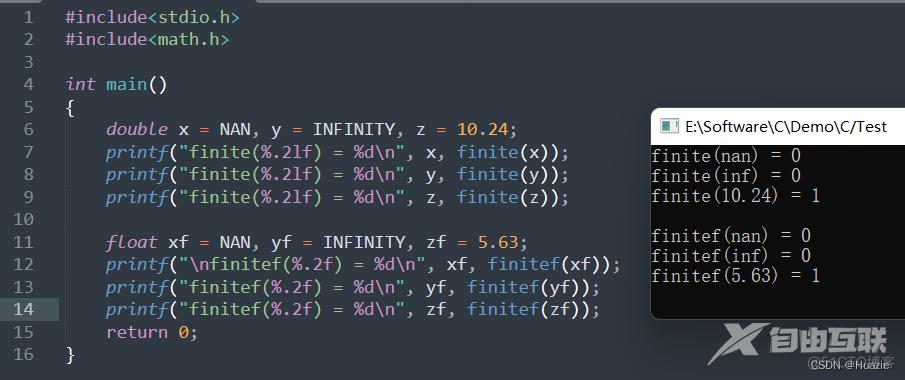
20. floodfill
20.1 函数说明
void floodfill(int x, int y, int border);
填充一个有界区域
20.2 演示示例
#include <graphics.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int gdriver = DETECT, gmode, errorcode;
int maxx, maxy;
initgraph(&gdriver, &gmode, "");
errorcode = graphresult();
if (errorcode != grOk)
{
printf("Graphics error: %s\n", grapherrormsg(errorcode));
printf("Press any key to halt:");
getch();
exit(1);
}
maxx = getmaxx();
maxy = getmaxy();
// select drawing color
setcolor(getmaxcolor());
// select fill color
setfillstyle(SOLID_FILL, getmaxcolor());
// draw a border around the screen
rectangle(0, 0, maxx, maxy);
// draw some circles
circle(maxx / 3, maxy /2, 50);
circle(maxx / 2, 20, 100);
circle(maxx-20, maxy-50, 75);
circle(20, maxy-20, 25);
getch();
// fill in bounded region
floodfill(2, 2, getmaxcolor());
getch();
closegraph();
return 0;
}
20.3 运行结果
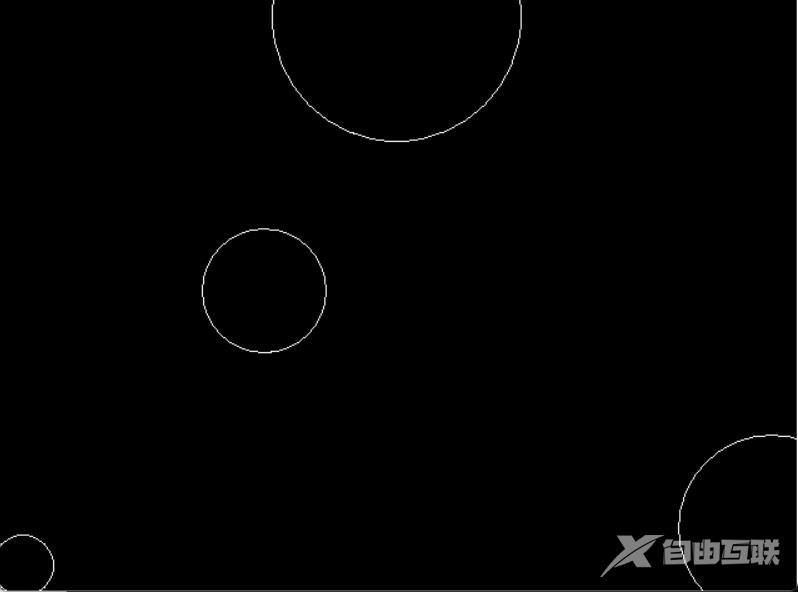
参考
- [API Reference Document]
- [fgets]
- [_findfirst]
- [MATH-标准C库]
