堆排序(heapsort)是一种比较快速的排序方式,它的时间复杂度为O(nlgn),并且堆排序具有空间原址性,任何时候只需要有限的空间来存储临时数据。我将用c++实现一个堆来简单分析一下
堆排序(heapsort)是一种比较快速的排序方式,它的时间复杂度为O(nlgn),并且堆排序具有空间原址性,任何时候只需要有限的空间来存储临时数据。我将用c++实现一个堆来简单分析一下。
堆排序的基本思想为:
1、升序排列,保持大堆;降序排列,保持小堆;
2、建立堆之后,将堆顶数据与堆中最后一个数据交换,堆大小减一,然后向下调整;直到堆中只剩下一个有效值;
下面我将简单分析一下:
第一步建立堆:
1、我用vector顺序表表示数组;
2、用仿函数实现大小堆随时切换,实现代码复用;
3、实现向下调整算法,时间复杂度为O(lgn);
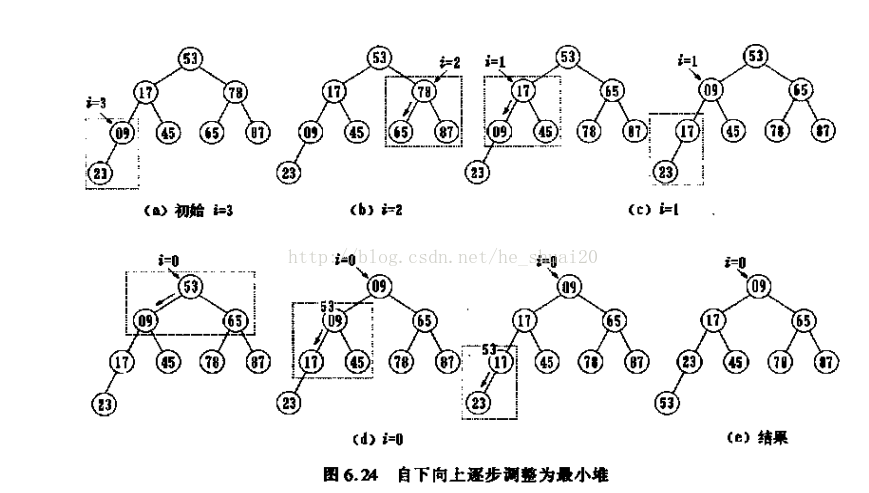
下面是我用某教材中的一个建最小堆的过程图,希望能更直观一些:
为了保证复用性,用仿函数重载了(),下面是复用的向下调整算法:
void _AdjustDown(int root,int size)
{
Camper camper; //仿函数
int parent = root;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child <= size) //保证访问不越界
{
if (child < size && camper(_vec[child+1] , _vec[child])) //保证存在右子树、同时判断右子树是否大于或小于左子树
{
child++;
}
if (camper(_vec[child], _vec[parent]))
{
swap(_vec[parent], _vec[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
排序算法思想:
1、将堆顶数据与堆中最后一个数据交换;
2、堆大小减一,然后调用向下调整算法;
3、结束条件:堆中剩下一个有效值;
排序算法实现:
void Sort()
{
size_t size = _vec.size(); //数据数量
while (size > 1)
{
swap(_vec[0], _vec[size - 1]);
size--;
_AdjustDown(size);
}
}
仿函数的实现:
template<class T>
struct Greater //大于
{
bool operator ()(const T& l, const T& p)
{
return l > p;
}
};
template<class T>
struct Less //小于
{
bool operator () (const T&l, const T& p)
{
return l < p;
}
};
完整的代码实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<vector>
template<class T>
struct Greater //大于
{
bool operator ()(const T& l, const T& p)
{
return l > p;
}
};
template<class T>
struct Less //小于
{
bool operator () (const T&l, const T& p)
{
return l < p;
}
};
template<class T,class Camper>
class HeapSort //建大堆
{
public:
HeapSort()
{}
HeapSort(T* arr, size_t n)
{
_vec.reserve(n);
if (arr != NULL)
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
_vec.push_back(arr[i]);
}
}
_AdjustDown(_vec.size());
}
void Sort()
{
size_t size = _vec.size(); //数据数量
while (size > 1)
{
swap(_vec[0], _vec[size - 1]);
size--;
_AdjustDown(size);
}
}
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _vec.size(); i++)
{
cout << _vec[i] <<" ";
}
cout << endl;
}
protected:
void _AdjustDown(int size)
{
int parent = (size - 2) / 2;
while (parent >= 0)
{
_AdjustDown(parent, size - 1);
parent--;
}
}
void _AdjustDown(int root,int size)
{
Camper camper; //仿函数
int parent = root;
int child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child <= size) //保证访问不越界
{
if (child < size && camper(_vec[child+1] , _vec[child])) //保证存在右子树、同时判断右子树是否大于或小于左子树
{
child++;
}
if (camper(_vec[child], _vec[parent]))
{
swap(_vec[parent], _vec[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
private:
vector<T> _vec;
};
测试用例代码:
void TextSort()
{
int a[] = { 10, 11, 13, 12, 16, 18, 15, 17, 14, 19 };
HeapSort<int,Greater<int>> h(a, sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]));
h.Print();
h.Sort();
h.Print();
}
感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!
