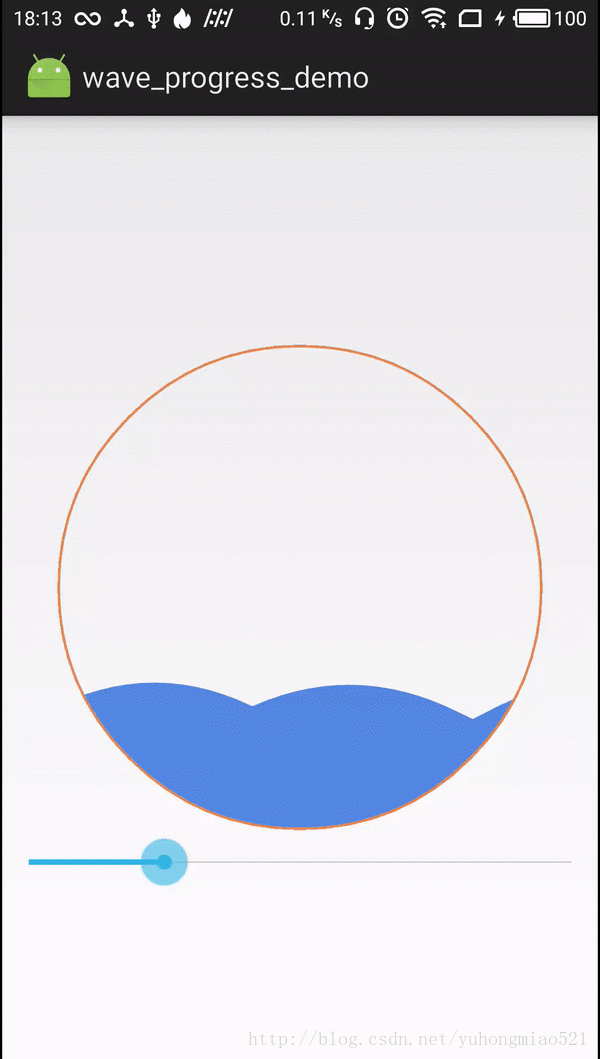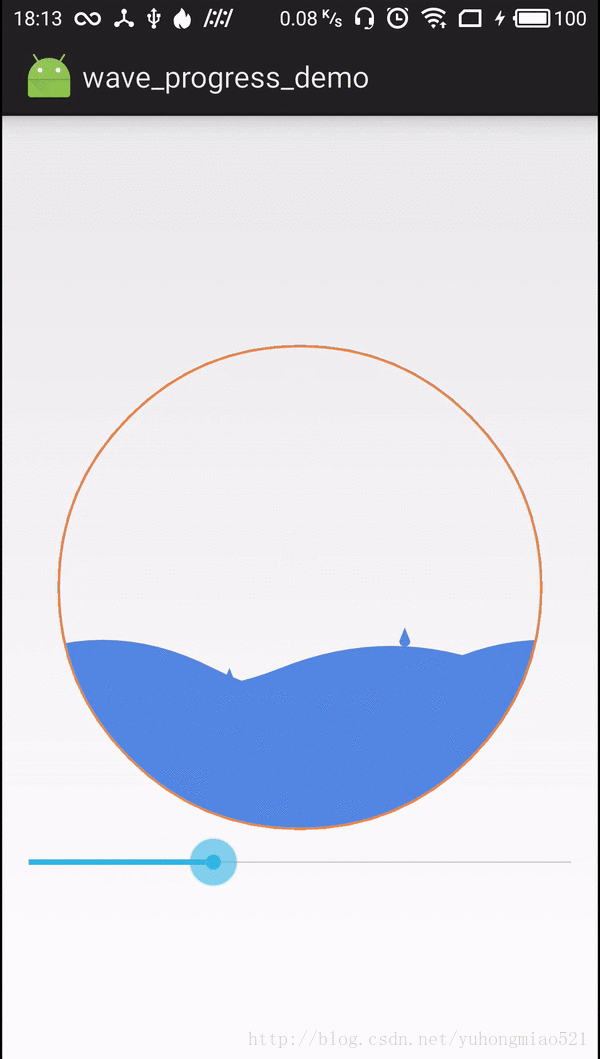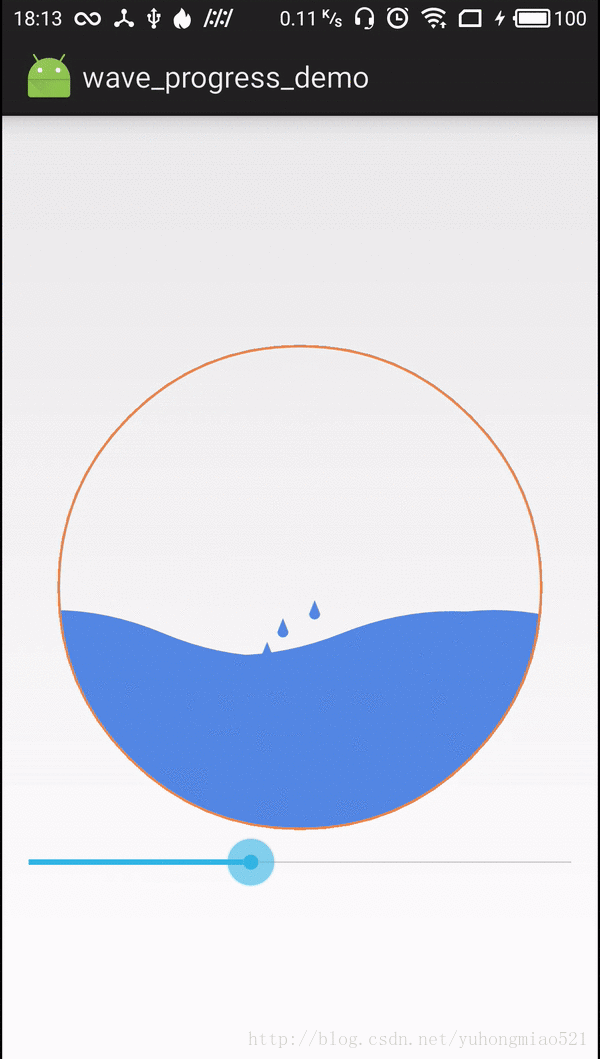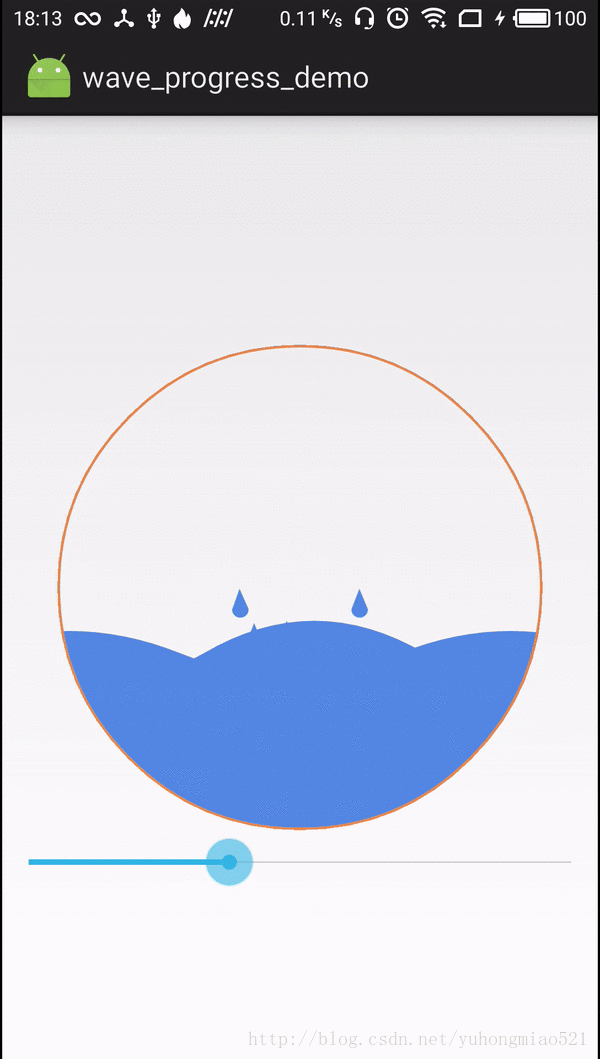
通过自定义view实现了一个水滴滴落到水波面,溅起水花并且水波流动上涨的进度条控件。之前看到过好多水波流动的进度条,感觉欠缺些东西,就想到了水滴到水平面,溅起水花然后水
通过自定义view实现了一个水滴滴落到水波面,溅起水花并且水波流动上涨的进度条控件。之前看到过好多水波流动的进度条,感觉欠缺些东西,就想到了水滴到水平面,溅起水花然后水流动上涨的进度条效果,于是自己动手写了出来。效果如下,视频录制有些卡顿,实际会流畅很多。
一.用法
1.布局文件中添加WaveProgressView,circleColor属性为圆环颜色,waterColor属性为水波水滴的颜色,progress属性为初始的进度
<com.yhongm.wave_progress_view.WaveProgressView android:id="@+id/wave_progress_view" android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="300dp" android:layout_centerInParent="true" app:circleColor="#e38854" app:progress="0" app:waterColor="#5488e3" />
2.WaveProgressView.setProgress()方法设置当前的进度
二.本文实现的逻辑
1,画水波流动,通过三阶贝塞尔曲线画波形,通过不断的改变waveOffsetX和waveOffsetY的值实现流动的效果
/**
* 生成水波流动
*
* @param begin 水波形开始的位置
* @param waveLength 水波的长度
* @param waveOffsetX 水波水平的偏移
* @param waveOffsetY 水波垂直方向的偏移
* @return
*/
private Path getWavePath(float begin, int waveLength, int waveOffsetX, int waveOffsetY) {
Path mPath = new Path();
mPath.reset();
mPath.moveTo(waveLength * begin, mCurrentHeight);
for (int i = 0; i < mWaveCount; i++) {
mPath.quadTo(waveLength * (begin + 0.25f) + (i * waveLength) + waveOffsetX, mCurrentHeight + waveOffsetY, (waveLength * (begin + 0.5f) + (i * waveLength) + waveOffsetX), mCurrentHeight);
mPath.quadTo(waveLength * (begin + 0.75f) + (i * waveLength) + waveOffsetX, mCurrentHeight - waveOffsetY, (waveLength * (begin + 1f) + (i * waveLength) + waveOffsetX), mCurrentHeight);
}
mPath.lineTo(mWidth, mHeight);
mPath.lineTo(0, mHeight);
mPath.close();
return mPath;
}
2.画水滴的形状,水滴的形状是通过一个三角形和一个弧形组成的
/**
* 水滴的Path
*
* @param x 水滴坐标x
* @param y 水滴坐标y
* @param size 水滴尺寸
* @return
*/
private Path waterDrop(float x, float y, int size) {
Path mDropPath = new Path();
mDropPath.moveTo(x - size, y);
mDropPath.lineTo(x, (float) (y - size * 2.5));
mDropPath.lineTo(x + size, y);
mDropPath.addArc(x - size, y - size, x + size, y + size, 0, 180);
return mDropPath;
}
3.画水滴滴落到水波的效果,就是沿轴Y轴不断的移动水滴
/**
* 根据位置画水滴
*
* @param x
* @param y
* @param canvas
*/
private void drawDropByLocation(Canvas canvas, int x, int y) {
Path mDropPath = waterDrop(x, y, 30);
if (y == (mCurrentHeight + 50)) {
mDropPaint.setAlpha(0);
}
canvas.drawPath(mDropPath, mDropPaint);
}
4.画最外两侧溅落的水滴,通过三阶贝塞尔曲线模拟左右两侧水滴溅落的路径,随机生成的水滴溅落路径都在这左右两侧内
/**
* 画两侧水滴飞溅的效果,并且随机生成水滴
*
* @param canvas
* @param x
* @param y 当前高度
*/
private synchronized void drawDropSplash(Canvas canvas, int x, int y) {
PathMeasure mLeftPathMeasure = getOnBothSidesOfPathMeasure(x, y, true);
PathMeasure mRightPathMeasure = getOnBothSidesOfPathMeasure(x, y, false);
float[] mLeftPos = new float[2];
float[] mRightPos = new float[2];
float[] mLeftTan = new float[2];
float[] mRightTan = new float[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 200; i++) {
float percent = i / 200f;
mLeftPathMeasure.getPosTan(mLeftPathMeasure.getLength() * percent, mLeftPos, mLeftTan);
mRightPathMeasure.getPosTan(mRightPathMeasure.getLength() * percent, mRightPos, mRightTan);
mLeftHashMapPath.put(Math.round(mLeftPos[1]), mLeftPos[0]);
mRightHashMapPath.put(Math.round(mRightPos[1]), mRightPos[0]);
}
if (mRandomHashMap.isEmpty() && mRandomHashMap.size() == 0) {
pushRandomDrag(y);
}
drawRandomDrag(canvas, x, y, mLeftHashMapPath, mRightHashMapPath);
drawOnBothSidesOfWaterDrop(canvas, mLeftPathMeasure);
drawOnBothSidesOfWaterDrop(canvas, mRightPathMeasure);
}
/**
* 产生随机的水滴
*
* @param y
*/
private void pushRandomDrag(int y) {
Random r = new Random();
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {
int randomY = r.nextInt(y);
if (mLeftHashMapPath.containsKey(randomY)) {
Float rightValue = mRightHashMapPath.get(randomY);
Float leftValue = mLeftHashMapPath.get(randomY);
int roundLeftValue = Math.round(leftValue);
int roundRightValue = Math.round(rightValue);
if (roundRightValue == roundLeftValue) {
roundRightValue++;
}
int roundMinus = Math.round(roundRightValue - roundLeftValue);//左右差值
float randomX = r.nextInt(roundMinus) + mLeftHashMapPath.get(randomY);//左右差值加上最小值,保证随机值在两者之间
mRandomHashMap.put(randomX, randomY);
}
}
}
5.随机生成的水滴沿着三阶贝塞尔曲线移动,形成溅落的效果
/**
* 画随机生成水滴溅起
*
* @param canvas
* @param x
* @param y
* @param size
* @param randomY
* @param randomX
*/
private void drawSmartDropOnPath(Canvas canvas, int x, int y, int size, int randomY, float randomX) {
Path smartDropPath = new Path();
smartDropPath.moveTo(x, y + 50);
if (x < randomX) {
smartDropPath.cubicTo(x, y + 50, randomX + 30, randomY - 20, randomX, randomY);
} else {
smartDropPath.cubicTo(x, y + 50, randomX - 30, randomY - 20, randomX, randomY);
}
smartDropPath.lineTo(randomX, randomY + 150);
PathMeasure pathMeasure = new PathMeasure();
pathMeasure.setPath(smartDropPath, false);
float[] pos = new float[2];
float[] tan = new float[2];
pathMeasure.getPosTan(pathMeasure.getLength() * mPercent, pos, tan);
Path path = waterDrop(pos[0], pos[1], size);
canvas.drawPath(path, mSplashPaint);
}
完整代码详见 点击打开Github本项目 感兴趣的话帮我点个Star
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持自由互联。
