- [源码解析] TensorFlow 分布式环境(5) --- Session
- 1. 概述
- 1.1 Session 分类
- 1.2 会话流程
- 1.2.1 MasterSession 生命周期
- 1.2.2 WorkerSession 生命周期
- 2. GrpcSession
- 2.1 定义
- 2.2 注册&工厂类
- 2.3 创建GrpcSession
- 2.4 创建MasterSession
- 2.4.1 GrpcRemoteMaster::CreateSession
- 2.4.2 GrpcMasterService::CreateSessionHandler
- 2.4.3 Master::CreateSession
- 3. MasterSession
- 3.1 定义
- 3.2 创建
- 3.2.1 创建计算图
- 3.2.2 创建 WorkerSession
- GrpcRemoteWorker
- GrpcWorkerService
- 4. WorkerSession
- 4.1 SessionMgr
- 4.1.1 定义
- 4.1.2 建立 Session
- 4.1.3 注册图
- 4.2 WorkerSession
- 4.2.1 定义
- 4.1 SessionMgr
- 0xFF 参考
- 1. 概述
会话机制是TensorFlow 分布式运行时的核心,我们接下来按照从 Client 到 worker 的流程,把 Session 机制从前到后走一边。
本系列其他文章是:
[翻译] TensorFlow 分布式之论文篇 "TensorFlow : Large-Scale Machine Learning on Heterogeneous Distributed Systems"
[翻译] TensorFlow 分布式之论文篇 "Implementation of Control Flow in TensorFlow"
[源码解析] TensorFlow 分布式环境(1) --- 总体架构
[源码解析] TensorFlow 分布式环境(2)---Master 静态逻辑
[源码解析] TensorFlow 分布式环境(3)--- Worker 静态逻辑
[源码解析] TensorFlow 分布式环境(4) --- WorkerCache
1. 概述 1.1 Session 分类分布式模式由如下 sessions 彼此协作完成了会话控制,其中:
- GrpcSession 位于 Client 之上,控制 Client 的会话生命周期;
- MasterSession 位于 Master 之上,可能存在多个 Client 同时接入到同一个 Master,Master 会为每个 Client 构建一个 MasterSession。MasterSession 控制 Master 的会话生命周 期;
- WorkerSession 位于 Worker 之上,可能存在多个 Master 接入到同一个 Worker,Worker 会为每个 Master 创建一个 WorkerSession。WorkerSession 控制 Worker 的会话生命周期;
如下图所示,这里 Master 和 Worker 都是一个 Server,每个 Server 之上运行一个 MasterService,一个 WorkerService,每个 Server 可能会扮演不同角色,具体取决于用户如何配置计算图和集群。因为存在这种两层一对多关系,为了区别这种不同的数据流和控制关系,有逻辑关系的这三个 session 绑定在同一个 session_handle 之上,每个 session_handle 标示一条完整的数据流。
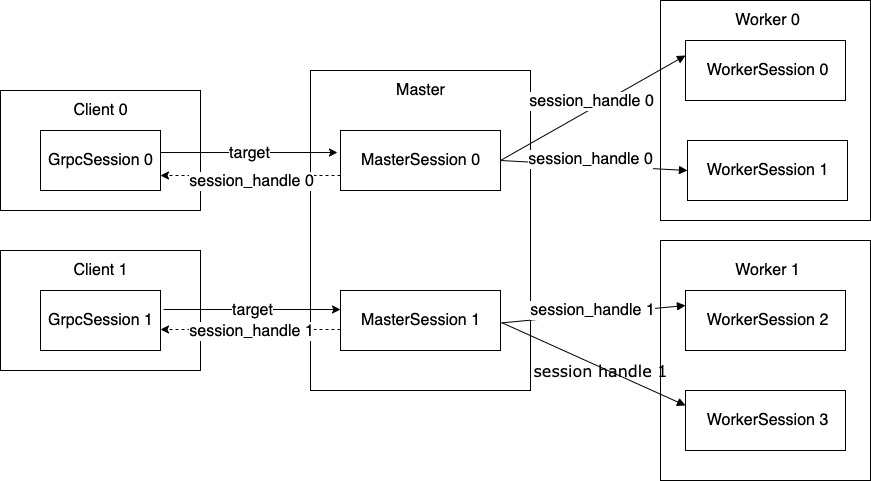
图 1 Session 关系
1.2 会话流程我们从 GrpcSession 入手,其基本功能如下:
- 创建会话
- 获取远端设备集;
- 在 Master 之上创建 MasterSession;
- 在各个 Worker 之上创建 WorkerSession;
- 迭代执行
- 启动执行;
- 图分裂;
- 注册子图;
- 运行子图;
- 关闭会话
- 关闭 MasterSession
- 关闭 WorkerSession;
在分布式模式下,Master 运行时被 MasterSession 控制,其生命周期如下图所示。

图 2 MasterSession 生命周期
1.2.2 WorkerSession 生命周期在分布式模式下,Worker 运行时由 WorkerSession 控制,其生命周期如下图所示。

图 3 WorkerSession 生命周期
2. GrpcSessionGrpcSession 是 tensorflow::grpc::MasterService 的简单封装。其使用远程设备集作为计算资源,使用 grpc 作为远端调用机制,让调用者在远端设备上对 TensorFlow 图进行计算。
2.1 定义我们依然只给出成员变量定义和部分重要函数,其就是利用 master_ 对 tensorflow::grpc::MasterService 进行调用。
class GrpcSession : public Session {
// 有多种创建方式
Status Create(const GraphDef& graph) override;
Status Create(const RunOptions& run_options, const GraphDef& graph) override;
Status Create(GraphDef&& graph) override;
Status Create(const RunOptions& run_options, GraphDef&& graph) override;
private:
const SessionOptions options_;
std::unique_ptr<MasterInterface> master_;
mutex mu_;
// handle_ returned by the master to identify this session.
string handle_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
// The current version of the graph.
int64_t current_graph_version_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
bool is_local_ = false;
};
GrpcSession 的使用是通过工厂类完成,比如:
Status NewSession(const SessionOptions& options, Session** out_session) {
SessionFactory* factory;
Status s = SessionFactory::GetFactory(options, &factory);
if (!s.ok()) {
*out_session = nullptr;
return s;
}
// Starts exporting metrics through a platform-specific monitoring API (if
// provided). For builds using "tensorflow/core/platform/default", this is
// currently a no-op.
session_created->GetCell()->Set(true);
s = factory->NewSession(options, out_session);
if (!s.ok()) {
*out_session = nullptr;
}
return s;
}
GrpcSession 由 GrpcSessionFactory 来多态创建,如果 protocal 使用了"grpc://",就会产生 GrpcSession。而 GrpcSessionFactory 会实现注册到系统之上。
const char* const kSchemePrefix = "grpc://";
const size_t kSchemePrefixLength = strlen(kSchemePrefix);
class GrpcSessionFactory : public SessionFactory {
public:
bool AcceptsOptions(const SessionOptions& options) override {
return absl::StartsWith(options.target, kSchemePrefix);
}
Status NewSession(const SessionOptions& options,
Session** out_session) override {
std::unique_ptr<GrpcSession> session;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(GrpcSession::Create(options, &session));
*out_session = session.release();
return Status::OK();
}
// Invokes the session specific static method to reset containers.
Status Reset(const SessionOptions& options,
const std::vector<string>& containers) override {
return GrpcSession::Reset(options, containers);
}
};
class GrpcSessionRegistrar {
public:
GrpcSessionRegistrar() {
SessionFactory::Register("GRPC_SESSION", new GrpcSessionFactory());
}
};
static GrpcSessionRegistrar registrar;
GrpcSession::Create 方法完成了获取工作。Client 通过 GrpcSession 调用 Master Service,但是具体如何与 Master Service 交互?则通过 MasterInterface。
所以说,这里最重要的就是如何构建 MasterInterface 实例。我们前文提到过,MasterInterface有两种实现,都是用来和 Master service 进行通信,分别对应了不同的应用场景。
- LocalMaster 用于进程间的直接通信,此时 Client 和 Master 在同一个进程。
- GrpcRemoteMaster 则使用 Grpc 来和 Master service 进行通信,此时Client 和 Master 分别部署在两个不同进程。GrpcRemoteMaster 其实就实现了 gRPC 客户端,它通过 Stub 访问远端 Master 上的 MasterService 服务。
图上两个矩形封装的 Master 代表实际的 Master 类,此类实现了具体 Master 功能。
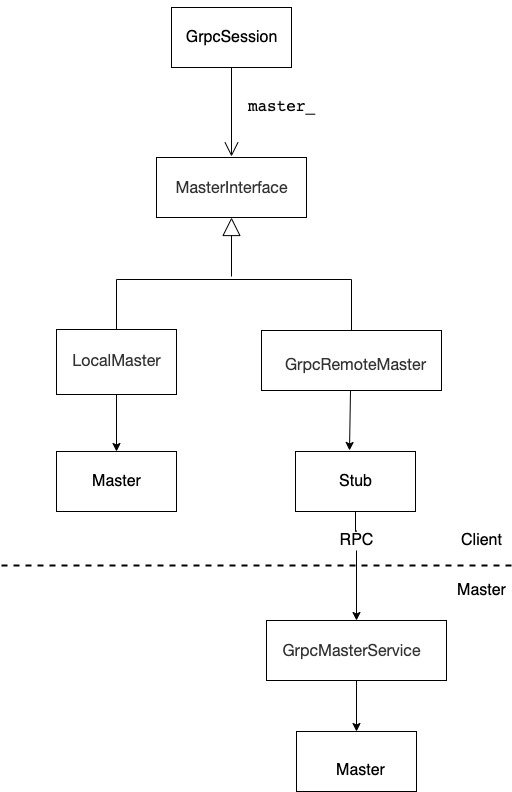
图 1 Master 逻辑关系
从下面代码可以看到,GrpcSession 会依据 options.target 来决定如何创建,options.target 一般就是"grpc://",如果通过 LocalMaster::Lookup 方法得到 LocalMaster 类,就直接使用,如果没有找到,就使用 NewGrpcMaster 来生成一个 GrpcRemoteMaster。
/* static */
Status GrpcSession::Create(const SessionOptions& options,
std::unique_ptr<GrpcSession>* out_session) {
std::unique_ptr<GrpcSession> session(new GrpcSession(options));
std::unique_ptr<MasterInterface> master;
// For testing, we enable the client to disable the use of the local
// master registry, so that the RPC stack is exercised.
if (!options.config.rpc_options().use_rpc_for_inprocess_master()) {
master = LocalMaster::Lookup(options.target);
}
if (!master) {
SharedGrpcChannelPtr master_channel;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
NewHostPortGrpcChannel(options.target.substr(kSchemePrefixLength),
&options.config.rpc_options(), &master_channel));
master.reset(NewGrpcMaster(master_channel));
} else {
session->is_local_ = true;
}
session->SetRemoteMaster(std::move(master));
*out_session = std::move(session);
return Status::OK();
}
在 GrpcSession 创建之后,系统会接着创建 MasterSession,这是通过 GrpcSession::Create(graph_def) 完成的。GrpcSession::Create(graph_def) 会构建 CreateSessionRequst 消息,然后通过 GrpcRemoteMaster 把初始计算图发给 Master。Master 收到 CreateSessionRequst 消息之后就构建相应的 MasterSession,然后返回 CreateSessionResponse 给 GrpcSession,消息包括。
- 该 MasterSession 的 session_handle。用于标识 Master 侧的 MasterSession 实例
- 初始计算图的版本号 graph_version。用于后续发起 ExtendSession 操作,比如往原始的计算图中追加新的节点。
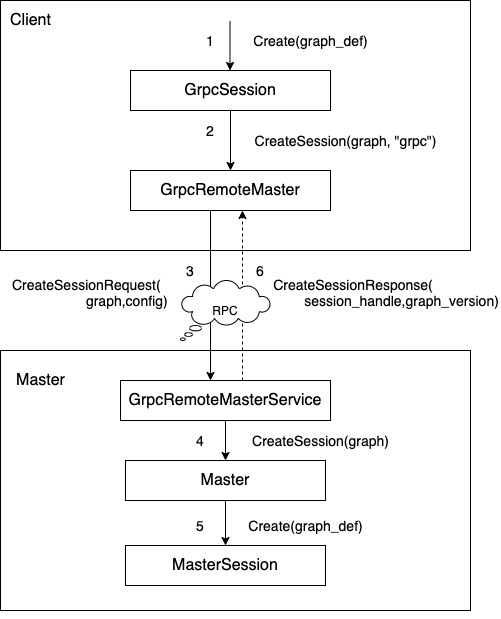
图 2 创建MasterSession
具体代码如下,首先是两个 create 方法,其最终调用到 CreateImpl。
Status GrpcSession::Create(const RunOptions& run_options,
const GraphDef& graph) {
return Create(run_options, GraphDef(graph));
}
Status GrpcSession::Create(GraphDef&& graph) {
CallOptions call_options;
call_options.SetTimeout(options_.config.operation_timeout_in_ms());
return CreateImpl(&call_options, std::move(graph));
}
CreateImpl 方法如下:
Status GrpcSession::CreateImpl(CallOptions* call_options, GraphDef graph) {
{
mutex_lock l(mu_);
if (!handle_.empty()) {
return errors::InvalidArgument("A session is alive.");
}
}
CreateSessionRequest req;
*req.mutable_config() = options_.config;
req.mutable_graph_def()->Swap(&graph);
req.set_target(options_.target);
ReEncodeConsts(req.mutable_graph_def());
CreateSessionResponse resp;
Status s = master_->CreateSession(call_options, &req, &resp);
if (s.ok()) {
SetHandleAndGraphVersion(resp.session_handle(), resp.graph_version());
}
return s;
}
GrpcRemoteMaster 是位于 Client 的 gRPC 客户端实现,它的 CreateSession 方法只是通过 gRPC stub 来调用 远端服务 MasterService 的 CreateSession 接口,其实就是发送一个 CreateSessionRequest 请求。
Status CreateSession(CallOptions* call_options,
const CreateSessionRequest* request,
CreateSessionResponse* response) override {
return CallWithRetry(call_options, request, response,
&MasterServiceStub::CreateSession);
}
GrpcMasterService 是 Master 提供的 gRPC 服务,收到 CreateSessionRequest 消息之后, 服务调用 GrpcMasterService::CreateSessionHandler 来处理消息,而真正业务处理是由 master_impl_(Master 类的实例)来完成,就是调用了 Master::CreateSession。
当 master_impl_ 处理完成后,会向 Client 返回 CreateSessionResponse 响应。
// RPC handler for creating a session.
void CreateSessionHandler(
MasterCall<CreateSessionRequest, CreateSessionResponse>* call) {
CreateSessionRequest* rewritten_req = new CreateSessionRequest;
rewritten_req->mutable_config()->MergeFrom(default_session_config_);
rewritten_req->MergeFrom(call->request);
master_impl_->CreateSession(rewritten_req, &call->response,
[call, rewritten_req](const Status& status) {
call->SendResponse(ToGrpcStatus(status));
delete rewritten_req;
});
ENQUEUE_REQUEST(CreateSession, true);
}
Master::CreateSession 会从线程池之中拿到一个线程,在线程之中会做如下处理:
- 如果定义了 clust_spec,则按照配置寻找所有的 worker。
- 获取远端设备。
- 获取远端worker。
- 通过factory 建立 MasterSession。
- 利用 worker_cache_factory,让 MasterSession 建立 WorkerSession 会话。
- 通过 sessions_.insert 在 Master 内部的 <session_handle, MasterSession> 二元组之中保存对应关系,这样后续 Master 就可以通过 session_handle 得到对应的 MasterSession。
void Master::CreateSession(const CreateSessionRequest* req,
CreateSessionResponse* resp, MyClosure done) {
SchedClosure([this, req, resp, done]() {
Status status;
WorkerCacheFactoryOptions worker_cache_factory_options;
string grpc_protocol("grpc");
worker_cache_factory_options.protocol = &grpc_protocol;
auto call_done = gtl::MakeCleanup([&status, &done] { done(status); });
status = ValidateExternalGraphDefSyntax(req->graph_def());
if (!status.ok()) return;
// The following 4 variables are set differently, depending on whether this
// session uses a client-provided clusterspec or not.
WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache = nullptr;
// Note: worker_cache_ptr will be null except if this session is using a
// client-supplied ClusterDef (ClusterSpec propagation).
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> worker_cache_ptr;
std::unique_ptr<DeviceSet> device_set;
// TODO(saeta): Convert to std::make_unique when available.
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Device>>> remote_devices(
new std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Device>>());
if (req->config().has_cluster_def()) { // 如果定义了集群
worker_cache_factory_options.cluster_def = &req->config().cluster_def();
// Set the server_def's job_name and task_index fields.
string normalized_string;
string grpc_protocol(kGrpcProtocol);
if (req->target().compare(0, grpc_protocol.length(), grpc_protocol) ==
0) {
normalized_string =
req->target().substr(grpc_protocol.length(), string::npos);
} else {
normalized_string = req->target();
}
for (auto&& job : req->config().cluster_def().job()) {
for (auto&& task : job.tasks()) {
if (task.second == normalized_string) {
if (worker_cache_factory_options.job_name != nullptr) {
return;
}
if (env_->local_devices[0]->parsed_name().job == job.name() &&
env_->local_devices[0]->parsed_name().task == task.first) {
return;
}
worker_cache_factory_options.job_name = &job.name();
worker_cache_factory_options.task_index = task.first;
}
}
}
worker_cache_factory_options.rpc_options = &req->config().rpc_options();
// Create the worker cache from the computed server_def.
status = env_->worker_cache_factory(worker_cache_factory_options,
&worker_cache);
if (!status.ok()) return;
worker_cache_ptr = std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface>(worker_cache);
// Ping all the workers and build the list of devices that the
// session will use.
// 获取设备
status =
DeviceFinder::GetRemoteDevices(req->config().device_filters(), env_,
worker_cache, remote_devices.get());
if (!status.ok()) return;
device_set.reset(new DeviceSet);
for (auto&& d : *remote_devices) {
device_set->AddDevice(d.get());
DeviceNameUtils::ParsedName name = d->parsed_name();
if (name.job == *worker_cache_factory_options.job_name &&
name.task == worker_cache_factory_options.task_index &&
name.type == "CPU" && name.id == 0) {
device_set->set_client_device(d.get());
}
}
} else { // 没有集群
worker_cache = env_->worker_cache;
// Ping all the workers and build the list of devices that the
// session will use.
// 获取远端设备
status =
DeviceFinder::GetRemoteDevices(req->config().device_filters(), env_,
worker_cache, remote_devices.get());
if (!status.ok()) return;
device_set.reset(new DeviceSet);
for (auto&& d : *remote_devices) {
device_set->AddDevice(d.get());
}
int num_local_devices = 0;
for (Device* d : env_->local_devices) {
device_set->AddDevice(d);
if (num_local_devices == 0) {
// Uses the first local device as the client device.
device_set->set_client_device(d);
}
num_local_devices++;
}
}
SessionOptions options;
options.config = req->config();
// 获取远端worker
std::vector<string> filtered_worker_list;
DeviceFinder::GetRemoteWorkers(req->config().device_filters(), env_,
worker_cache, &filtered_worker_list);
// 通过factory找到会话
MasterSession* session = env_->master_session_factory(
options, env_, std::move(remote_devices), std::move(worker_cache_ptr),
std::move(device_set), std::move(filtered_worker_list));
GraphDef* gdef =
const_cast<CreateSessionRequest*>(req)->mutable_graph_def();
// 建立会话,把图传给会话
status = session->Create(std::move(*gdef), worker_cache_factory_options);
if (!status.ok()) {
session->Close().IgnoreError();
session->Unref();
return;
}
resp->set_session_handle(session->handle());
// Insert into the session map, which takes ownership of the session.
{
mutex_lock l(mu_);
CHECK(sessions_.insert({session->handle(), session}).second);
}
});
}
MasterSession 位于 Master 之上,可能存在多个 Client 同时接入到同一个 Master,Master 会为每个 Client 构建一个 MasterSession。MasterSession 控制 Master 的会话生命周 期。
3.1 定义MasterSession 的定义如下。
// MasterSession wraps ClientGraph in a reference counted object.
// This way, MasterSession can clear up the cache mapping Run requests to
// compiled graphs while the compiled graph is still being used.
class MasterSession::ReffedClientGraph : public core::RefCounted {
public:
ReffedClientGraph(const string& handle, const BuildGraphOptions& bopts,
std::unique_ptr<ClientGraph> client_graph,
const SessionOptions& session_opts,
const StatsPublisherFactory& stats_publisher_factory,
bool is_partial, WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache,
bool should_deregister)
: session_handle_(handle),
bg_opts_(bopts),
client_graph_before_register_(std::move(client_graph)),
session_opts_(session_opts),
is_partial_(is_partial),
callable_opts_(bopts.callable_options),
worker_cache_(worker_cache),
should_deregister_(should_deregister),
collective_graph_key_(
client_graph_before_register_->collective_graph_key) {
VLOG(1) << "Created ReffedClientGraph for node with "
<< client_graph_before_register_->graph.num_node_ids();
stats_publisher_ = stats_publisher_factory(handle, bopts, session_opts);
// Initialize a name to node map for processing device stats.
for (Node* n : client_graph_before_register_->graph.nodes()) {
name_to_node_details_.emplace(
n->name(),
NodeDetails(n->type_string(),
strings::StrCat(
"(", absl::StrJoin(n->requested_inputs(), ", "))));
}
}
~ReffedClientGraph() override {
if (should_deregister_) {
DeregisterPartitions();
} else {
for (Part& part : partitions_) {
worker_cache_->ReleaseWorker(part.name, part.worker);
}
}
}
private:
const string session_handle_;
const BuildGraphOptions bg_opts_;
// NOTE(mrry): This pointer will be null after `RegisterPartitions()` returns.
std::unique_ptr<ClientGraph> client_graph_before_register_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
const SessionOptions session_opts_;
const bool is_partial_;
const CallableOptions callable_opts_;
WorkerCacheInterface* const worker_cache_; // Not owned.
struct NodeDetails {
explicit NodeDetails(string type_string, string detail_text)
: type_string(std::move(type_string)),
detail_text(std::move(detail_text)) {}
const string type_string;
const string detail_text;
};
std::unordered_map<string, NodeDetails> name_to_node_details_;
const bool should_deregister_;
const int64_t collective_graph_key_;
std::atomic<int64_t> execution_count_ = {0};
// Graph partitioned into per-location subgraphs.
struct Part {
// Worker name.
string name;
// Maps feed names to rendezvous keys. Empty most of the time.
std::unordered_map<string, string> feed_key;
// Maps rendezvous keys to fetch names. Empty most of the time.
std::unordered_map<string, string> key_fetch;
// The interface to the worker. Owned.
WorkerInterface* worker = nullptr;
// After registration with the worker, graph_handle identifies
// this partition on the worker.
string graph_handle;
Part() : feed_key(3), key_fetch(3) {}
};
// partitions_ is immutable after RegisterPartitions() call
// finishes. RunPartitions() can access partitions_ safely without
// acquiring locks.
std::vector<Part> partitions_;
mutable mutex mu_;
// Partition initialization and registration only needs to happen
// once. `!client_graph_before_register_ && !init_done_.HasBeenNotified()`
// indicates the initialization is ongoing.
Notification init_done_;
// init_result_ remembers the initialization error if any.
Status init_result_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
std::unique_ptr<StatsPublisherInterface> stats_publisher_;
};
MasterSession::Create(graph_def) 的工作如下:
- 调用 MakeForBaseGraph 来初始化计算图,并生成 SimpleGraphExecutionState 实例;
- 调用 CreateWorkerSessions,如果动态配置集群,则广播通知给所有 Worker,让其创建对应的 WorkerSession。
Status MasterSession::Create(GraphDef&& graph_def,
const WorkerCacheFactoryOptions& options) {
if (session_opts_.config.use_per_session_threads() ||
session_opts_.config.session_inter_op_thread_pool_size() > 0) {
return errors::InvalidArgument(
"Distributed session does not support session thread pool options.");
}
if (session_opts_.config.graph_options().place_pruned_graph()) {
session_opts_.config.mutable_graph_options()->set_place_pruned_graph(false);
}
GraphExecutionStateOptions execution_options;
execution_options.device_set = devices_.get();
execution_options.session_options = &session_opts_;
{
mutex_lock l(mu_);
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(GraphExecutionState::MakeForBaseGraph(
std::move(graph_def), execution_options, &execution_state_));
}
should_delete_worker_sessions_ = true;
return CreateWorkerSessions(options);
}
这里会构建 GraphExecutionState,依据 GraphDef 构建对应的 FullGraph。
GraphDef 是原始图结构,ConvertGraphDefToGraph 完成从 GraphDef 到 Graph 的格式转换,GraphDef 包含了图的元数据,Graph 则包含图结构的其他信息,被运行时系统所使用。
/* static */ Status GraphExecutionState::MakeForBaseGraph(
GraphDef&& graph_def, const GraphExecutionStateOptions& options,
std::unique_ptr<GraphExecutionState>* out_state) {
auto flib_def = absl::make_unique<FunctionLibraryDefinition>(
OpRegistry::Global(), graph_def.library());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(AddDefaultAttrsToGraphDef(&graph_def, *flib_def, 0));
if (options.session_options->config.graph_options().place_pruned_graph() ||
!options.session_options->config.experimental()
.optimize_for_static_graph()) {
auto ret = absl::WrapUnique(new GraphExecutionState(
absl::make_unique<GraphDef>(std::move(graph_def)), std::move(flib_def),
options));
// When place_pruned_graph is true, a different Graph* will be initialized
// each time we prune the original graph, so there is no need to
// construct a Graph* in this case.
if (!options.session_options->config.graph_options().place_pruned_graph()) {
auto base_graph = absl::make_unique<Graph>(OpRegistry::Global());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ConvertGraphDefToGraph({}, *ret->original_graph_def_,
base_graph.get()));
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ret->InitBaseGraph(std::move(base_graph)));
}
*out_state = std::move(ret);
} else {
auto ret = absl::WrapUnique(
new GraphExecutionState(nullptr, std::move(flib_def), options));
auto base_graph = absl::make_unique<Graph>(OpRegistry::Global());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
ConvertGraphDefToGraph({}, std::move(graph_def), base_graph.get()));
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ret->InitBaseGraph(std::move(base_graph)));
*out_state = std::move(ret);
}
return Status::OK();
}
InitBaseGraph 会调用 Placer.run 完成算子编排。就是把计算图之中的算子放到最适合的设备上计算,这样可以最大化效率。Placer 会对 Graph 做分析,并且结合用户的要求对每个Node如何放置进行微调,具体原则有如下四种:
- 尽量满足用户的要求。用户可以通过 device 信息或者 loc 来制定设备,尽量优先满足。
- 尽量使用快速设备。TF 系统之中每个设备都有优先级,级别越高计算性能越好,优先选择级别高的设备。
- 尽量保证程序可运行。如果某个 Node 指定了在某种设备上执行,但是系统之中没有,则会选择一个可用的设备来重写 Placement。
- 尽量考虑近邻性。比如尽量让 Consumer 和 Producer 在同一个设备上,避免无意义的跨设备拷贝。
Status GraphExecutionState::InitBaseGraph(std::unique_ptr<Graph>&& new_graph) {
// Save stateful placements before placing.
RestoreStatefulNodes(new_graph.get());
GraphOptimizationPassOptions optimization_options;
optimization_options.session_handle = session_handle_;
optimization_options.session_options = session_options_;
optimization_options.graph = &new_graph;
optimization_options.flib_def = flib_def_.get();
optimization_options.device_set = device_set_;
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(OptimizationPassRegistry::Global()->RunGrouping(
OptimizationPassRegistry::PRE_PLACEMENT, optimization_options));
Placer placer(new_graph.get(), "", flib_def_.get(), device_set_,
/* default_local_device= */ nullptr,
session_options_ == nullptr ||
session_options_->config.allow_soft_placement(),
session_options_ != nullptr &&
session_options_->config.log_device_placement());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(placer.Run());
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(OptimizationPassRegistry::Global()->RunGrouping(
OptimizationPassRegistry::POST_PLACEMENT, optimization_options));
for (const Node* n : new_graph->nodes()) {
node_name_to_cost_id_map_[n->name()] = n->cost_id();
}
SaveStatefulNodes(new_graph.get());
graph_ = new_graph.release();
return Status::OK();
}
当 MasterSession 创建成功后,如果没有动态配置集群 (默认的分布式配置环境), 则不会广播所有 Worker 动态地创建 WorkerSession。事实上,每个 Worker 都存在一个 SessionMgr 实例,它持有一个名为 legacy_session_ 的 WorkerSession 实例。因此,每个 Worker 存在一个全局唯一的 WorkerSession 实例。
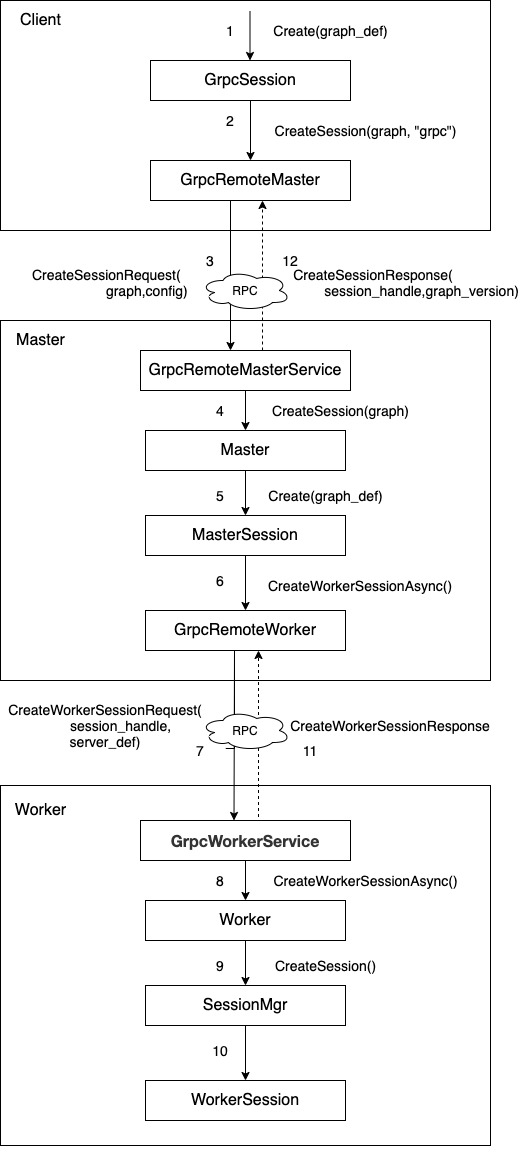
图 3 创建 WorkerSession
逻辑如下:
- 首先,调用 ReleaseWorker 来释放已有的 workers。
- 其次,调用 GetOrCreateWorker 重新在缓存之中获取 Worker,如果没有,缓存自会构建。
- 最后,遍历 Workers,调用 CreateWorkerSessionAsync 来让每个 Worker 各自创建一个 WorkerSession,每个请求都会用 set_session_handle(handle_) 来把 MasterSession 的 session_handle 设置进入,这样每个 WorkerSession 都和 MasterSession 共享同样的 session_handle,它们都隶属于同一个 MasterSession。
为了收集全部 Workers 返回的消息,这里使用了计数器 BlockingCounter 来等待,其会把初始数值设置为 Worker 数目,当收集全部 Workers 的 CreateWorkerSessionResponse 响应消息之后,计数器会减少为 0,则 BlockingCounter 会被唤醒。
Status MasterSession::CreateWorkerSessions(
const WorkerCacheFactoryOptions& options) {
const std::vector<string> worker_names = filtered_worker_list_;
WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache = get_worker_cache();
struct WorkerGroup {
// The worker name. (Not owned.)
const string* name;
// The worker referenced by name. (Not owned.)
WorkerInterface* worker = nullptr;
// Request and responses used for a given worker.
CreateWorkerSessionRequest request;
CreateWorkerSessionResponse response;
Status status = Status::OK();
};
BlockingCounter done(worker_names.size());
std::vector<WorkerGroup> workers(worker_names.size());
// Release the workers.
auto cleanup = gtl::MakeCleanup([&workers, worker_cache] {
for (auto&& worker_group : workers) {
if (worker_group.worker != nullptr) {
worker_cache->ReleaseWorker(*worker_group.name, worker_group.worker);
}
}
});
string task_name;
string local_device_name;
DeviceNameUtils::SplitDeviceName(devices_->client_device()->name(),
&task_name, &local_device_name);
const int64_t client_device_incarnation =
devices_->client_device()->attributes().incarnation();
Status status = Status::OK();
// Create all the workers & kick off the computations.
for (size_t i = 0; i < worker_names.size(); ++i) {
workers[i].name = &worker_names[i];
workers[i].worker = worker_cache->GetOrCreateWorker(worker_names[i]);
workers[i].request.set_session_handle(handle_);
workers[i].request.set_master_task(task_name);
workers[i].request.set_master_incarnation(client_device_incarnation);
if (session_opts_.config.share_cluster_devices_in_session() ||
session_opts_.config.experimental()
.share_cluster_devices_in_session()) {
for (const auto& remote_dev : devices_->devices()) {
*workers[i].request.add_cluster_device_attributes() =
remote_dev->attributes();
}
if (!session_opts_.config.share_cluster_devices_in_session() &&
session_opts_.config.experimental()
.share_cluster_devices_in_session()) {
}
}
DeviceNameUtils::ParsedName name;
if (!DeviceNameUtils::ParseFullName(worker_names[i], &name)) {
status = errors::Internal("Could not parse name ", worker_names[i]);
return status;
}
if (!name.has_job || !name.has_task) {
status = errors::Internal("Incomplete worker name ", worker_names[i]);
return status;
}
if (options.cluster_def) {
*workers[i].request.mutable_server_def()->mutable_cluster() =
*options.cluster_def;
workers[i].request.mutable_server_def()->set_protocol(*options.protocol);
workers[i].request.mutable_server_def()->set_job_name(name.job);
workers[i].request.mutable_server_def()->set_task_index(name.task);
// Session state is always isolated when ClusterSpec propagation
// is in use.
workers[i].request.set_isolate_session_state(true);
} else {
// NOTE(mrry): Do not set any component of the ServerDef,
// because the worker will use its local configuration.
workers[i].request.set_isolate_session_state(
session_opts_.config.isolate_session_state());
}
if (session_opts_.config.experimental()
.share_session_state_in_clusterspec_propagation()) {
// In a dynamic cluster, the ClusterSpec info is usually propagated by
// master sessions. However, in data parallel training with multiple
// masters
// ("between-graph replication"), we need to disable isolation for
// different worker sessions to update the same variables in PS tasks.
workers[i].request.set_isolate_session_state(false);
}
}
for (size_t i = 0; i < worker_names.size(); ++i) {
auto cb = [i, &workers, &done](const Status& s) {
workers[i].status = s;
done.DecrementCount();
};
workers[i].worker->CreateWorkerSessionAsync(&workers[i].request,
&workers[i].response, cb);
}
done.Wait();
for (size_t i = 0; i < workers.size(); ++i) {
status.Update(workers[i].status);
}
return status;
}
GrpcRemoteWorker 是 gRPC 的客户端,通过 stub 调用远端 WorkerService 相应的服务接口。
void CreateWorkerSessionAsync(const CreateWorkerSessionRequest* request,
CreateWorkerSessionResponse* response,
StatusCallback done) override {
IssueRequest(request, response, createworkersession_, std::move(done));
}
远端 Worker 之中,接收到消息是在 GrpcWorkerService 之中,当收到 CreateWorkerSessionRequest 消息,将 由 CreateWorkerSessionHandler 回调处理,CreateWorkerSessionHandler 是一个宏,其在线程池中启动一个可运行的线程,触发 Worker(就是GrpcWorker) 的 CreateWorkerSession 方法来动态创建 WorkerSession 实例。
#define HANDLE_CALL(method, may_block_on_compute_pool) \
void method##Handler(WorkerCall<method##Request, method##Response>* call) { \
auto closure = [this, call]() { \
Status s = worker_->method(&call->request, &call->response); \
if (!s.ok()) { \
VLOG(3) << "Bad response from " << #method << ": " << s; \
} \
call->SendResponse(ToGrpcStatus(s)); \
}; \
if ((may_block_on_compute_pool)) { \
worker_->env()->env->SchedClosure(std::move(closure)); \
} else { \
worker_->env()->compute_pool->Schedule(std::move(closure)); \
} \
ENQUEUE_REQUEST(method, false); \
}
HANDLE_CALL(CreateWorkerSession, false);
其实,GrpcWorker 最终调用的是 WorkerInterface.CreateWorkerSession 方法。
Status CreateWorkerSession(const CreateWorkerSessionRequest* request,
CreateWorkerSessionResponse* response) {
return CallAndWait(&ME::CreateWorkerSessionAsync, request, response);
}
CreateWorkerSessionRequest 消息之中携带了 MasterSession 分配的 session_handle,GrpcWorker 将据此创建一个 WorkerSession,session_handle 在这个 Worker 之内唯一标识这个 WorkerSession。
在 GrpcWorker 的 WorkerEnv 上下文之中有一个 SessionMgr,SessionMgr 负责统一管理和维护所有的 WorkerSession 生命周期。SessionMgr 与 WorkerSession 是一对多的关系,每个 WorkerSession 实例使用 session_handle 标识。
void Worker::CreateWorkerSessionAsync(const CreateWorkerSessionRequest* request,
CreateWorkerSessionResponse* response,
StatusCallback done) {
Status s = env_->session_mgr->CreateSession(
request->session_handle(), request->server_def(),
request->cluster_device_attributes(), request->isolate_session_state(),
request->master_task(), request->master_incarnation());
done(s);
}
重点是如下,维护了 session_handle 和 WorkerSession 之间的对应关系,每个 WorkerSession 由 session_handle 来标识。
-
std::map<string, std::shared_ptr
> sessions_ :维护了对应关系。 -
std::shared_ptr
legacy_session_ :本地 WorkerSession 实例。

图 4 SessionMgr
class SessionMgr {
public:
typedef std::function<Status(const ServerDef&, WorkerCacheInterface**)>
WorkerCacheFactory;
explicit SessionMgr(
WorkerEnv* worker_env, const string& default_worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> default_worker_cache,
WorkerCacheFactory worker_cache_factory);
~SessionMgr() {}
// Allocates state for a new session.
Status CreateSession(const string& session, const ServerDef& server_def,
bool isolate_session_state);
Status CreateSession(
const string& session, const ServerDef& server_def,
const protobuf::RepeatedPtrField<DeviceAttributes>& device_attributes,
bool isolate_session_state);
// Create WorkerSession from the master with the given `master_task` and
// `master_incarnation`. We first look for existing WorkerSessions associated
// with the specified master task. If there are sessions created by the same
// master but with a different incarnation, it indicates that the remote
// master has restarted before deleting the sessions on worker. When it
// happens, old sessions associated with the master will be automatically
// removed before the new session is created.
Status CreateSession(
const string& session, const ServerDef& server_def,
const protobuf::RepeatedPtrField<DeviceAttributes>& device_attributes,
bool isolate_session_state, string master_task,
int64_t master_incarnation);
void ResetDefaultWorkerCache(WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache);
// Updates state (worker cache, devices) of worker session identified by
// session name (`session`) based on a new server_def and set of devices.
Status UpdateSession(const string& session, const ServerDef& server_def,
const protobuf::RepeatedPtrField<DeviceAttributes>&
cluster_device_attributes,
bool isolate_session_state);
// Locates the worker session for a given session handle
Status WorkerSessionForSession(const string& session_handle,
std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession>* out_session);
std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession> LegacySession();
Status DeleteSession(const string& session);
static string WorkerNameFromServerDef(const ServerDef& server_def);
void SetLogging(bool active);
void RetrieveLogs(int64_t step_id, LoggingResponse* response);
void ClearLogs();
private:
WorkerEnv* const worker_env_; // Not owned.
// A note about destruction:
// We must delete graph_mgr before device_mgr, due to shared
// ownership of OpKernels in the executors. (The graph_mgr will
// free all stateless OpKernels, and pass over borrowed stateful
// OpKernels, which are also held in their respective devices'
// OpSegments.)
//
// legacy_session_ owns the worker_env_.device_mgr, and so we must ensure
// that sessions_'s WorkerSessions are deleted (which do not own the
// underlying devices, but instead own RenamedDevices) before
// legacy_session_ is deleted. Further, we must ensure that WorkerSession's
// device_mgr is deleted after WorkerSession's graph_mgr.
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> default_worker_cache_;
std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession> legacy_session_;
bool is_logging_active_ = false;
const WorkerCacheFactory worker_cache_factory_;
Status WorkerSessionForSessionLocked(
const string& session_handle, std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession>* out_session)
TF_EXCLUSIVE_LOCKS_REQUIRED(mu_);
mutex mu_;
// A map from session identifier to internal session structure.
std::map<string, std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession>> sessions_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
// Incarnation and WorkerSession handle associated with a master task.
struct MasterAssociatedSession {
const int64_t master_incarnation;
const string session_handle;
};
// A map from master task name to its associated worker sessions.
std::unordered_multimap<string, MasterAssociatedSession>
master_to_associated_sessions_ TF_GUARDED_BY(mu_);
};
CreateSession 方法会创建 WorkerSession 和 GraphMgr。
Status SessionMgr::CreateSession(
const string& session, const ServerDef& server_def,
const protobuf::RepeatedPtrField<DeviceAttributes>&
cluster_device_attributes,
bool isolate_session_state, string master_task,
int64_t master_incarnation) {
mutex_lock l(mu_);
if (session.empty()) {
return errors::InvalidArgument("Session must be non-empty.");
}
// For given master task name, check if one or more `WorkerSession`s have been
// created previously on this worker, and if so garbage collect the expired
// `WorkerSession`s. This happens when the master fails before sending
// `DeleteSession` requests, which can cause `WorkerSession`s to be leaked.
if (!master_task.empty()) {
auto it_range = master_to_associated_sessions_.equal_range(master_task);
if (it_range.first != it_range.second &&
it_range.first->second.master_incarnation != master_incarnation) {
auto it = it_range.first;
while (it != it_range.second) {
auto session_it = sessions_.find(it->second.session_handle);
if (session_it != sessions_.end()) {
sessions_.erase(session_it);
}
it = master_to_associated_sessions_.erase(it);
}
}
}
WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache = nullptr;
string worker_name;
if (server_def.cluster().job().empty()) {
worker_cache = new WorkerCacheWrapper(default_worker_cache_.get());
worker_name = legacy_session_->worker_name();
} else {
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(worker_cache_factory_(server_def, &worker_cache));
worker_name = WorkerNameFromServerDef(server_def);
}
if (worker_cache != nullptr && default_worker_cache_ != nullptr) {
worker_cache->SetLogging(this->is_logging_active_);
}
std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession> worker_session;
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Device>> cluster_devices;
if (isolate_session_state || server_def.cluster().job_size()) {
// Create a private copy of the DeviceMgr for the WorkerSession.
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Device>> renamed_devices;
for (Device* d : worker_env_->local_devices) {
renamed_devices.push_back(RenamedDevice::NewRenamedDevice(
worker_name, d, false, isolate_session_state));
}
auto device_mgr = MakeUnique<StaticDeviceMgr>(std::move(renamed_devices));
LookupLocalDevice cb = [&device_mgr](StringPiece name, Device** device) {
return device_mgr->LookupDevice(name, device);
};
AsRemoteDevices(worker_env_->env, cluster_device_attributes, cb,
&cluster_devices);
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_devices;
if (!cluster_device_attributes.empty()) {
remote_devices = MakeUnique<DynamicDeviceMgr>();
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
remote_devices->AddDevices(std::move(cluster_devices)));
}
auto graph_mgr = MakeUnique<GraphMgr>(worker_env_, device_mgr.get());
worker_session.reset(
new WorkerSession(session, worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface>(worker_cache),
std::move(device_mgr), std::move(graph_mgr),
std::move(remote_devices)));
} else {
AsRemoteDevices(worker_env_->env, cluster_device_attributes, nullptr,
&cluster_devices);
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_devices;
if (!cluster_device_attributes.empty()) {
remote_devices = MakeUnique<DynamicDeviceMgr>();
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
remote_devices->AddDevices(std::move(cluster_devices)));
}
// Borrow the WorkerEnv's DeviceMgr for the WorkerSession, so
// that resources using it can use its devices after the
// WorkerSession has been deleted.
auto graph_mgr = MakeUnique<GraphMgr>(worker_env_, worker_env_->device_mgr);
worker_session = WorkerSession::CreateWithBorrowedDeviceMgr(
session, worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface>(worker_cache),
worker_env_->device_mgr, std::move(graph_mgr),
std::move(remote_devices));
}
sessions_.insert(std::make_pair(session, std::move(worker_session)));
if (!master_task.empty()) {
MasterAssociatedSession s{master_incarnation, session};
master_to_associated_sessions_.emplace(master_task, s);
}
return Status::OK();
}
我们用 RegisterGraphAsync 为例来看看 worker 内部功能。可以看到其使用 GraphMgr 完成了基础功能。
void Worker::RegisterGraphAsync(const RegisterGraphRequest* request,
RegisterGraphResponse* response,
StatusCallback done) {
std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession> session;
Status s;
if (request->create_worker_session_called()) {
s = env_->session_mgr->WorkerSessionForSession(request->session_handle(),
&session);
} else {
session = env_->session_mgr->LegacySession();
}
if (s.ok()) {
s = session->graph_mgr()->Register(
request->session_handle(), request->graph_def(), session.get(),
request->graph_options(), request->debug_options(),
request->config_proto(), request->collective_graph_key(),
session->cluster_flr(), response->mutable_graph_handle());
}
done(s);
}
WorkerSession 之中比较重要的几个成员变量包括几个管理类 GraphMgr,DeviceMgr,DynamicDeviceMgr:
-
string session_name_ :Session 名称。
-
string worker_name_ :Worker 名称,比如 /job:mnist/replica:0/task:1。
-
std::shared_ptr
worker_cache_ :Worker 缓存。 -
std::unique_ptr
graph_mgr_ :本 session 注册的计算图,每个 Worker 可以注册和运行多个计算图,每个计算图使用 graph)handle 标识。 -
std::unique_ptr
device_mgr_ :本地计算设备集合信息。
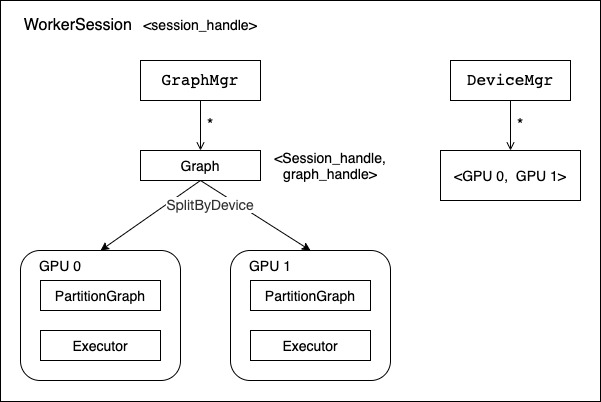
图 5 WorkerSession 概念
// WorkerSession encapsulates all of the state relating to a given session.
class WorkerSession {
public:
// Collection of local devices. These devices are typically
// RenamedDevices in all except the SessionMgr.legacy_session_ and
// sessions created with `isolate_session_state == false`. In the
// those cases, this method returns a pointer to a borrowed
// DeviceMgr (typically the `worker_env.device_mgr`).
DeviceMgr* device_mgr() {
return device_mgr_ ? device_mgr_.get() : borrowed_device_mgr_;
}
DynamicDeviceMgr* remote_device_mgr() { return remote_device_mgr_.get(); }
const string& session_name() const { return session_name_; }
const string& worker_name() const { return worker_name_; }
WorkerCacheInterface* worker_cache() const {
tf_shared_lock l(worker_session_state_mu_);
return worker_cache_.get();
}
GraphMgr* graph_mgr() const { return graph_mgr_.get(); }
ClusterFunctionLibraryRuntime* cluster_flr() const {
return cluster_flr_.get();
}
WorkerSession(const string& session_name, const string& worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> worker_cache,
std::unique_ptr<DeviceMgr> device_mgr,
std::unique_ptr<GraphMgr> graph_mgr,
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_device_mgr);
static std::shared_ptr<WorkerSession> CreateWithBorrowedDeviceMgr(
const string& session_name, const string& worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> worker_cache,
DeviceMgr* borrowed_device_mgr, std::unique_ptr<GraphMgr> graph_mgr,
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_device_mgr);
// In the eager runtime we allow WorkerSession to be updated, where the
// worker cache will be recreated. If WorkerSession upate is expected and a
// worker in the cache is used in RPCs, the caller should hold a shared
// pointer to avoid the workers getting deleted.
std::shared_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> GetSharedWorkerCache() {
tf_shared_lock l(worker_session_state_mu_);
return worker_cache_;
}
// Update an existing worker session with new set of remote workers and
// devices. Added devices will be owned by the worker session, and removed
// devices will be freed by their names.
Status UpdateWorkerCacheAndDevices(
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> new_worker_cache,
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Device>> added_remote_devices,
const std::vector<Device*>& removed_remote_devices);
~WorkerSession();
private:
WorkerSession(const string& session_name, const string& worker_name,
std::unique_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> worker_cache,
DeviceMgr* borrowed_device_mgr,
std::unique_ptr<GraphMgr> graph_mgr,
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_device_mgr);
// The name of the session.
const string session_name_;
// The name of the worker. E.g., /job:mnist/replica:0/task:1.
const string worker_name_;
mutable mutex worker_session_state_mu_;
// Object from which WorkerInterface instances can be obtained.
std::shared_ptr<WorkerCacheInterface> worker_cache_
TF_GUARDED_BY(worker_session_state_mu_);
// graph_mgr keeps track of the registered graphs of this session.
//
// Note: graph_mgr must be deleted before rendezvous_mgr!
// Note: graph_mgr must be deleted before device_mgr!
const std::unique_ptr<GraphMgr> graph_mgr_;
std::unique_ptr<ClusterFunctionLibraryRuntime> cluster_flr_;
const std::unique_ptr<DeviceMgr> device_mgr_;
DeviceMgr* const borrowed_device_mgr_; // Not owned.
std::unique_ptr<DynamicDeviceMgr> remote_device_mgr_;
};
至此,session 基本流程我们梳理完成,下面就会对业务进行详细分析。
0xFF 参考TensorFlow中的Placement启发式算法模块——Placer
